Information
Landmark: Museum of Viminacium (Kostolac)City: Belgrade
Country: Serbia
Continent: Europe
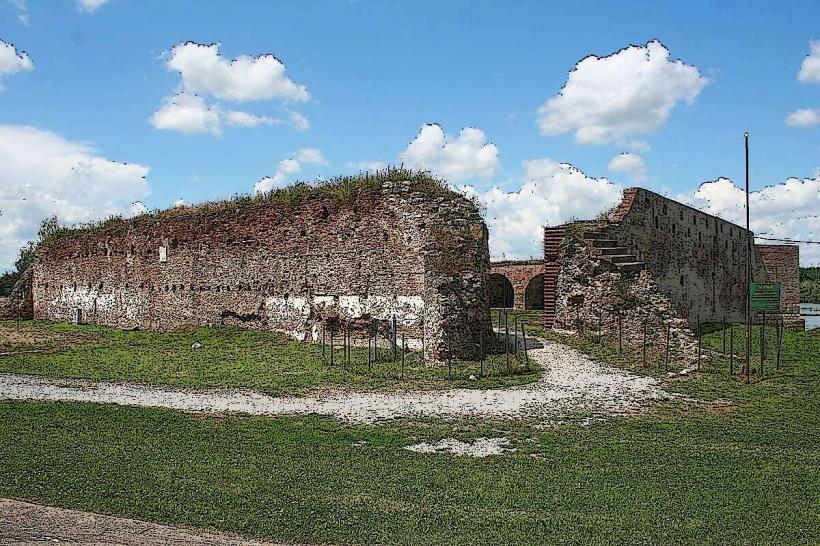
The Museum of Viminacium, located near the town of Kostolac in eastern Serbia, is part of the Viminacium Archaeological Park, which preserves the remains of the ancient Roman city and military camp of Viminacium. Once a significant center of Roman culture, governance, and military power, Viminacium offers a fascinating look into the Roman era of the Balkans. The museum and its surrounding archaeological site are among the most important historical and cultural landmarks in Serbia. Here’s an in-depth look:
Historical Background of Viminacium
Roman Origins:
- Viminacium was established in the 1st century AD as a military camp (castrum) for the Roman Empire. It quickly grew into a major urban and administrative center.
- By the 3rd century AD, it became the capital of the Roman province of Moesia Superior and later Moesia Prima.
- It was strategically located at the confluence of the Danube and Mlava rivers, making it an important hub for trade, transportation, and military operations.
City and Military Importance:
- Viminacium housed Legio VII Claudia, one of the most important Roman legions in the region.
- The city had a population of over 30,000 inhabitants, making it one of the largest Roman settlements in the Balkans at the time.
- It boasted public buildings, a forum, baths, temples, an amphitheater, and an aqueduct.
Destruction and Rediscovery:
- Viminacium was heavily damaged during the Hun invasion in the 5th century and was eventually abandoned.
- The site was rediscovered in the 19th century, with systematic archaeological excavations beginning in the 1970s and continuing to this day.
The Museum of Viminacium
Establishment:
- The museum is part of the larger Viminacium Archaeological Park, established to preserve, study, and showcase the artifacts and structures uncovered at the site.
Exhibits and Collections:
- The museum houses a wide range of Roman artifacts, including:
- Sculptures and busts of Roman deities and emperors.
- Coins, jewelry, and other items of daily life, showcasing the wealth and sophistication of Viminacium’s residents.
- Ceramics and pottery with intricate designs.
- Weapons and military equipment used by Roman soldiers.
- Frescoes and mosaics that adorned the walls and floors of Roman buildings.
- One of the most significant exhibits is the collection of Roman sarcophagi, which provides insights into burial customs and the beliefs of the time.
Reconstructed Roman Buildings:
- Visitors can see reconstructed parts of the ancient city, including Roman baths, amphitheaters, and a mausoleum, helping to visualize what life in Viminacium was like during its peak.
Special Attractions:
- The museum also features the remains of a mammoth skeleton, discovered near the site. This is a unique exhibit, blending natural history with archaeology.
The Archaeological Park
Tombs and Frescoes:
- Some of the most impressive discoveries at Viminacium are the Roman tombs, decorated with stunning frescoes. These are displayed in situ or preserved in the museum.
- The tomb paintings depict scenes of Roman mythology, daily life, and religious rituals.
Amphitheater:
- The ruins of the Roman amphitheater, which could hold several thousand spectators, demonstrate the cultural and entertainment life of ancient Viminacium.
Thermae (Bathhouses):
- The remains of Roman bathhouses, complete with heating systems, show the advanced engineering and daily habits of the city’s residents.
Legionary Camp:
- The reconstructed parts of the military camp offer a glimpse into the life of Roman soldiers stationed at Viminacium.
Interactive and Educational Features
Guided Tours:
- Visitors can explore the museum and archaeological park with the help of expert guides, who provide detailed explanations about the exhibits and the history of Viminacium.
Workshops and Events:
- The museum organizes workshops, including ancient crafts, Roman cuisine, and archaeological digging experiences, making it an interactive destination for families and students.
3D Reconstructions:
- Modern technology is used to create 3D reconstructions of the city, allowing visitors to visualize what Viminacium would have looked like in Roman times.
Archaeological Excavations:
- Visitors can observe ongoing archaeological work, as new discoveries are still being made at the site.
Cultural and Historical Significance
A Window into Roman Serbia:
- The museum and park provide invaluable insights into the Romanization of the Balkans and the life of a bustling Roman city.
Preservation Efforts:
- Viminacium is a UNESCO World Heritage Site candidate, highlighting its global historical importance.
Contribution to Serbian Tourism:
- As one of Serbia’s most prominent archaeological sites, the Museum of Viminacium plays a crucial role in promoting cultural tourism in the country.
Visiting the Museum
Location:
- The museum is located near Kostolac, approximately 80 kilometers (50 miles) southeast of Belgrade. It’s easily accessible by car or organized tours.
Hours and Fees:
- The museum is open year-round, with longer hours during the summer season.
- Entrance fees are affordable and often include access to guided tours and certain exhibits.
Facilities:
- The site offers parking, a souvenir shop, a café, and interactive spaces for visitors.
Why Visit the Museum of Viminacium?
Immersive History:
- The museum offers a unique opportunity to step back in time and experience the grandeur of the Roman Empire in Serbia.
Rich Exhibits:
- The artifacts and reconstructions make Viminacium one of the most comprehensive archaeological museums in the region.
Family-Friendly Destination:
- With interactive activities and workshops, the museum is an excellent destination for families, schools, and history enthusiasts.
Natural and Cultural Fusion:
- The juxtaposition of ancient Roman ruins and the fossilized mammoth skeleton adds a unique dimension to the experience.
Conclusion
The Museum of Viminacium is a treasure trove of Roman history, culture, and archaeology. With its rich collection of artifacts, reconstructed sites, and educational programs, it serves as a vital link to Serbia’s ancient past and a must-visit for anyone interested in Roman history.