Information
Country: French GuianaContinent: South America
French Guiana is an overseas region and department of France located on the northeastern coast of South America. It is bordered by Brazil to the south and east, Suriname to the west, and the Atlantic Ocean to the north. Although it is geographically part of South America, French Guiana is politically and administratively part of France, making it an integral part of the European Union (EU).
Geography and Climate
Size: French Guiana covers an area of around 83,534 square kilometers, making it the largest region of France. It is approximately the size of the U.S. state of Indiana, but it is sparsely populated.
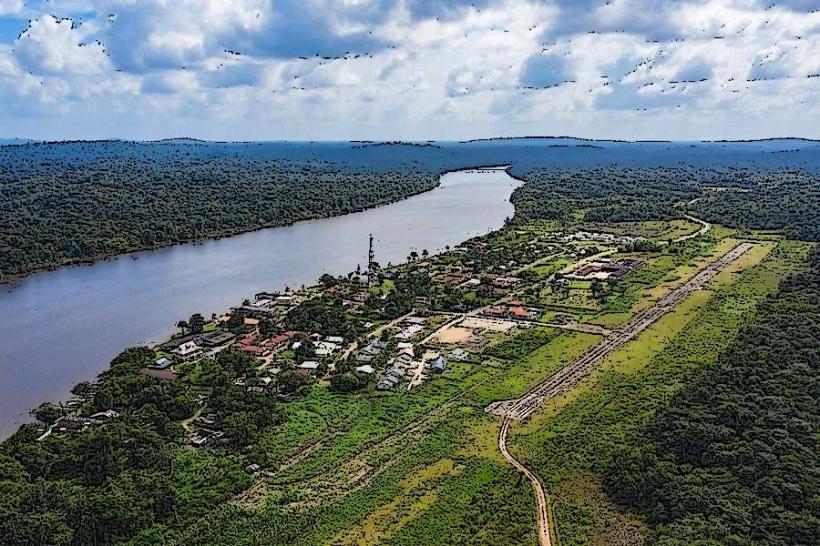
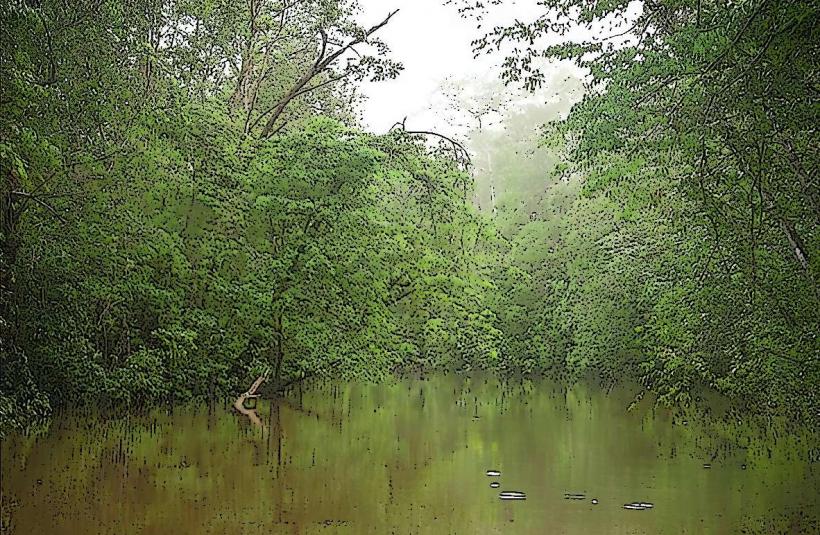
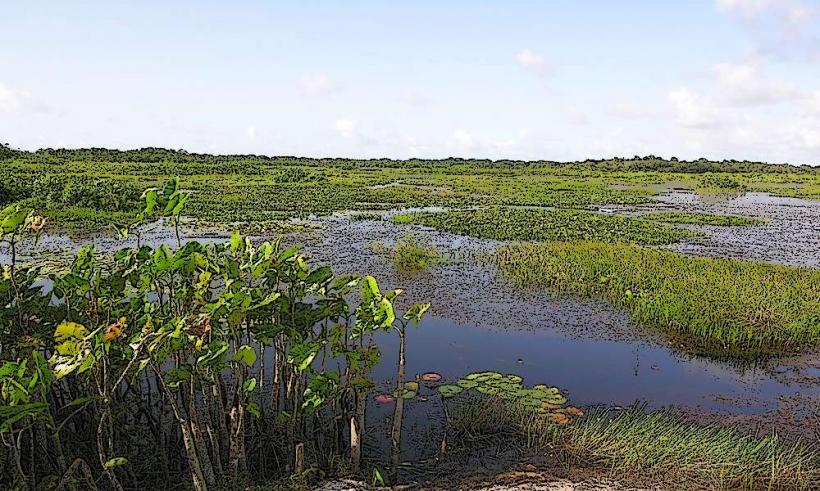
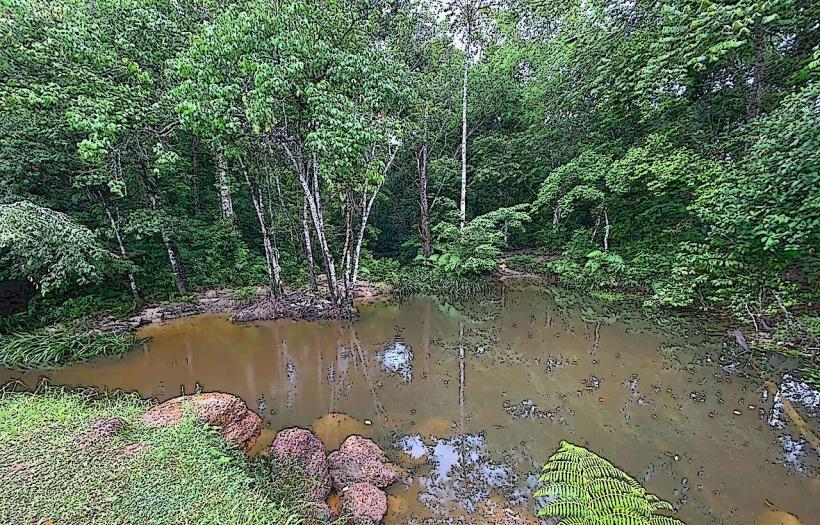
Landscape: The region is characterized by a combination of tropical forests, marshlands, and coastal plains. The Guiana Shield, which is a large geological formation of ancient rocks, extends through much of French Guiana and forms the region’s interior. In the coastal areas, mudflats and swamps are common, while the rainforests in the interior are rich in biodiversity.
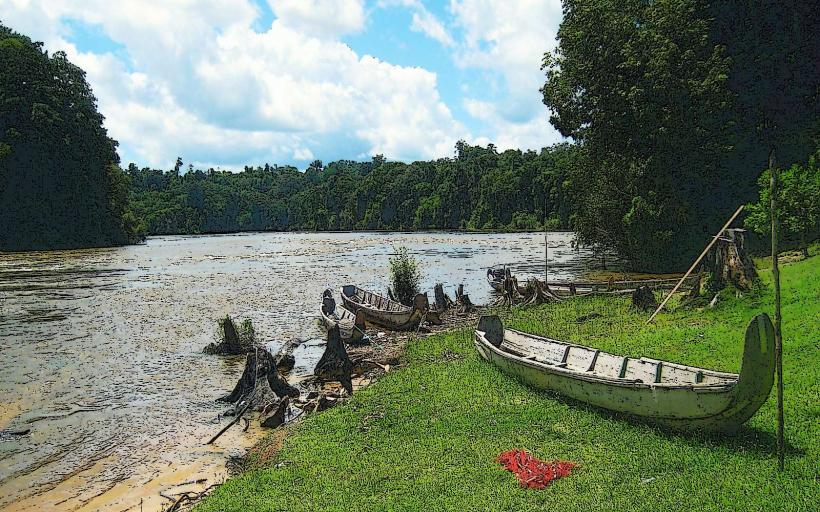
Rivers: French Guiana is home to several large rivers, including the Maroni River (which forms part of the border with Suriname) and the Oyapock River (which forms part of the border with Brazil). These rivers are crucial for transportation, fishing, and trade.
Climate: French Guiana has a tropical climate with two distinct seasons: a rainy season (from December to July) and a dry season (from August to November). The temperature remains relatively constant throughout the year, typically ranging from 24°C to 31°C (75°F to 88°F). Humidity is high year-round, and the region experiences frequent rainfall, particularly during the rainy season.
Population and Society
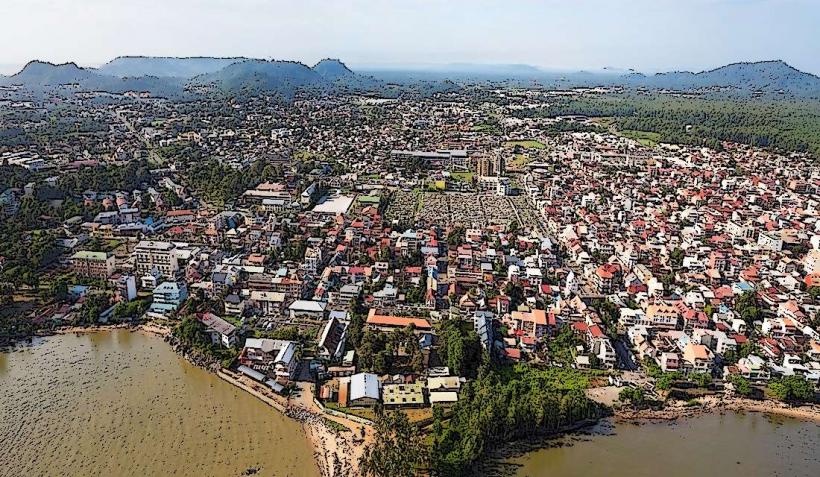
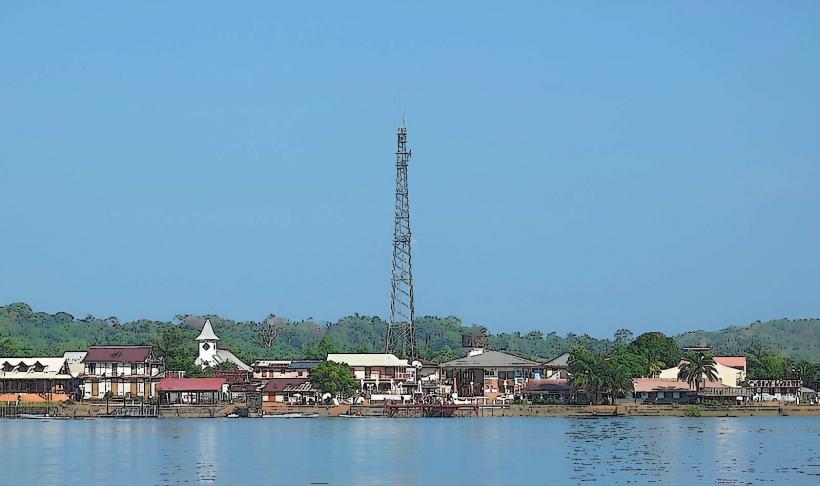
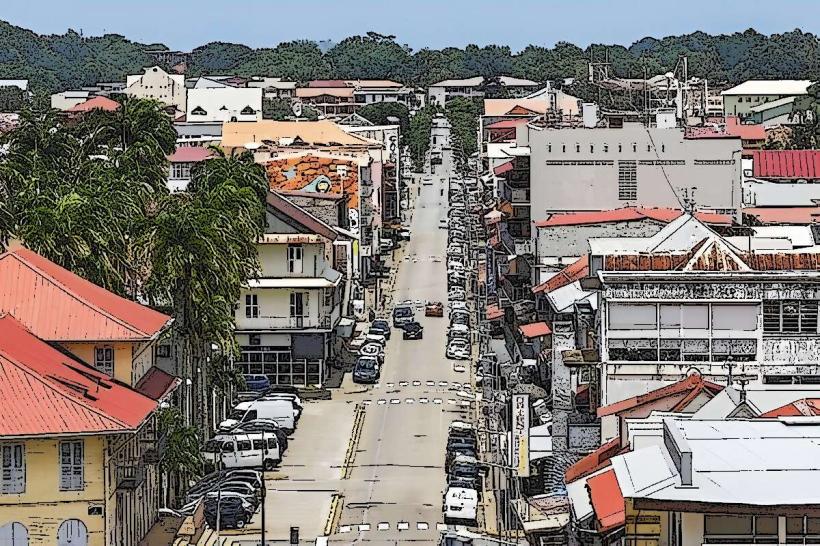
Demographics: As of the latest estimates, the population of French Guiana is around 300,000 people. It is one of the least densely populated regions in France, with the majority of the population residing in and around the capital city, Cayenne.
Ethnic Composition: French Guiana is ethnically diverse. The population is composed of a mix of Creole people, indigenous groups, Hmong (a group from Southeast Asia), Bushinengué (descendants of escaped African slaves), and people of Chinese and Lebanese descent. There are also Brazilian and Surinamese immigrants, especially in the border regions.
Languages: The official language is French, and it is used for government, education, and media. However, many local languages and dialects are spoken by the various ethnic communities, including Creole (the most widely spoken language), Wayana, Teko, and Hmong. Portuguese and Dutch are also spoken by some communities, particularly in the border areas.
Economy
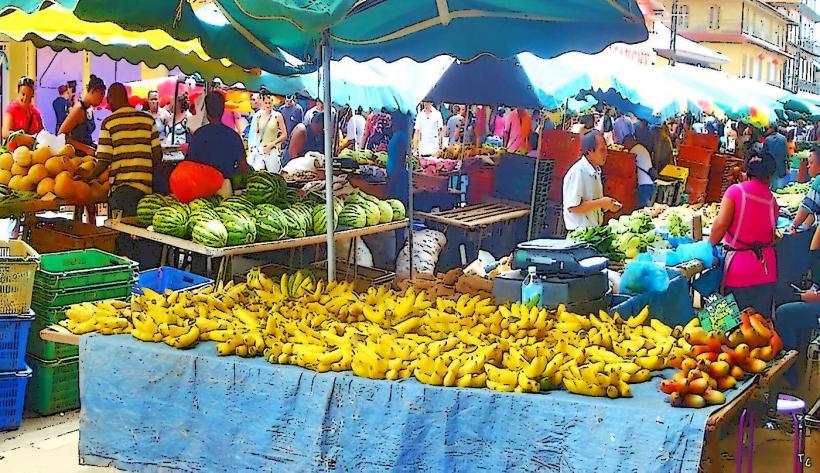
Agriculture: French Guiana's economy is primarily based on agriculture, although it is relatively underdeveloped compared to other French territories. Key agricultural products include rice, cassava, plantains, bananas, and tropical fruits. The region is also involved in fishing, particularly for shrimp.
Forestry: The dense rainforests of French Guiana provide significant opportunities for the timber industry. Logging, however, faces challenges due to environmental concerns and sustainable practices.
Gold Mining: French Guiana has a substantial gold mining industry. Gold mining is one of the region’s most important economic activities, especially in the interior areas. However, mining operations often raise concerns regarding environmental damage and illegal activities.
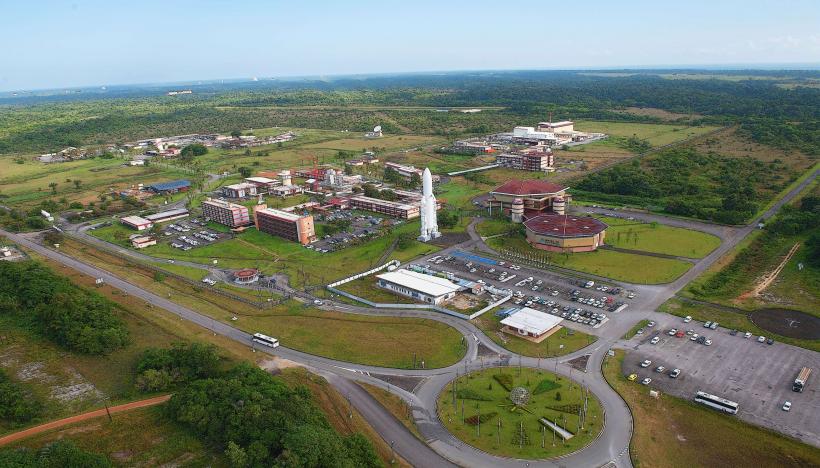
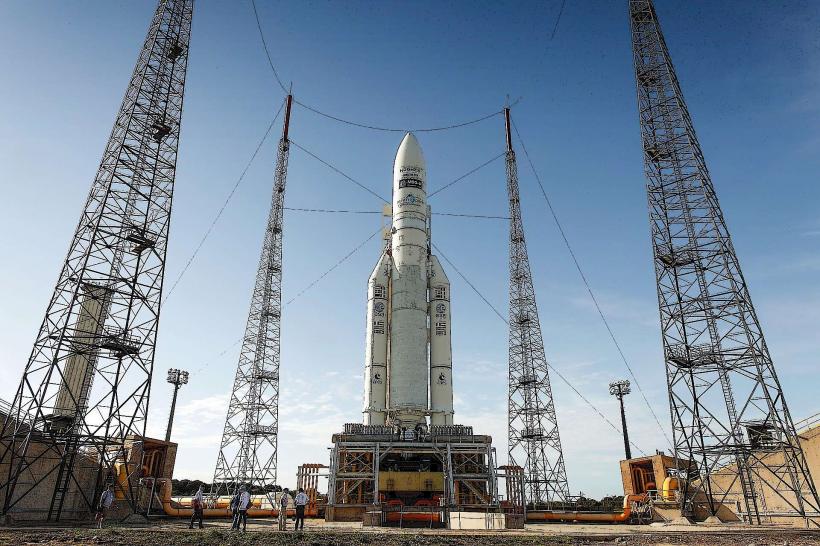
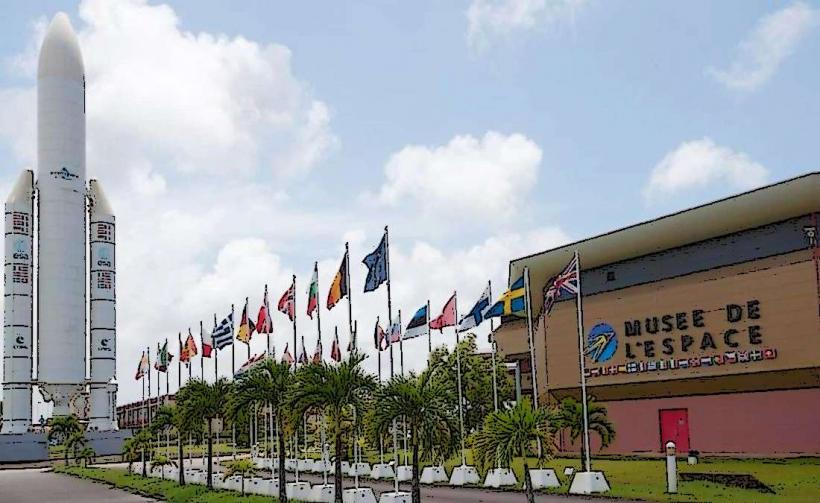
Spaceport: One of the most notable aspects of the economy is the presence of the Guiana Space Centre (Centre Spatial Guyanais), located near the city of Kourou. This spaceport serves as a major European launch site for Arianespace and ESA (European Space Agency) missions. It is one of the region's most important sources of employment and income.
Government Funding: As an overseas region of France, French Guiana receives substantial financial assistance from the French government. This funding supports infrastructure projects, social services, and public administration.
Culture
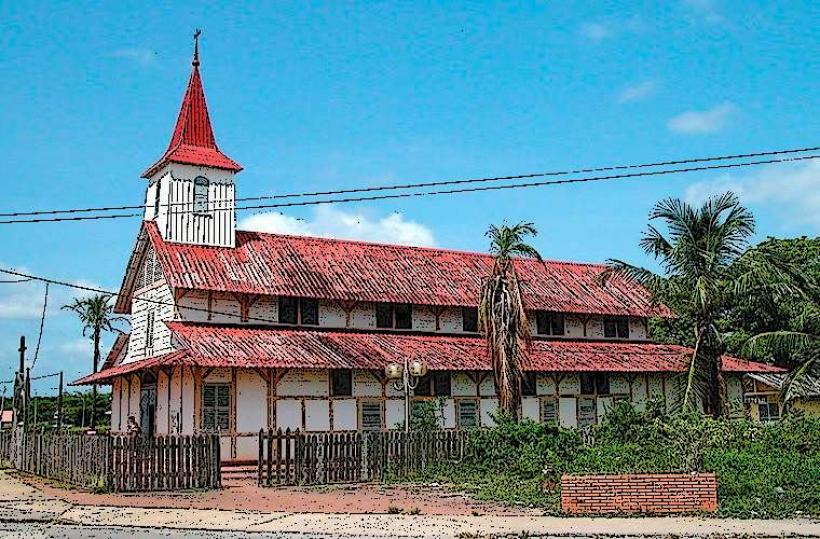
Influence of France: French culture plays a significant role in the daily life and traditions of the people of French Guiana, as the region is an integral part of the French Republic. French is the official language, and the educational system follows the same curriculum as mainland France.
Festivals and Traditions: The region celebrates several festivals, the most prominent of which is the Carnival of French Guiana. The carnival season is an important cultural event, filled with parades, music, dancing, and costumes, reflecting both Afro-Caribbean and indigenous cultural influences.
Music and Dance: Music plays an important role in the cultural life of French Guiana. The region’s traditional music incorporates creole rhythms, afro-descendant influences, and French styles. Popular music genres include kassé kriol, zouk, and biguine. The Maroon and indigenous communities have contributed traditional songs and dances that celebrate their histories.
Biodiversity and Environment
Rainforests: French Guiana's tropical rainforests are home to a wide variety of flora and fauna, including unique species of birds, mammals, and insects. The rainforests are an important part of the region's ecosystem, providing critical services such as carbon storage, water regulation, and biodiversity conservation.
Wildlife: French Guiana is home to a vast array of wildlife, including jaguars, capybaras, giant river otters, and a variety of monkeys. The region also hosts more than 500 species of birds, including the harpy eagle and scarlet ibis, as well as thousands of species of insects, amphibians, and reptiles.
Conservation: French Guiana's diverse ecosystems are protected by a number of nature reserves and parks. The Tumuc-Humac Mountains and Grand Terre are important conservation areas, aiming to protect biodiversity and indigenous habitats. However, illegal logging, mining, and deforestation remain ongoing challenges for conservation efforts.
Political and Administrative Structure
Governance: As a French overseas region, French Guiana is governed according to French laws and is represented in the French National Assembly. The administrative capital is Cayenne, and the region has its own regional council, which is responsible for managing local affairs in coordination with the French government.
Legal Status: French Guiana is considered an overseas department and is fully integrated into the French Republic. This means that the region adheres to French law, and its residents enjoy the same rights as those in mainland France, including healthcare, education, and social benefits.
Relations with Brazil and Suriname: Given its geographic location, French Guiana shares close ties with its neighboring countries, particularly Brazil and Suriname. These relationships involve cross-border trade, migration, and cooperation on issues such as illegal immigration and environmental protection.
Challenges and Opportunities
Development Issues: While French Guiana benefits from financial assistance from the French government, it still faces significant development challenges. These include high unemployment rates, poverty, and a reliance on public sector jobs. Infrastructure in rural areas is underdeveloped, and healthcare and education services can be limited in remote regions.
Illegal Activities: The region also struggles with illegal activities such as gold mining, drug trafficking, and illegal immigration from neighboring Brazil and Suriname. The government has implemented various initiatives to combat these issues, but they remain a persistent challenge.
Conclusion
French Guiana is a unique and vibrant region with a rich cultural heritage, diverse wildlife, and a strategic location in South America. Despite its small population, it plays an important role within the French Republic and the European Union, particularly in space exploration, environmental conservation, and agriculture. However, the region faces several challenges, including economic underdevelopment, environmental concerns, and social inequality. Nonetheless, French Guiana offers a rich blend of French, Afro-Caribbean, and indigenous cultures, making it an intriguing place for both residents and visitors alike.