Information
Landmark: Crique SaramacaCity: Cayenne
Country: French Guiana
Continent: South America
Crique Saramaca is a river located in the French Guiana region, situated to the east of the capital city Cayenne. The river is part of the Oyapock River system, which drains a significant portion of southern French Guiana. Crique Saramaca is a smaller tributary of the Oyapock, but it holds ecological and geographical importance within its region.
Geographic Location and Features
- Location: The river is found in the southeastern part of French Guiana, flowing primarily through dense tropical rainforests. It is positioned near the border with Brazil and is part of the broader Amazon Basin.
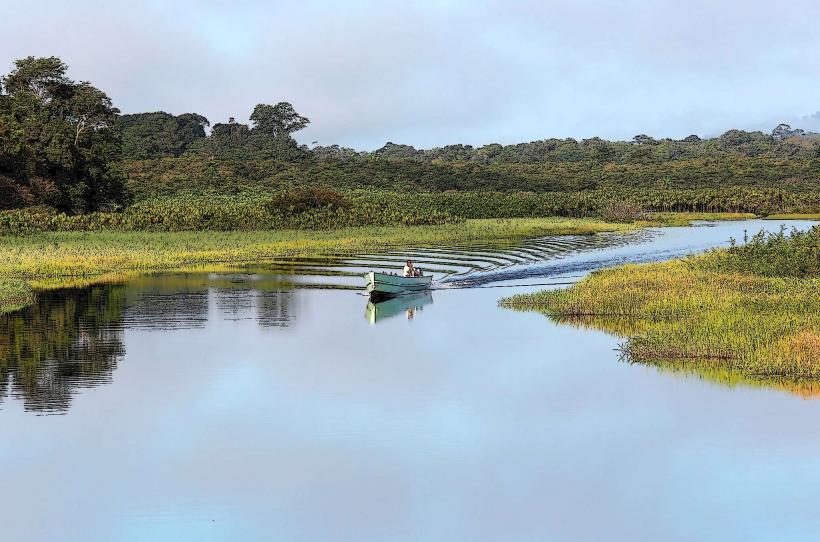
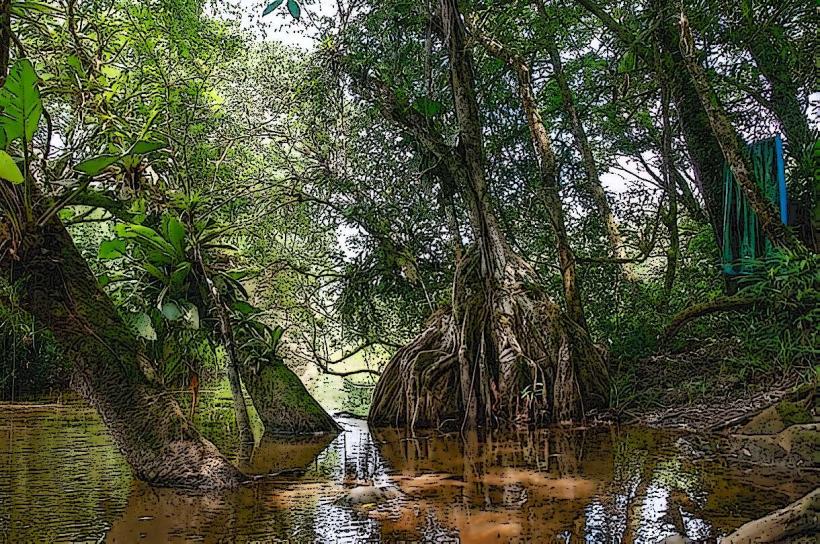
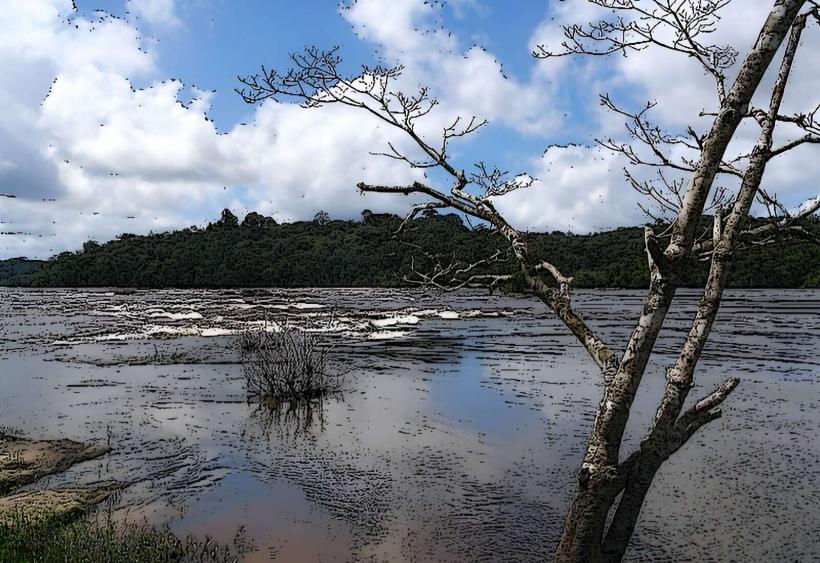
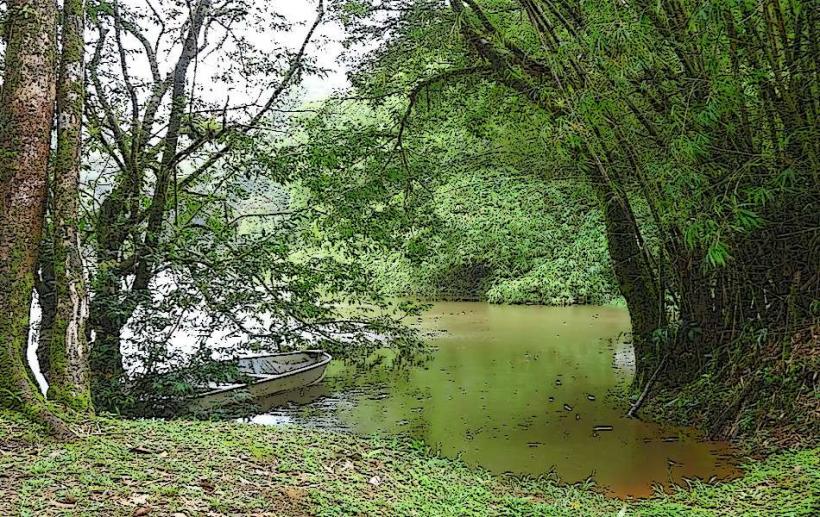
- Watercourse: Crique Saramaca is a relatively short, winding river, which flows through tropical landscapes and meanders through various ecosystems, including wetlands, forests, and floodplains.
- Tributary System: It is a tributary of the Oyapock River, which is one of the major rivers that forms the natural border between French Guiana and Brazil. The Oyapock River is crucial in the hydrology of the region, draining the inland areas and facilitating water transport.
Ecological Significance
Crique Saramaca is situated in a biodiversity-rich region and is integral to the ecology of the surrounding rainforests, wetlands, and riverine environments.
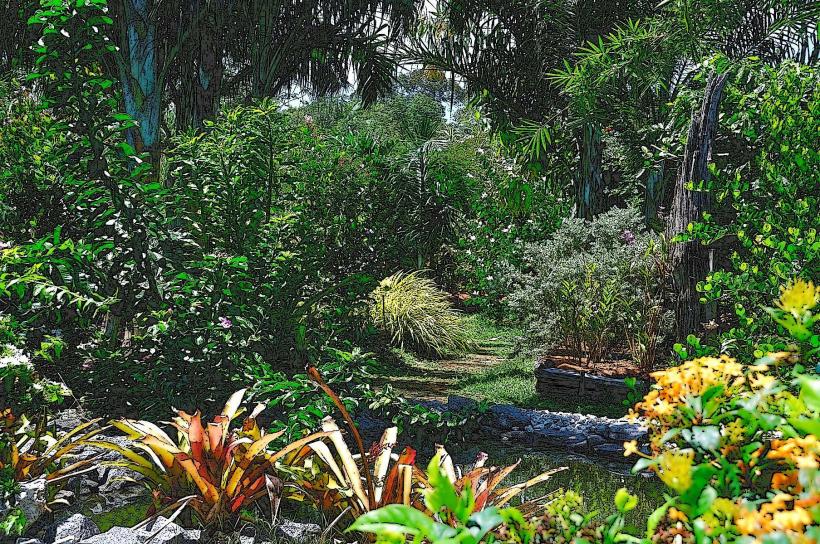
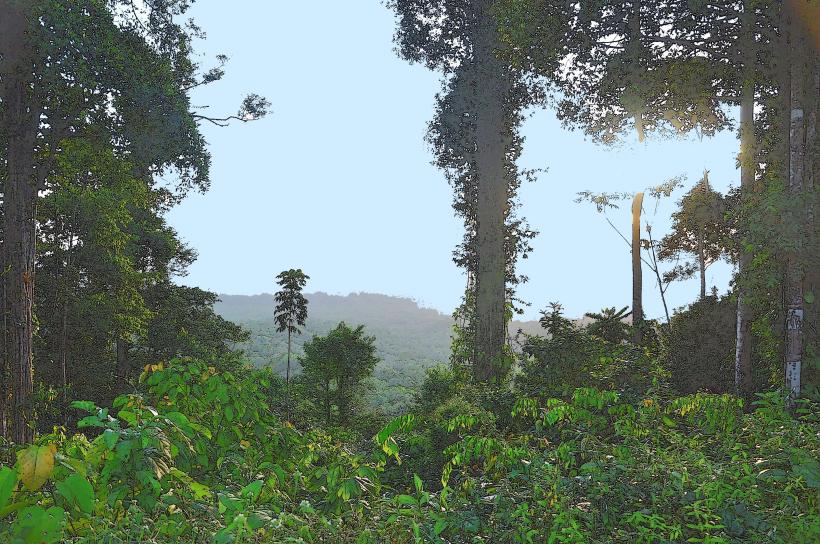
- Tropical Rainforests: The river flows through dense rainforests that are home to numerous species of flora and fauna. These forests are part of the larger Amazon Rainforest, one of the most biodiverse ecosystems in the world.
- Wetlands and Floodplains: The river meanders through wetland ecosystems where species like caimans, river turtles, and fish thrive. The surrounding floodplains and low-lying areas are flooded during the rainy season, creating vital habitats for aquatic plants, insects, and animals.
- Biodiversity: The river and its surrounding areas support a variety of species, including jaguars, monkeys, parrots, and toucans. The rainforests and waterways along Crique Saramaca are also crucial habitats for various aquatic species such as fish and amphibians.
- Wetland Habitats: The wetlands near Crique Saramaca contribute to the overall health of the region's ecosystem services, such as water purification, flood control, and carbon storage.
Human Interaction and Conservation
- Limited Human Settlement: The area surrounding Crique Saramaca is sparsely populated, with few settlements in the immediate vicinity. The remoteness of the region and its thick forests make it difficult for large-scale human activities to take place.
- Conservation Efforts: While the area is not as well known as other protected regions in French Guiana, it remains part of the broader efforts to conserve the Amazon Rainforest and the Guiana Shield. The forests and wetlands in the vicinity are protected under local conservation regulations, and efforts to preserve the river’s ecosystem from illegal logging, mining, and other human encroachments are ongoing.
- Cultural Importance: Some Indigenous communities in the region may utilize resources along the river for subsistence fishing, hunting, and gathering. Their traditional practices are important for the sustainable management of the area.
Challenges
- Illegal Activities: Like many areas of French Guiana, the region around Crique Saramaca faces challenges from illegal gold mining, logging, and hunting, which can damage the environment and biodiversity. Enforcement of environmental protections is crucial to maintain the health of the river and surrounding ecosystems.
- Climate Change: As part of the Amazon Basin, the river’s ecosystems are vulnerable to climate change, including altered rainfall patterns, droughts, and rising temperatures, which could impact the delicate balance of the surrounding rainforests and wetlands.
Conclusion
Crique Saramaca is an important river within the Oyapock River system and plays a significant role in the ecology of the southeastern part of French Guiana. The river is vital for its surrounding tropical rainforests, wetlands, and biodiversity. Despite limited human settlement, the area faces challenges from illegal activities and environmental changes. Continued conservation efforts are essential to protect the river’s unique ecosystems and the biodiversity it supports.