Information
Landmark: El JulánCity: El Hierro
Country: Canary Islands
Continent: Europe
El Julán is a historic and significant archaeological site located on the island of El Hierro, part of the Canary Islands. The site is particularly notable for its ancient rock engravings and the remains of settlements from the Bimbache people, the indigenous inhabitants of El Hierro before the Spanish conquest in the 15th century. El Julán is a protected area and a key point of interest for those exploring the island’s pre-Hispanic past, as it offers a fascinating glimpse into the early civilization of the Canaries.
Location and Access
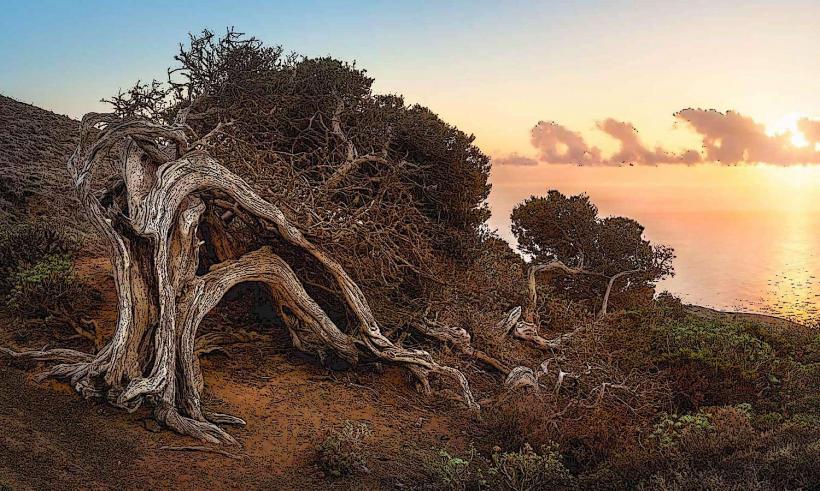
- Location: El Julán is located in the northeastern part of El Hierro, within the municipality of Valverde, the island’s capital. It is set in a rugged and isolated part of the island, amidst volcanic landscapes, which helped protect it over the centuries.
- Access: The site is accessible by road, although the journey involves navigating narrow and winding paths. Visitors need to be prepared for a somewhat rugged access route, but the journey is worthwhile for those interested in archaeology and history.
Archaeological Significance
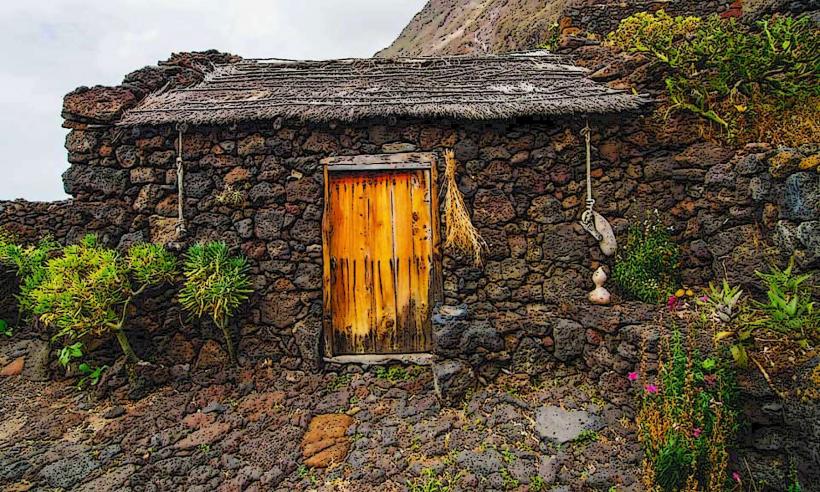
- Pre-Hispanic Settlement: El Julán is known for the remains of Bimbache settlements, dating back to the Guanches, the indigenous people of the Canary Islands. The Bimbache were the inhabitants of El Hierro and lived in this area for centuries before the Spanish conquest.
- Archaeological Discoveries: Among the most notable features of El Julán are the ancient stone structures, which were once used for domestic, religious, and ritual purposes. The site contains remnants of stone houses, pits, and other architectural elements that reveal the daily life of the Bimbache people.
- The Bimbache were known for their agricultural practices, including the cultivation of cereals, and for their use of terracing in the difficult terrain of the island. The stone buildings and structures found at El Julán give valuable insight into how these early islanders adapted to their harsh volcanic environment.
Petroglyphs and Rock Art
- Petroglyphs: El Julán is also renowned for its rock art, with petroglyphs carved into the volcanic rocks. These ancient engravings depict geometric patterns, figures of animals, and symbolic representations, believed to have had a ritualistic or spiritual significance for the Bimbache people.
- The petroglyphs at El Julán are among the best-preserved examples of Canarian prehistoric art, providing key insights into the religious beliefs, cultural practices, and social structure of the island’s early inhabitants.
Cultural and Historical Importance
- Cultural Heritage: El Julán is not only important for its archaeological significance but also for its role in the cultural heritage of the Canary Islands. The site is a link between the ancient past of the island and the more modern history that followed the arrival of the Spanish.
- Connection to Bimbache Traditions: The Bimbache people are known to have had a rich culture, including specific religious beliefs and social customs. El Julán, with its remnants of dwellings and rock art, provides important clues about their worldview, practices, and way of life.
Conservation and Protection
- Protected Site: El Julán is a protected archaeological site, and efforts have been made to preserve its unique structures and rock art. It is an important part of El Hierro’s cultural landscape, and visiting the site is regulated to ensure that it is not damaged by human activity.
- UNESCO World Heritage: While the site itself is not currently listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, El Julán is part of the Cultural Landscape of the Canary Islands and is included in the island's overall heritage protection measures.
Visitor Experience
- Guided Tours: Visiting El Julán requires prior planning, as access to the site is typically accompanied by guided tours that offer in-depth explanations of the archaeological findings. The guides are knowledgeable about the history of the site, the significance of the petroglyphs, and the lifestyle of the Bimbache people.
- Historical Context: Tour guides explain the importance of the petroglyphs and the structures found at the site, helping visitors understand their cultural and historical context. The site offers an educational experience for those interested in learning about the island’s indigenous cultures.
Hiking and Nature
- Scenic Hiking: The area surrounding El Julán is also ideal for hiking. The volcanic landscapes and natural beauty of the area provide a stunning backdrop for those who enjoy outdoor activities. Visitors can explore the rugged terrain while discovering more about the island's environment and history.
- The hike to El Julán itself takes visitors through beautiful and remote parts of El Hierro, showcasing the island’s dramatic landscapes of volcanic cliffs, deep ravines, and lush vegetation.
Best Time to Visit
- Spring and Autumn: The best times to visit El Julán are during the spring and autumn, when the weather is milder, and the hiking conditions are more comfortable. These seasons also allow for better visibility and more pleasant conditions for exploring the archaeological site.
- Summer: While summer is also a good time to visit, temperatures can be quite high on El Hierro, and visitors should be prepared for the heat and bring adequate water supplies.
Conclusion
El Julán is an invaluable archaeological site that provides a fascinating glimpse into the ancient history of El Hierro and the Canary Islands. With its well-preserved rock engravings, stone structures, and insight into the Bimbache culture, the site offers an enriching experience for history and archaeology enthusiasts. The combination of ancient art, stunning volcanic landscapes, and the tranquility of El Hierro makes El Julán a unique destination for visitors seeking to explore the island’s pre-Hispanic heritage.