Information
Landmark: Walloon ParliamentCity: Namur
Country: Belgium
Continent: Europe
The Walloon Parliament (Parlement de la Wallonie) is the legislative body of the Walloon Region of Belgium, which is one of the three regions of the country, alongside Flanders and Brussels-Capital. The Walloon Parliament plays a key role in the governance of the Walloon Region, which covers the southern part of Belgium and is predominantly French-speaking.
Structure and Functions
Legislative Role: The primary function of the Walloon Parliament is to pass laws that govern the Walloon Region, covering a wide range of areas, including economy, transportation, education, environment, health, social services, and regional development. It also plays a role in shaping policy on issues that affect the French-speaking population of the region.
Members: The Walloon Parliament is composed of 75 members, known as Parliamentarians or Deputies, who are elected through proportional representation for a five-year term. These deputies represent the various political parties within the region, and the composition of the Parliament reflects the political landscape of Wallonia.
The President: The Parliament is presided over by the President of the Walloon Parliament, who is responsible for ensuring the proper conduct of parliamentary procedures and overseeing the legislative process. The President is elected by the members of the Parliament at the beginning of each legislative term.
The Government: The Walloon Parliament also plays a role in overseeing the Walloon Government, which is responsible for the execution of regional laws and policies. The Government consists of the Minister-President and other regional ministers, who are appointed by the Parliament.
Key Responsibilities
Legislation: The Walloon Parliament has the authority to introduce, amend, and pass laws that apply specifically to the Walloon Region. For example, it can legislate on issues like regional economic development, environmental protection, public transportation, and social welfare programs.
Budget Approval: The Walloon Parliament is responsible for approving the regional budget, which outlines the allocation of public funds for regional projects and services. This includes funding for education, healthcare, infrastructure, and economic development.
Oversight and Accountability: The Walloon Parliament holds the regional government accountable through question sessions and debates. It can scrutinize the actions of ministers and request information on the implementation of policies and the use of public funds.
Interregional Relations: The Parliament plays a role in the broader governance of Belgium, participating in discussions with the Flemish Parliament and the Brussels-Capital Parliament on issues that affect multiple regions, such as infrastructure, energy policy, and environmental concerns.
Location and History
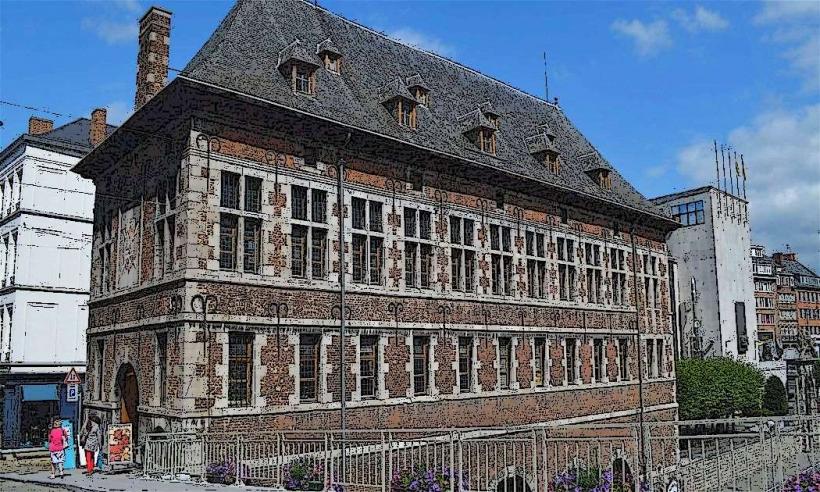
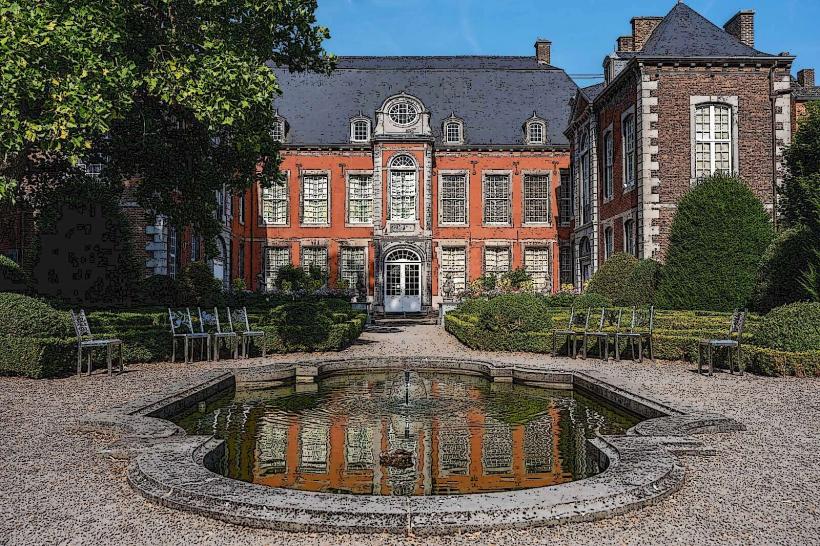
Location: The Walloon Parliament is located in the Hôtel de Région Wallonne (Walloon Regional Government Building) in the city of Namur, the capital of the Walloon Region. The building itself is a modern structure that serves as the headquarters for the Parliament and the regional government.
History: The Walloon Parliament was established as part of the Belgian federal structure following the reforms of the 1980s, which gave more autonomy to the regions. Wallonia, historically a French-speaking region, gained legislative powers over areas such as economic development, education, and environmental regulation, which were previously managed by the central federal government in Brussels.
Political Landscape
Political Parties: The Walloon Parliament is composed of a variety of political parties, reflecting the diverse political views of the Walloon population. Key political parties in Wallonia include:
- Parti Socialiste (PS): A left-wing, social-democratic party, which is traditionally the largest party in Wallonia.
- Mouvement Réformateur (MR): A centrist party that represents liberal and pro-European interests.
- Ecolo: A green party focused on environmental and social justice issues.
- Centre démocrate humaniste (cdH): A Christian-democratic party.
- Other regional and nationalist parties: Various smaller parties also play a role in the Parliament, often focusing on specific regional issues.
Coalitions: Since no single party usually has an outright majority, the Walloon Parliament often operates through coalitions. These coalitions are formed after elections and are essential for securing a majority to pass legislation and approve the regional budget.
Elections
- Electoral System: Members of the Walloon Parliament are elected every five years through a proportional representation system. This means that the number of seats each party receives is proportional to the number of votes cast in the election. Elections are held at the same time as elections for the Parliament of the French Community (which governs education and culture for French speakers) and, often, for the municipal councils.
Legislative Process
Introduction of Bills: A new law or policy proposal is introduced to the Walloon Parliament by the Minister-President, regional ministers, or a member of Parliament. These bills go through several readings and debates in committees and plenary sessions.
Committees: The Walloon Parliament has several committees that specialize in different areas, such as health, transport, finance, and social affairs. These committees review proposed legislation, examine policies, and monitor the work of the Walloon Government.
Plenary Sessions: After committee reviews, the full Parliament holds plenary sessions, where members debate the proposed laws and vote on them. A bill must pass multiple votes before becoming law.
Recent Developments
- In recent years, the Walloon Parliament has focused on a range of key issues, including:
- Environmental policies, particularly related to sustainable development and energy transition.
- Social welfare and addressing inequality in the region.
- Economic recovery efforts, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, focusing on support for businesses and employment in the region.
- Regional Autonomy: The Walloon Parliament continues to play a significant role in increasing regional autonomy, working to ensure that Wallonia has greater control over areas that directly affect its residents, such as economic policy, healthcare, and infrastructure.
Conclusion
The Walloon Parliament is a crucial institution in the governance of the Walloon Region of Belgium. Through its legislative powers, the Parliament addresses a wide array of issues that impact the daily lives of Walloon citizens. The political dynamics in the region reflect a balance between economic development, social policies, and environmental concerns, with the Parliament playing a central role in shaping the future of Wallonia.