Information
Landmark: Maripa RiverCity: Cayenne
Country: French Guiana
Continent: South America
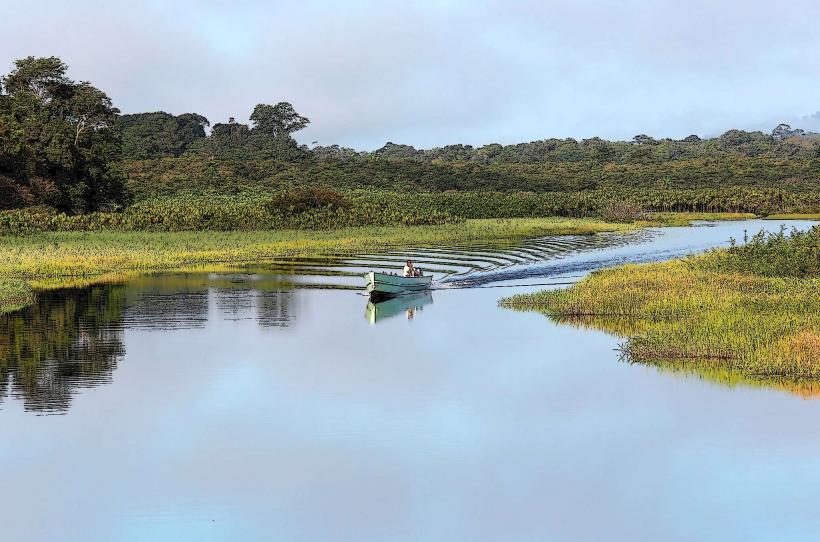
The Maripa River is a river located in French Guiana, in the northeastern part of South America. It is one of the smaller rivers in the region but is an important part of the Oyapock River system. The Maripa River flows through dense tropical forests and contributes to the diverse and ecologically significant waterways of the region.
Geographic Location and Features
- Location: The Maripa River is located in the southern part of French Guiana, near the border with Brazil. It is part of the broader Oyapock River system, which forms part of the natural boundary between French Guiana and Brazil.
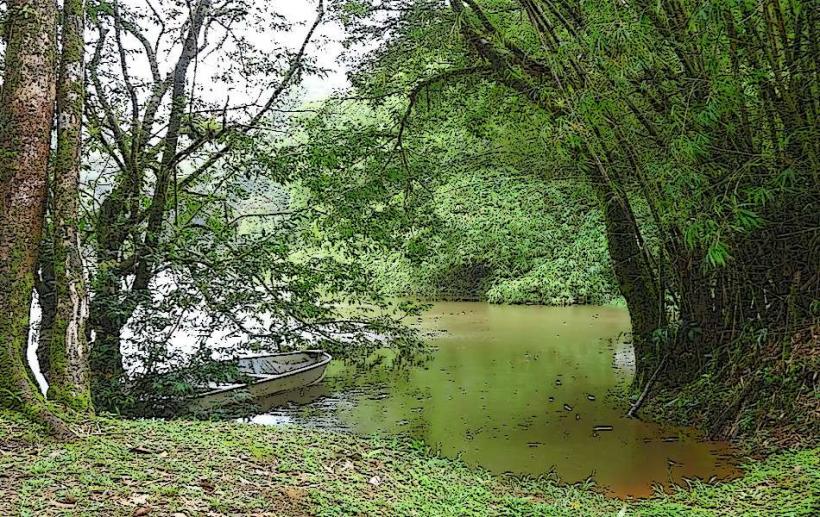
- Course and Tributary System: The Maripa River is a tributary of the Oyapock River, which is one of the major rivers that run through the region. The Maripa itself is relatively short in comparison to other rivers in the region but plays a key role in the local hydrology.
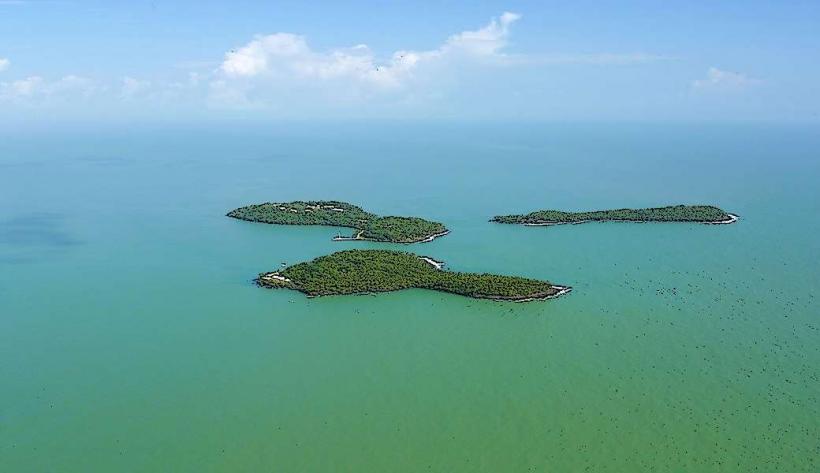
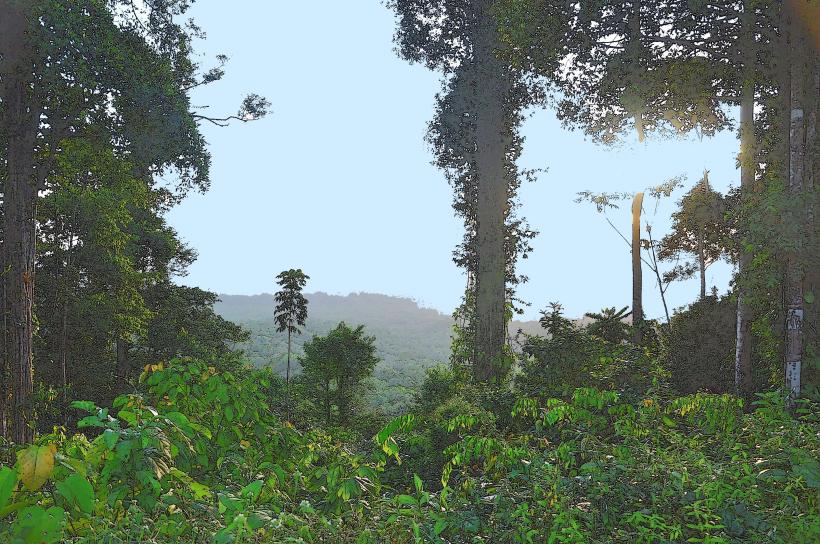
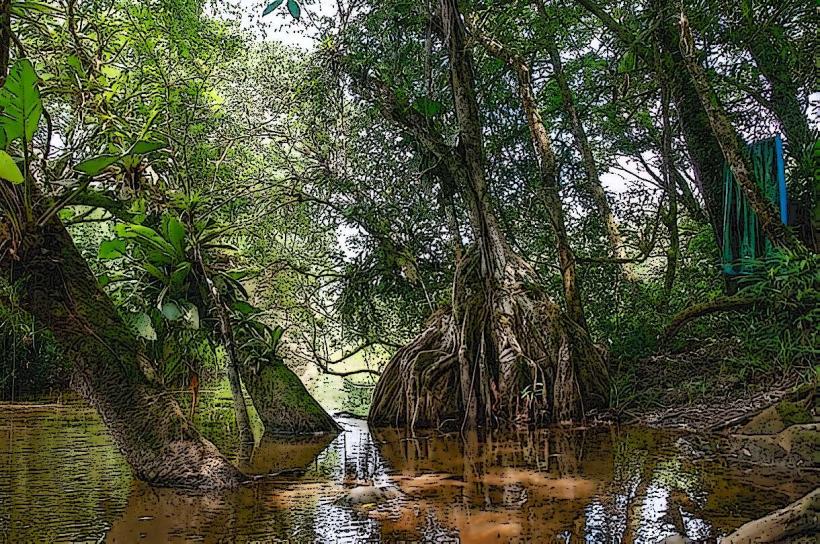
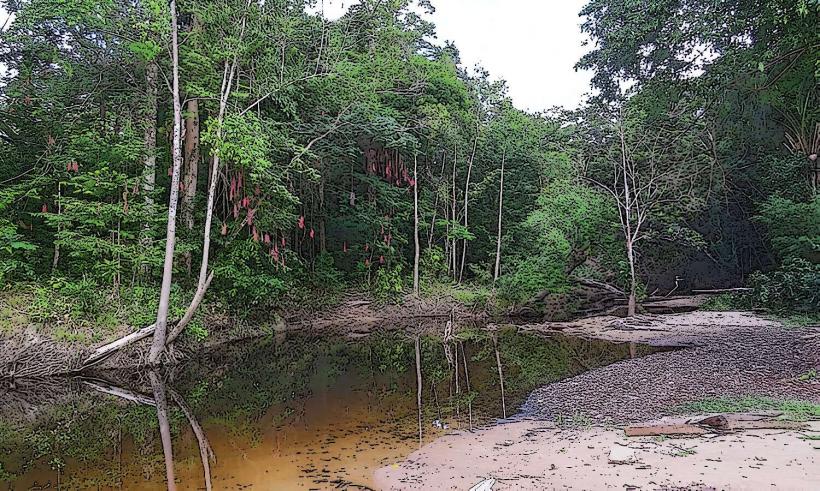
- Tropical Landscape: The river flows through dense tropical rainforest and wetland ecosystems, which are vital for the biodiversity of the region. The terrain around the river includes lowland forests, floodplains, and riverine environments.
Ecological Importance
The Maripa River and its surrounding ecosystems are part of the larger Amazon Rainforest system, known for its extraordinary biodiversity. The river and the surrounding landscapes support a wide range of species and provide critical environmental services.
- Rainforest Ecosystem: The river is bordered by tropical rainforests, which are home to many species of plants, animals, and insects. These forests are rich in biodiversity, with towering trees, dense undergrowth, and a variety of flora and fauna.
- Aquatic Biodiversity: The Maripa River is home to a variety of aquatic species, including fish, amphibians, and reptiles. The river provides critical breeding and feeding grounds for many species, such as river turtles, caimans, and freshwater fish.
- Wetland Habitats: The floodplains and wetlands surrounding the river are vital habitats for species such as wading birds, waterfowl, and invertebrates. These wetlands also serve important ecological functions, including water purification, flood regulation, and carbon sequestration.
- Terrestrial Fauna: The rainforests around the Maripa River are home to a variety of land animals, including jaguars, pumas, howler monkeys, capuchin monkeys, and a diversity of bird species like parrots and toucans.
Human Interaction and Conservation
- Human Settlement: The area around the Maripa River is sparsely populated, with only small settlements located along the riverbanks. The remoteness of the area makes large-scale human development difficult, but some Indigenous groups may still live in the broader region, relying on the river for subsistence activities like fishing, hunting, and gathering.
- Conservation Efforts: While the Maripa River itself may not be the focus of dedicated conservation programs, it is part of the larger conservation efforts to protect the Amazon Rainforest and Guiana Shield ecosystems. The area is subject to legal protections aimed at preserving biodiversity and limiting deforestation, logging, and other forms of environmental degradation.
- Protected Areas: French Guiana has several protected areas that include parts of the region around the Maripa River, such as nature reserves, national parks, and areas designated for environmental conservation. These efforts are vital for maintaining the health of the river’s ecosystems.
Challenges
- Illegal Activities: Despite the river's protected status, the area around the Maripa River faces threats from illegal logging, gold mining, and poaching. These activities can result in habitat destruction, water pollution, and disturbances to wildlife.
- Climate Change: The ecosystems surrounding the Maripa River are vulnerable to climate change, with risks such as changing rainfall patterns, higher temperatures, and the potential for more extreme weather events. These changes can impact water levels, biodiversity, and ecosystem stability.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species into the region could pose a threat to the local flora and fauna, disrupting the delicate balance of the river’s ecosystems.
Conclusion
The Maripa River is an important waterway in French Guiana, contributing to the Oyapock River system and supporting a rich and diverse set of ecosystems. Its surrounding rainforests, wetlands, and aquatic habitats make it a vital part of the region's environmental landscape. Despite being less well-known than some larger rivers in the region, the Maripa River plays a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity and providing ecosystem services. However, the river and its ecosystems face challenges from human activities, climate change, and environmental threats, making ongoing conservation efforts essential to protect the region’s natural resources.