Information
Landmark: Nikola Tesla MuseumCity: Belgrade
Country: Serbia
Continent: Europe
The Nikola Tesla Museum in Belgrade, Serbia, is dedicated to the life, work, and legacy of Nikola Tesla, one of the most brilliant and influential inventors, electrical engineers, and physicists in history. Tesla's groundbreaking contributions to science, especially in the development of alternating current (AC) electricity and wireless communication, have left an indelible mark on the modern world. The museum is a major cultural and educational institution, offering visitors a chance to learn about Tesla's inventions and his profound impact on technology and society.
Historical Background:
Nikola Tesla was born on July 10, 1856, in Smiljan, which was then part of the Austrian Empire (today in Croatia). Tesla's work in electrical engineering, particularly his development of alternating current (AC) electrical systems, revolutionized power generation and distribution. Although he lived in various countries, including the United States, where he conducted much of his pioneering research, Tesla's Serbian roots make the museum in Belgrade an important tribute to his legacy.
The museum in Belgrade was established in 1952, just a few years after Tesla's death in 1943 in New York City. It was created to preserve his scientific legacy and honor his contributions to modern technology.
Museum Collections:
The Nikola Tesla Museum houses an extensive collection of materials related to Tesla’s life and work. The museum's exhibits span his early life, scientific discoveries, inventions, and the later years of his career, focusing on his visionary ideas and inventions.
Original Tesla Inventions and Models: The museum’s collection includes original models, working devices, and patents that Tesla developed throughout his career. Some of the most significant items on display are models of his alternating current (AC) motor, Tesla coil, and transformers, as well as his radio transmitter and wireless energy transmission devices. These exhibits showcase Tesla’s innovative approach to electrical engineering and his foresight in many areas of modern technology.
Tesla’s Personal Belongings: The museum also holds a collection of Tesla's personal items, including photographs, letters, and documents. These materials provide insight into his personal life and his relationships with other scientists and prominent figures of his time. Tesla’s notebooks and original scientific manuscripts are part of the museum’s valuable archives, offering a deeper look into the mind of the inventor.
Tesla's Patents and Scientific Works: A significant portion of the museum’s collection focuses on Tesla’s contributions to the field of electrical engineering. This includes numerous patents Tesla obtained for his inventions, many of which were groundbreaking at the time and continue to influence modern technology. Tesla’s work on the AC power system, induction motor, and radio waves is extensively covered.
Tesla Coils and Demonstrations: One of the most visually impressive displays in the museum is the Tesla Coil, a device Tesla invented for generating high-voltage, low-current electricity. The museum has functioning models of the Tesla Coil, which are often used for live demonstrations. These demonstrations show how Tesla's invention works, sparking interest and wonder with dazzling electrical arcs and resonant frequencies.
Exhibits on Wireless Transmission: Tesla's visionary ideas about wireless communication and energy transmission are explored in depth at the museum. His attempts to send electrical power wirelessly across long distances, particularly through his Wardenclyffe Tower project in the United States, are discussed through displays of plans, diagrams, and photographs. Though Tesla’s ambitions in wireless energy transmission were not fully realized during his lifetime, his work laid the foundation for future advances in wireless technology and communication systems.
Multimedia and Interactive Exhibits: The museum also utilizes multimedia exhibits to enhance the visitor experience. There are interactive displays, short films, and educational videos that explain Tesla’s scientific contributions and the historical context of his work. The museum also hosts temporary exhibitions related to Tesla’s legacy and modern applications of his inventions.
The Museum Building:
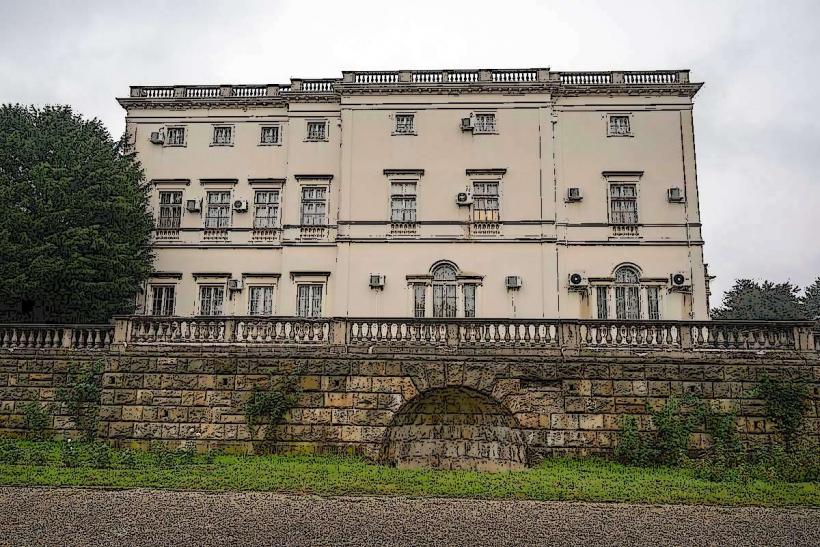
The museum is housed in a neoclassical-style building in the center of Belgrade, near the Vračar neighborhood. The structure is elegant and well-maintained, reflecting the significance of its contents. The museum is designed to showcase Tesla’s life and work in a way that is both educational and accessible to visitors of all ages.
Tesla’s Legacy:
Nikola Tesla's legacy is vast, and his inventions continue to shape modern society. Some of his most important contributions include:
Alternating Current (AC) Power System: Tesla is perhaps best known for his work on the alternating current (AC) power system, which became the standard for electrical power transmission. His development of the AC induction motor and the polyphase system of electrical transmission was revolutionary and led to the widespread adoption of AC for electrical grids, making long-distance electrical transmission possible.
Wireless Communication and Energy: Tesla was also a pioneer in the field of wireless communication, envisioning a world where energy could be transmitted without wires. He experimented with wireless transmission of power, and although he didn’t achieve all his goals, his ideas paved the way for technologies like radio, television, and modern wireless communication.
Radio and Remote Control: Tesla was one of the early pioneers of radio waves and radio communication. Though Guglielmo Marconi is often credited with inventing the radio, Tesla's experiments with wireless transmission of information preceded Marconi’s work. Tesla was also the first to demonstrate remote control using radio waves, an invention that is fundamental to the development of technologies like remote-controlled devices and drones.
X-rays and Early Medical Innovations: Tesla's experiments with electricity also contributed to the early understanding of X-rays and their applications in medicine. He was among the first to explore the potential uses of X-rays for medical imaging, although he did not receive the same recognition as other pioneers in the field.
Educational and Cultural Importance:
The Nikola Tesla Museum serves not only as a memorial to Tesla's genius but also as an educational center that inspires future generations of scientists, engineers, and inventors. It offers educational programs, workshops, and lectures to help students and enthusiasts alike understand Tesla’s work and his impact on the world.
Educational Programs: The museum offers various educational programs and workshops for school groups, students, and young scientists. These programs are designed to inspire interest in science and technology, particularly in the fields of electrical engineering and physics.
Tesla Day Celebrations: Each year, the museum holds special events to celebrate Nikola Tesla's birthday (July 10), where the public can enjoy lectures, exhibitions, and demonstrations dedicated to his life and work. These celebrations are a way to honor Tesla’s contributions to science and his enduring influence.
Conclusion:
The Nikola Tesla Museum in Belgrade is an essential destination for anyone interested in the life and legacy of one of history’s greatest inventors. It offers a unique opportunity to explore Tesla’s groundbreaking contributions to science and technology while celebrating the visionary ideas that shaped the modern world. Through its diverse collection of artifacts, interactive displays, and educational programs, the museum ensures that Tesla’s legacy continues to inspire and educate people of all ages.