Information
Landmark: El Hierro Biosphere ReserveCity: El Hierro
Country: Canary Islands
Continent: Europe
El Hierro, the smallest of the Canary Islands, is renowned for its stunning natural landscapes, and it was designated a Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO in 2000. The island is located in the Atlantic Ocean, southwest of Tenerife, and is known for its rich biodiversity, unique geological features, and cultural heritage. Here's a detailed look at the El Hierro Biosphere Reserve:
Geography and Climate
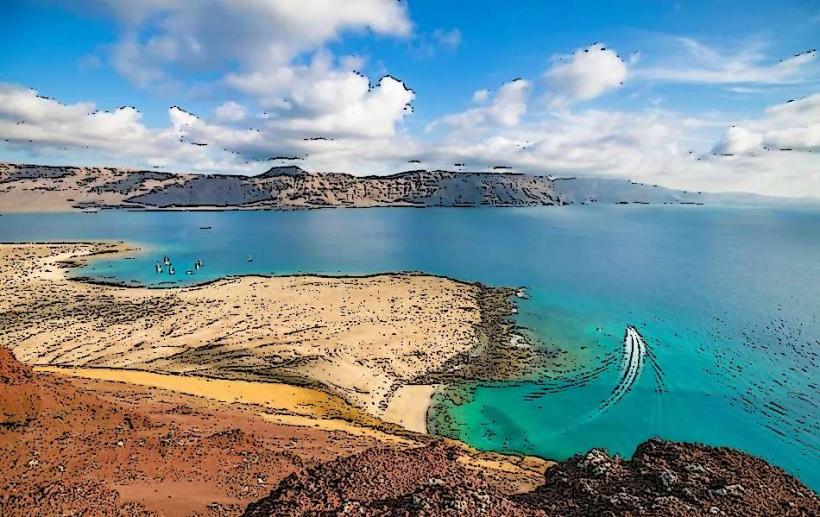
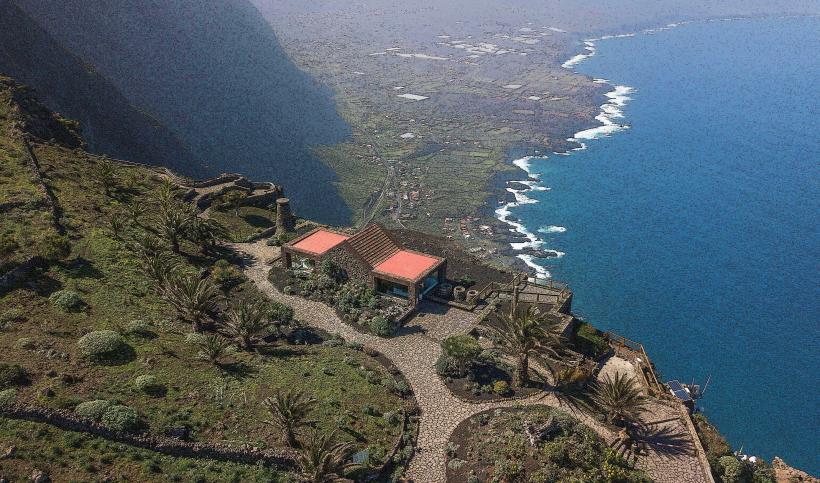
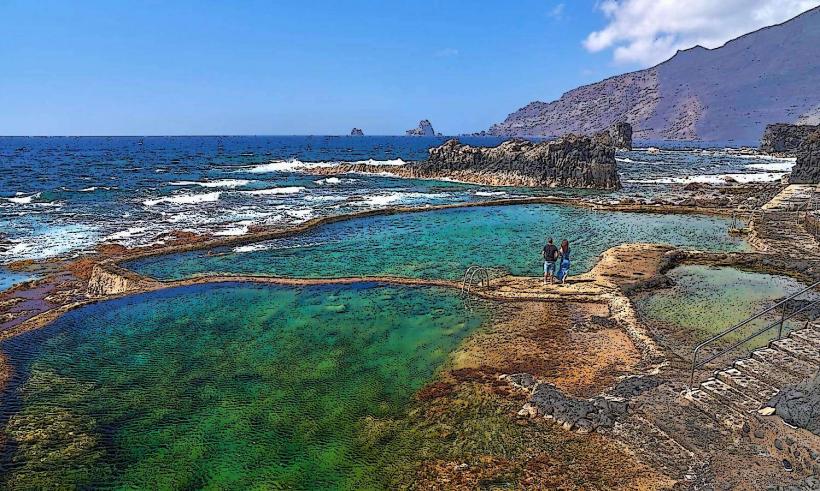
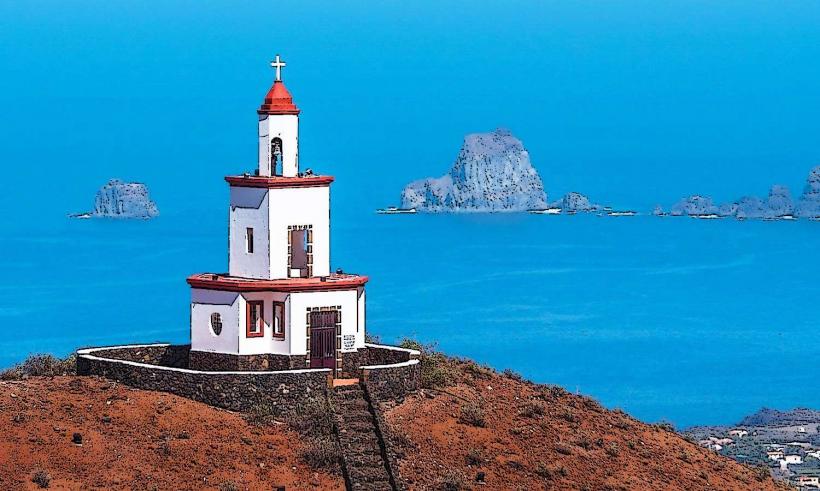
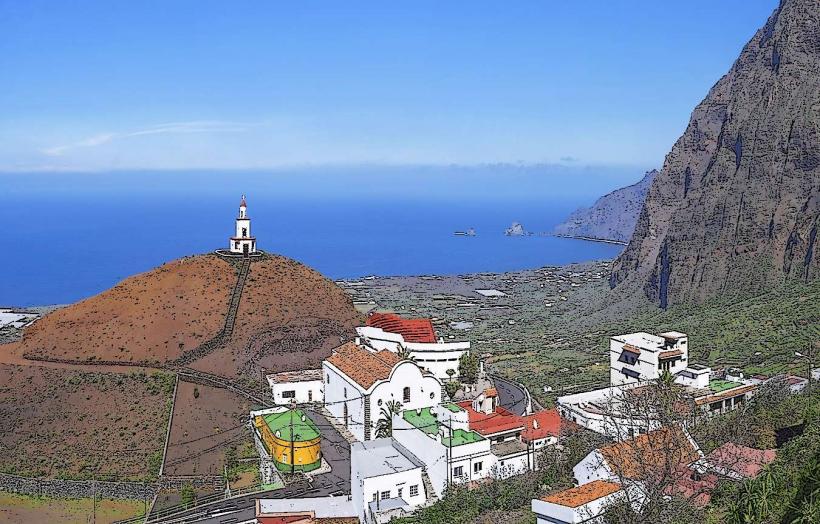
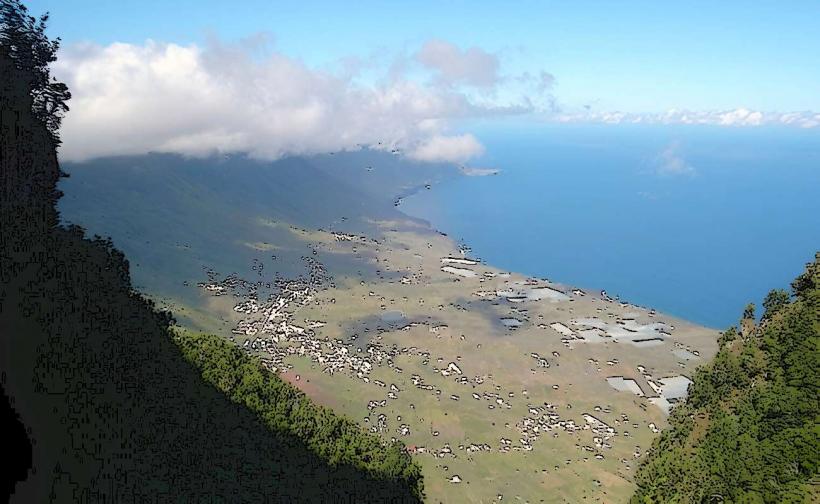
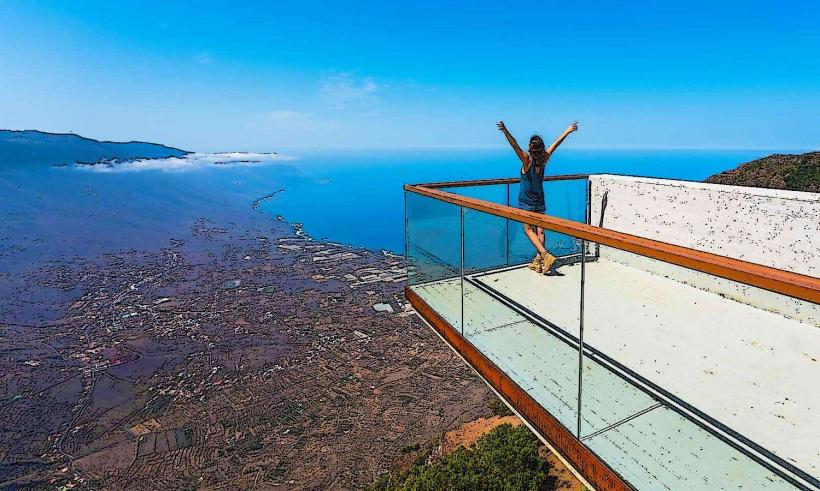
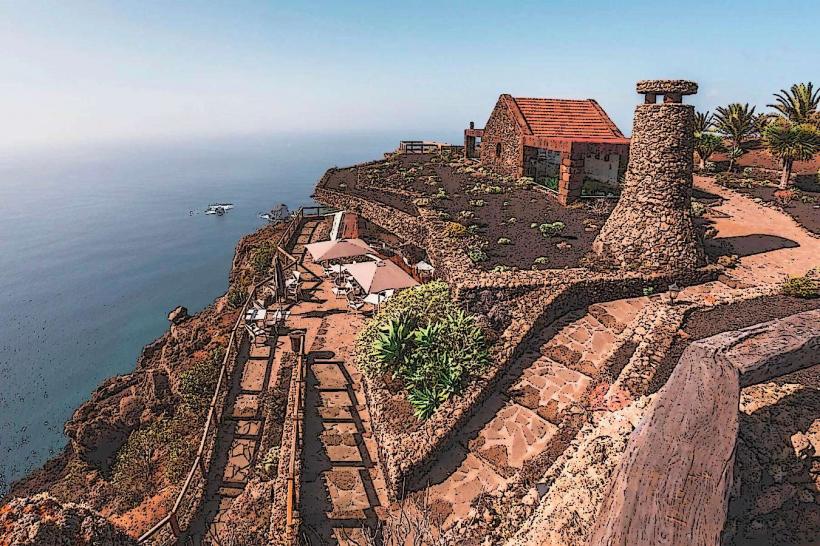
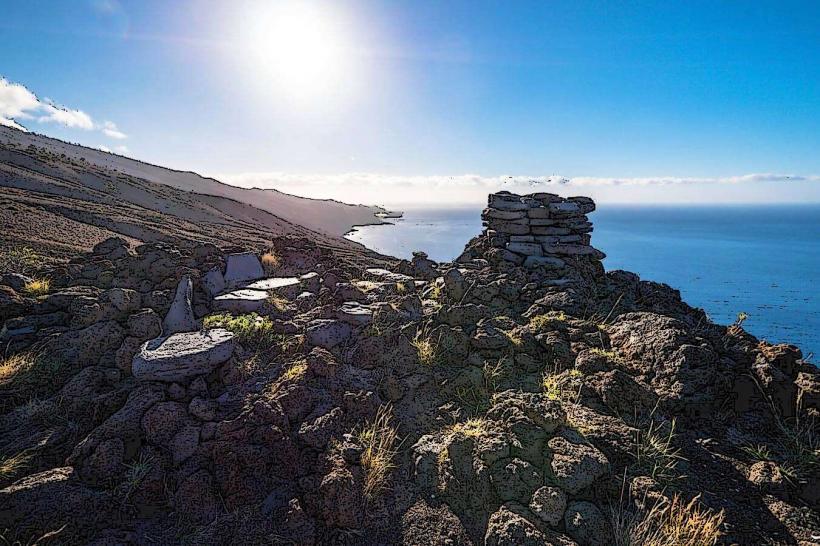
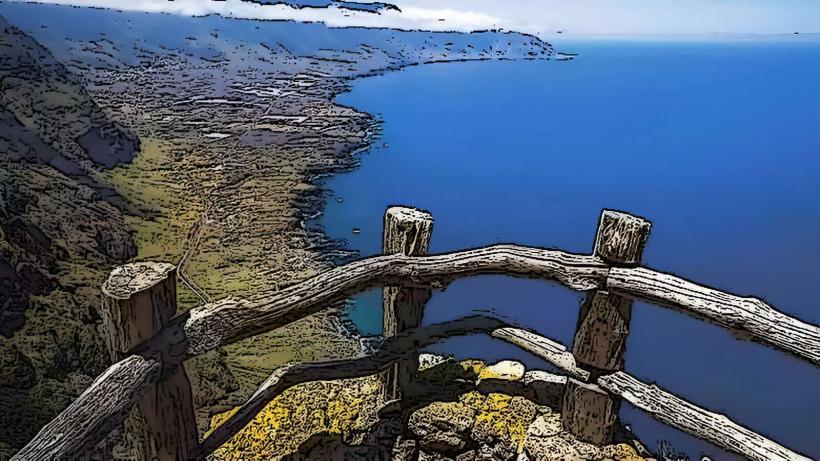
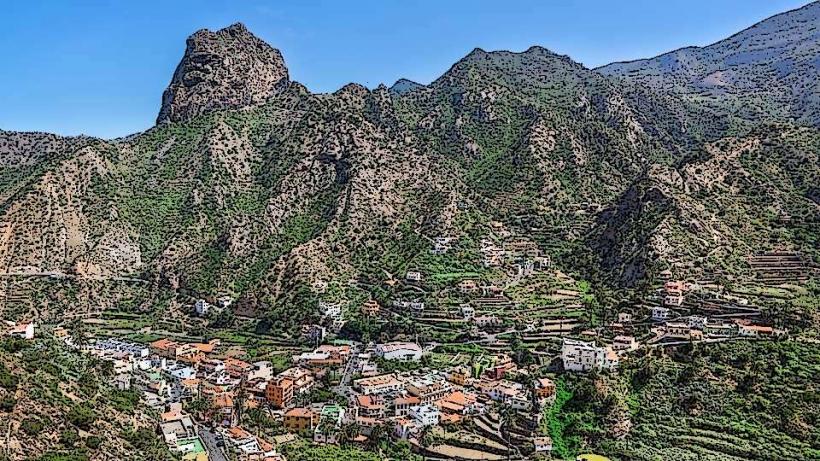
El Hierro is a volcanic island with dramatic landscapes that include rugged cliffs, craggy coastlines, lush forests, and volcanic craters. It is part of the Canary Islands, which are situated off the northwest coast of Africa. The island's climate is subtropical, with warm temperatures throughout the year, but the varied terrain creates microclimates, from arid zones in the lowlands to lush, temperate forests in the higher altitudes.
Biosphere Reserve Designation
El Hierro was designated as a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve due to its exceptional combination of environmental diversity, ecological importance, and sustainable management practices. It serves as a model for the integration of biodiversity conservation with sustainable development, promoting the harmonious balance between human activity and nature.
Flora and Fauna
The flora and fauna of El Hierro are characterized by a high degree of endemism, meaning many species are found nowhere else in the world. Some of the notable species and ecosystems include:
- Flora: The island's plant life is diverse, with forests of Canarian pine, laurel forests (laurisilva), and endemic species such as Hierro thyme (Thymus herbanioides). The higher altitudes feature extensive vegetation, while the coastal zones have plant species adapted to arid conditions.
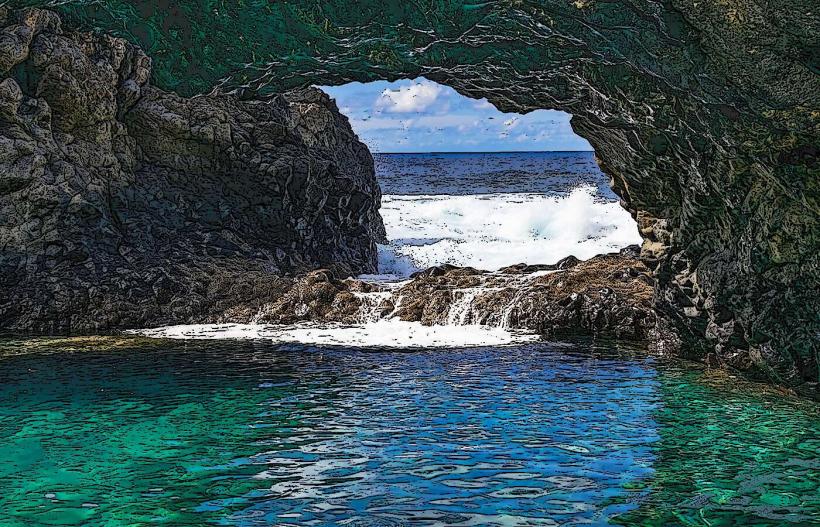
- Fauna: El Hierro is home to unique species of birds, including the endemic El Hierro giant lizard (Gallotia simonyi), and various species of seabirds. Marine life around the island is also rich, particularly in the clear waters around its coastal areas, making it a popular destination for divers. El Hierro is a key location for the conservation of marine biodiversity, with several species of fish and marine mammals.
Protected Areas and Natural Parks
The island is home to several protected areas, each contributing to the overall integrity of the biosphere reserve. Some notable ones include:
- Pinar de El Hierro: A significant area of Canarian pine forest, offering a habitat for a variety of species and important for maintaining the island’s ecological balance.
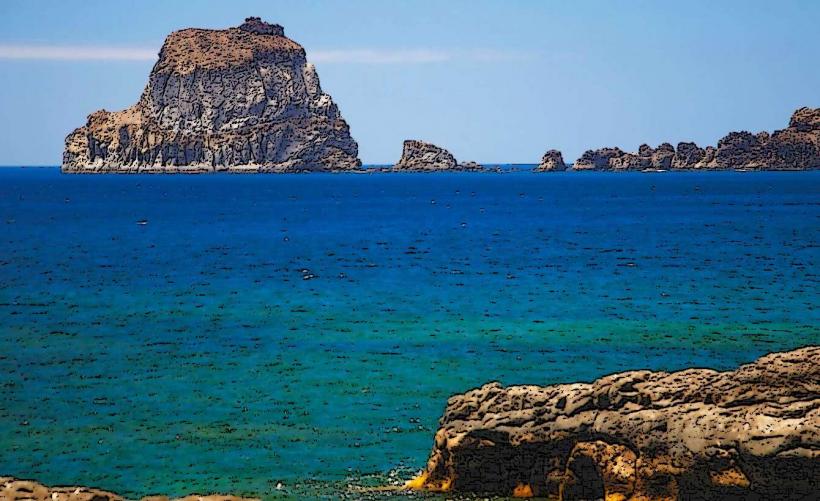
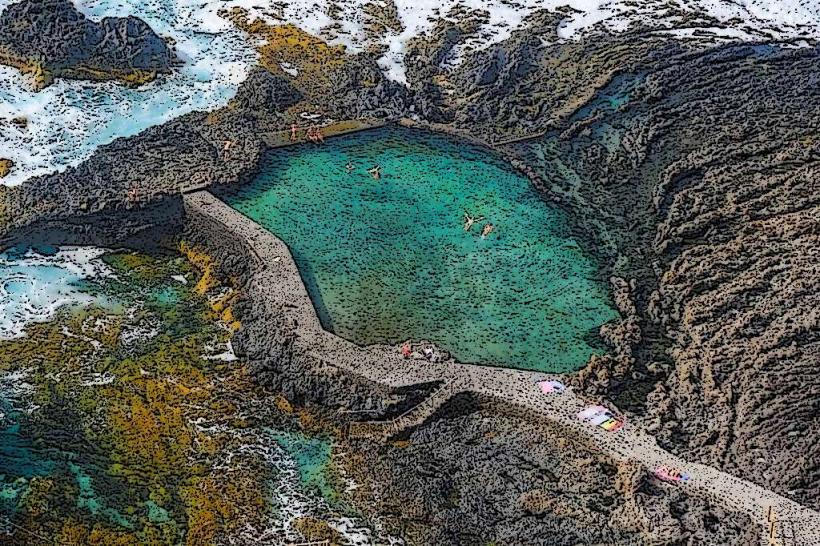
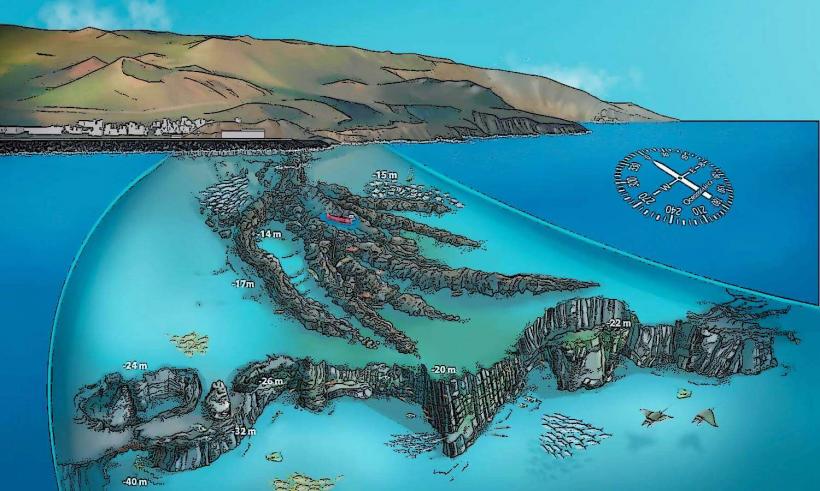
- La Restinga Marine Reserve: This marine protected area is known for its rich underwater ecosystems, including coral reefs and a variety of fish species. It's a popular site for underwater tourism, particularly for diving.
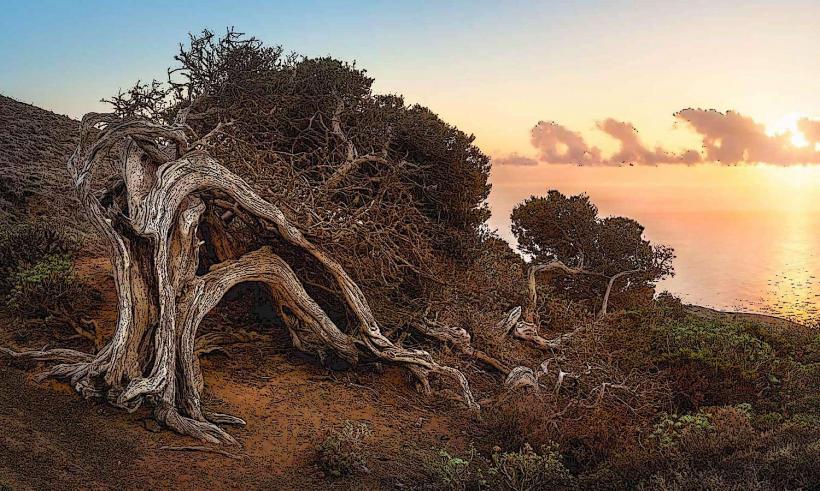
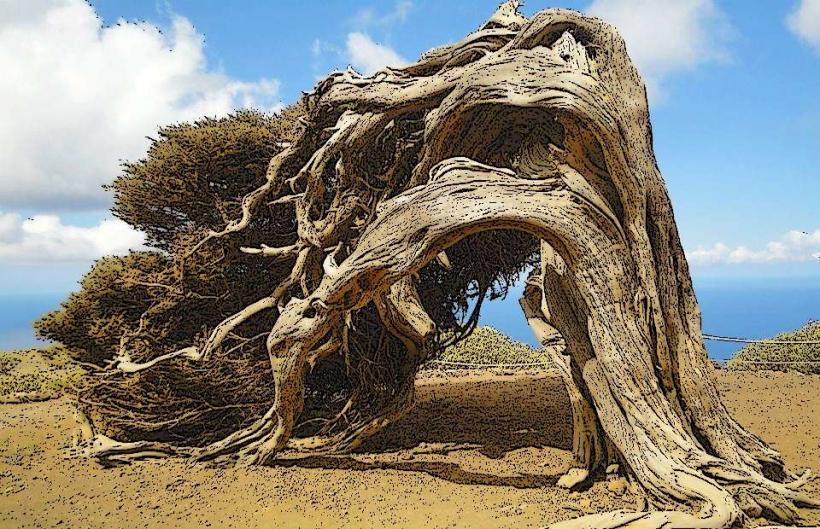
- El Sabinar: A forest of ancient juniper trees that have been shaped by the strong winds of the island. These trees create a unique, windswept landscape that is visually striking.
Sustainable Practices and Renewable Energy
El Hierro is also recognized for its pioneering efforts in sustainable living. The island has become a leader in renewable energy, especially with its ambitious project to achieve energy self-sufficiency. A combination of wind, solar, and hydroelectric power now provides the island with virtually all of its energy needs. The El Hierro wind-hydro system is considered one of the most advanced and successful renewable energy projects in the world, making the island a model for sustainability.
Cultural Heritage
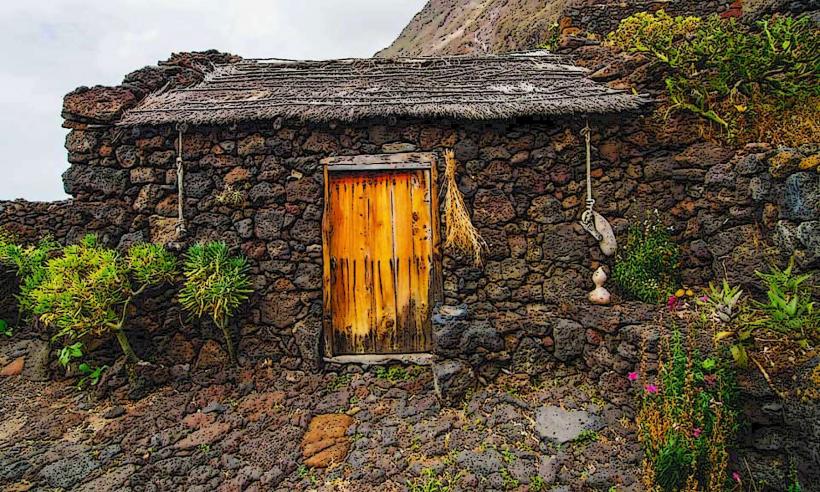
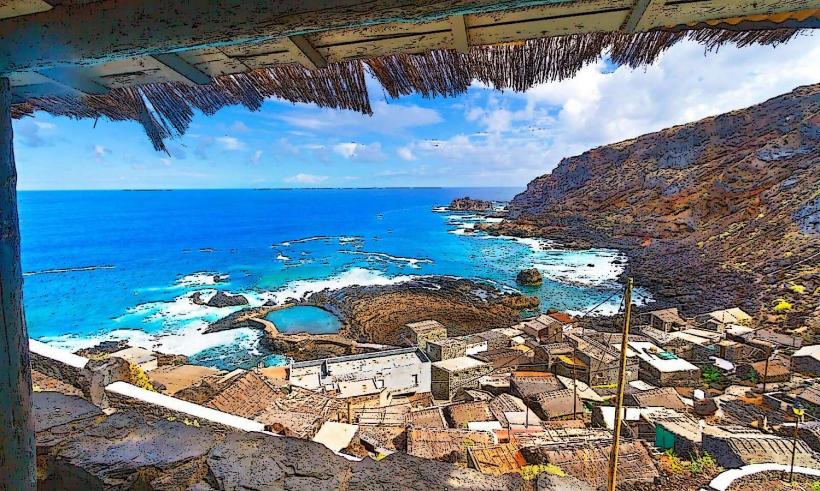
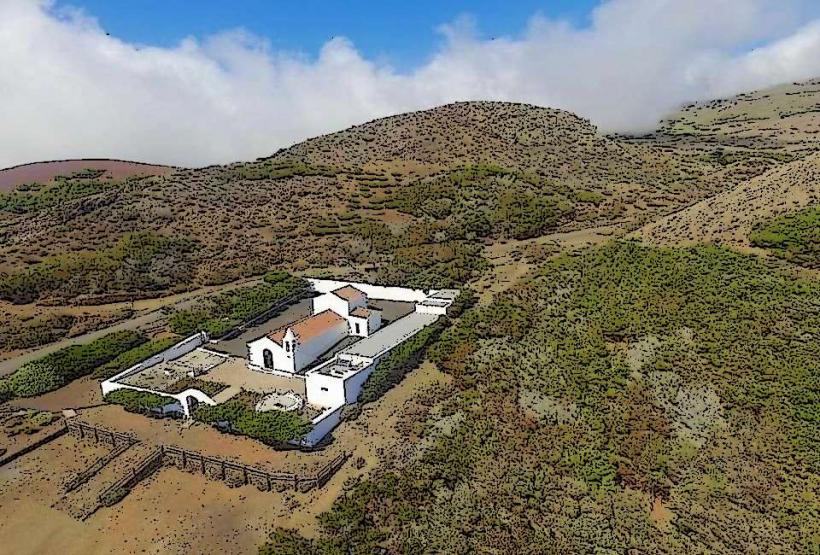
In addition to its natural beauty, El Hierro has a rich cultural heritage. The island's traditional architecture, particularly in the rural areas, reflects its historic ties to fishing, agriculture, and maritime activities. The islanders have preserved many ancient practices, including farming techniques that are sustainable and adapted to the challenging island environment.
The island is also known for its unique form of popular celebrations, particularly during the Fiesta de la Virgen de los Reyes, a religious festival that takes place annually and is integral to the island's social fabric.
Tourism and Education
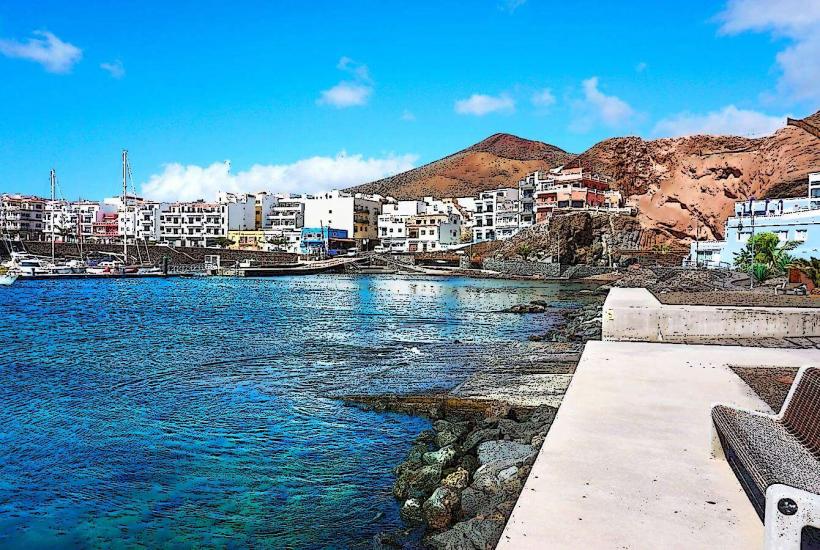
While El Hierro remains relatively less developed compared to other Canary Islands, it attracts visitors who are interested in sustainable tourism, nature reserves, and eco-friendly experiences. Its diverse landscapes provide opportunities for hiking, birdwatching, diving, and exploring the pristine environment.
Additionally, the island has a strong focus on environmental education, promoting awareness of biodiversity conservation, renewable energy, and sustainable practices through visitor centers, nature trails, and educational programs.
Conservation Efforts
The El Hierro Biosphere Reserve focuses on the conservation of both terrestrial and marine ecosystems, and the island has implemented various programs to protect its biodiversity. Key efforts include:
- Ecosystem restoration: Reforestation projects and habitat restoration have been undertaken to combat erosion and desertification.
- Marine conservation: The island's surrounding waters are protected to maintain healthy marine life, including the establishment of marine reserves.
- Sustainable agriculture: Agricultural practices on the island are being shifted toward sustainability, including organic farming and the promotion of local products.
Conclusion
The El Hierro Biosphere Reserve is an exceptional example of an island ecosystem that integrates environmental conservation with human development. Its rich biodiversity, sustainable practices, and efforts to promote renewable energy make it a vital region not only for the Canary Islands but for global environmental stewardship.