Information
Landmark: Mount Karkar VolcanoCity: Provice Area
Country: Papua New Guinea
Continent: Australia
Mount Karkar is an active stratovolcano located in the Madang Province of Papua New Guinea (PNG), situated off the northern coast of the mainland, near the Bismarck Sea. The volcano is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, an area known for its frequent volcanic activity and earthquakes. Mount Karkar is one of the more prominent volcanic features in PNG, and it is known for its relatively frequent eruptions and its influence on the local environment and communities.
Geography and Location
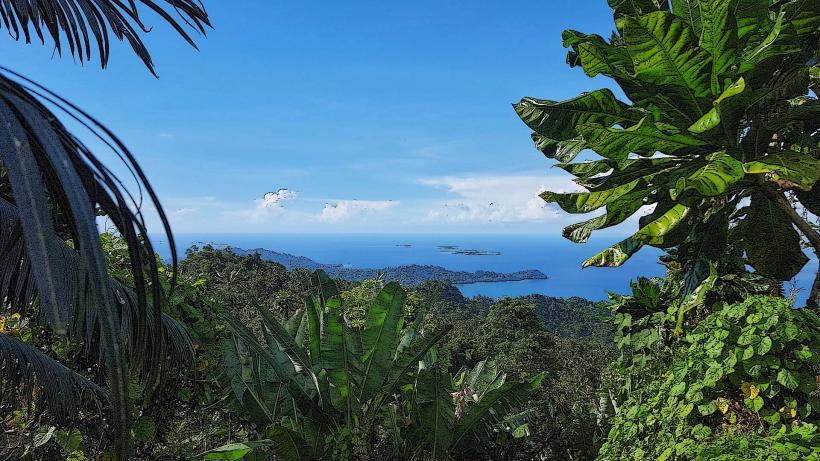
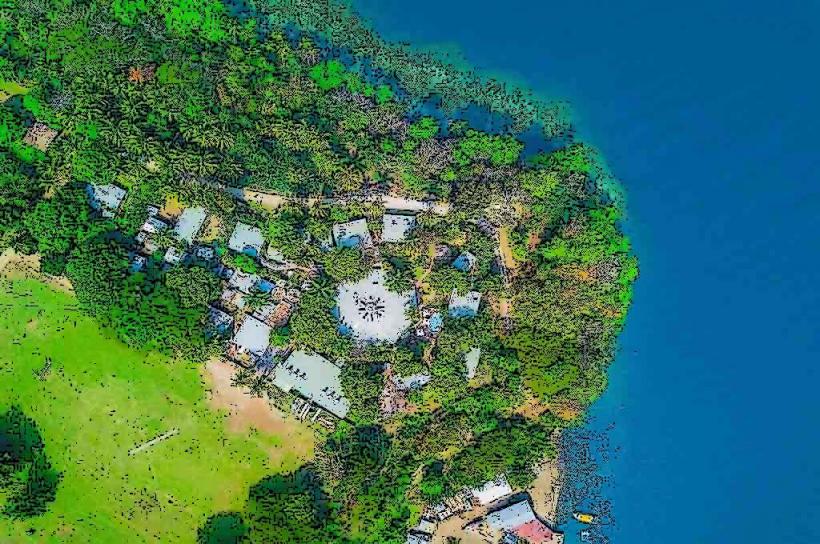
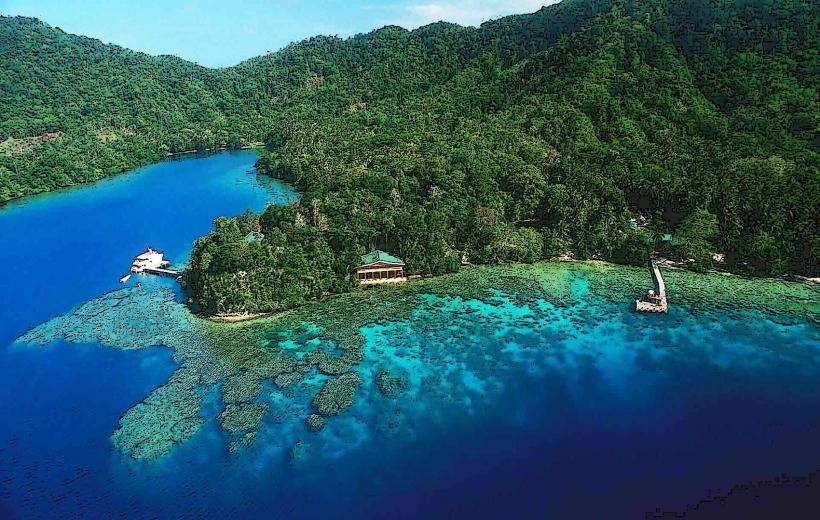
- Location: Mount Karkar is located approximately 60 kilometers (37 miles) from the town of Madang, one of the main cities in Madang Province. It is situated on Karkar Island, a small island in the Bismarck Sea to the north of the mainland. The island itself is part of the Admiralty Islands, which belong to the larger New Guinea Archipelago.
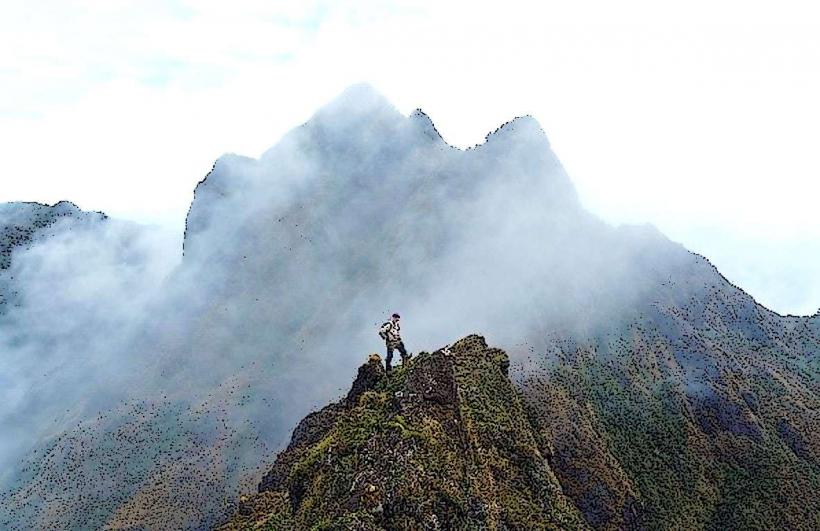
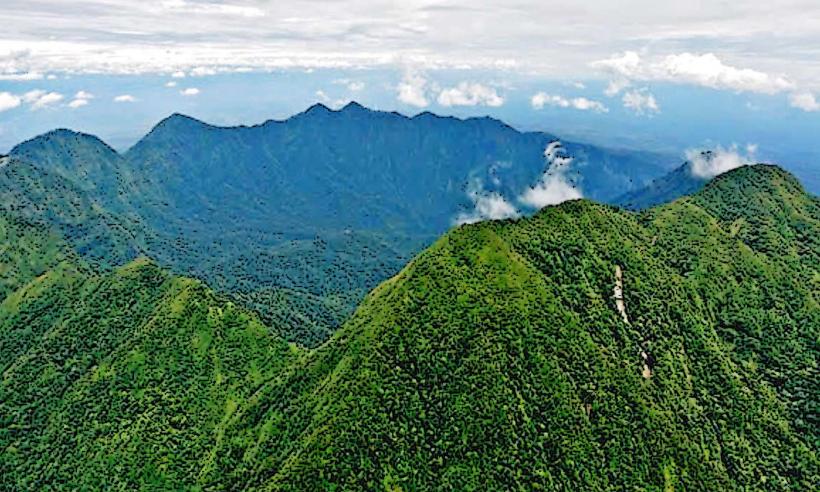
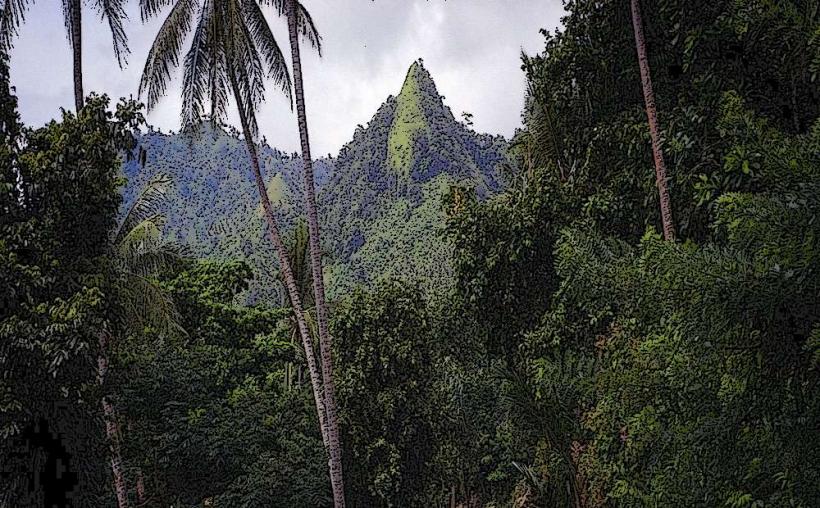
- Elevation: The volcano stands at an elevation of 2,050 meters (6,726 feet) above sea level, making it one of the taller volcanic peaks in the region. Its prominent summit is a recognizable feature in the area.
- Isolated Location: Karkar Island and Mount Karkar are relatively isolated, with limited infrastructure. This isolation has helped preserve the unique characteristics of the island and its ecosystems, but it also makes access to the volcano and surrounding areas challenging.
Volcanic Activity
- Type of Volcano: Mount Karkar is a stratovolcano, meaning it is built up by layers of solidified lava flows, volcanic ash, and tephra. Stratovolcanoes are typically steep-sided and can produce explosive eruptions.
- Eruptions: Mount Karkar has been actively erupting for much of its recorded history. Its eruptions have been a mix of both explosive and effusive events. The volcano is known for its frequent eruptions, which often involve lava flows, ash plumes, and pyroclastic flows.
- The most recent eruption occurred in 2021, which involved increased seismic activity and the release of ash and volcanic gases, prompting authorities to monitor the volcano for potential further eruptions.
- Earlier eruptions in 1975 and 2005 caused significant ash fallout in nearby communities and affected local agriculture and air travel. The eruption in 2005 was particularly notable for its ashfall, which spread over a large area, affecting villages, crops, and infrastructure on Karkar Island and the surrounding areas.
- Volcanic Hazards: The primary hazards associated with eruptions from Mount Karkar include ash fall, lava flows, landslides, and the potential for tsunamis triggered by underwater volcanic activity. The eruption plume can travel far, affecting areas in Madang and beyond. The volcanic ash can also impact agriculture, water sources, and health in nearby communities.
Geological Features
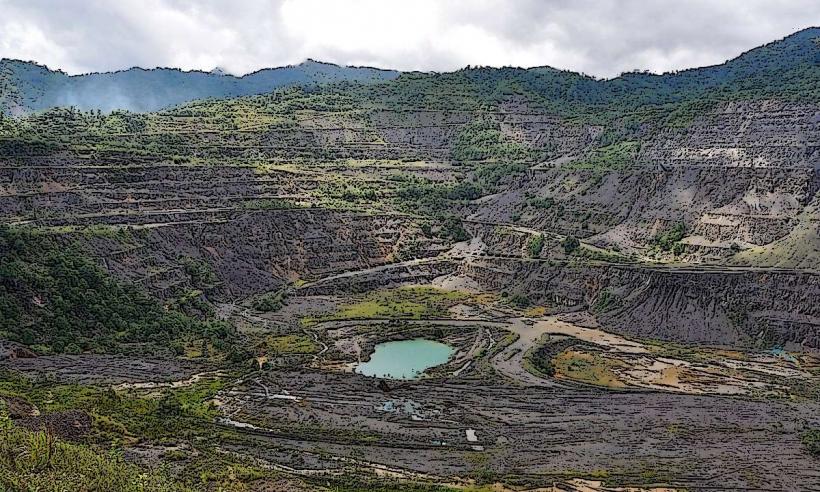
- Crater and Summit: The summit of Mount Karkar features a crater, which has been shaped by past eruptions. The crater is often filled with lava domes or lava lakes after significant eruptions, and volcanic gases can sometimes be seen escaping from the summit.
- Lava Flows and Pyroclastic Deposits: The surrounding areas of the volcano contain deposits of lava flows, pyroclastic flows, and tephra (volcanic ash). These deposits provide evidence of the repeated volcanic activity and help scientists study the history and behavior of the volcano.
- Geothermal Activity: Like many active volcanoes, Mount Karkar exhibits signs of geothermal activity such as hot springs and fumaroles (vents releasing steam and gases), which further indicate its active status.
Ecological and Environmental Impact
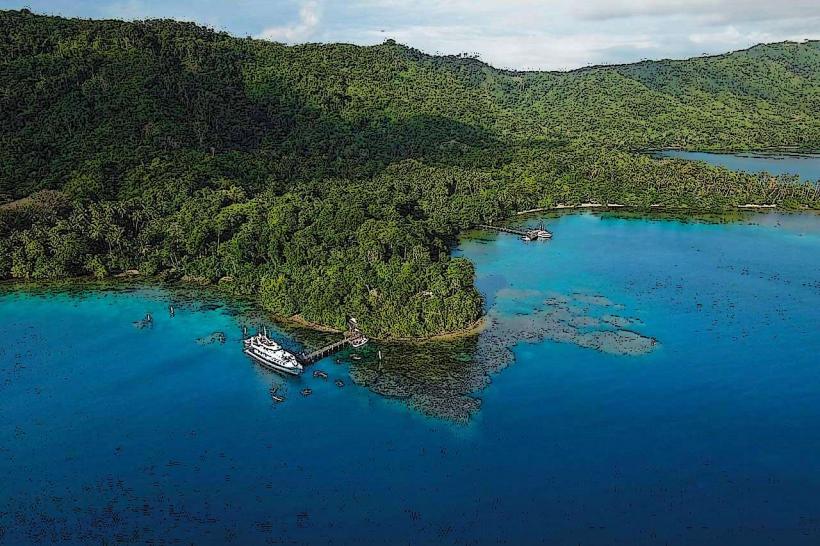
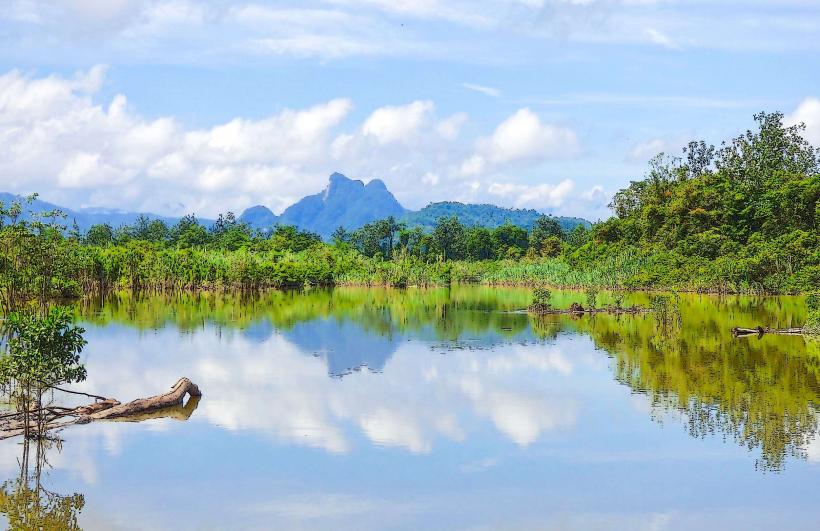
- Ecosystems: The island of Karkar, despite its volcanic activity, is home to a variety of ecosystems, ranging from tropical rainforests to coastal areas. The volcanic soils, enriched by ash and other volcanic materials, are fertile and support diverse vegetation.
- Agriculture: Local agriculture, particularly on Karkar Island and the nearby mainland, has been impacted by volcanic eruptions. Crops like coconut, taro, sweet potatoes, and cocoa are grown in the region, and volcanic ash can either be beneficial by enriching the soil or harmful by covering crops and contaminating water supplies.
- Wildlife: The forests of Karkar Island are home to various species of birds, insects, and reptiles, as well as bats and mammals like the wild pig. Some species may be directly impacted by the eruptions, but others have adapted to the dynamic volcanic environment.
Human Impact and Settlement
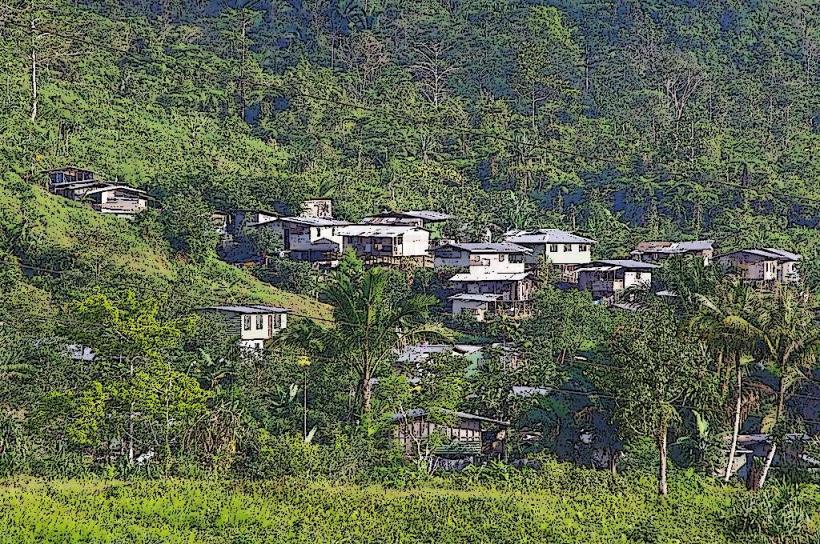
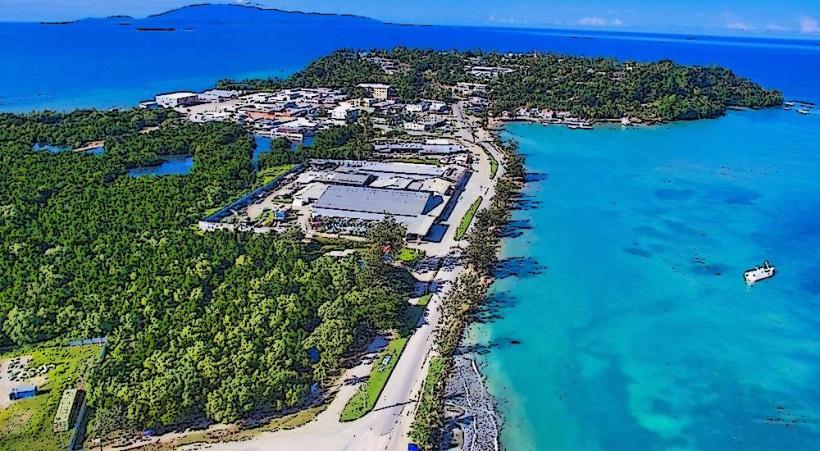
- Local Communities: The inhabitants of Karkar Island are primarily engaged in subsistence agriculture and fishing. The nearby mainland areas, including Madang, also benefit from the fertile soils that volcanic activity has produced.
- Despite the threat of eruptions, many people live on the island and around the surrounding areas, relying on the land for farming and fishing. The eruption of Mount Karkar in 2005, for example, forced evacuations and disrupted daily life, but the community has recovered in subsequent years.
- Evacuation Plans: The PNG government, in collaboration with local authorities, has developed disaster preparedness plans for the area, including early warning systems and evacuation routes in case of an eruption. However, the challenges of communication and transport on the island make evacuations complicated.
Tourism and Scientific Interest
- Tourism: Although the island's volcanic activity can be hazardous, Mount Karkar is a point of interest for adventurers, volcanologists, and ecotourists. The island’s natural beauty, the volcanic landscapes, and its remote location attract visitors seeking to explore one of PNG's most active volcanoes. Eco-tourism opportunities are present, with guided tours to observe the volcano and the surrounding flora and fauna.
- Volcanological Research: Mount Karkar is of significant interest to volcanologists studying the dynamics of active stratovolcanoes in the Pacific Ring of Fire. The relatively frequent eruptions and the presence of geothermal activity make it an important site for monitoring volcanic behavior and improving eruption prediction models.
Conclusion
Mount Karkar is a dynamic and active stratovolcano that plays an important role in the geography, ecology, and culture of the surrounding regions. Its frequent eruptions, stunning landscapes, and role in the lives of local communities make it a focal point in Madang Province. While it presents volcanic hazards, it also provides valuable natural resources, fertile soils, and opportunities for scientific research and eco-tourism. Its continuing activity underscores the significance of volcanoes in shaping both the physical and human landscapes of Papua New Guinea.