Information
Landmark: Archaeological Museum of NamurCity: Namur
Country: Belgium
Continent: Europe
Archaeological Museum of Namur, Namur, Belgium, Europe
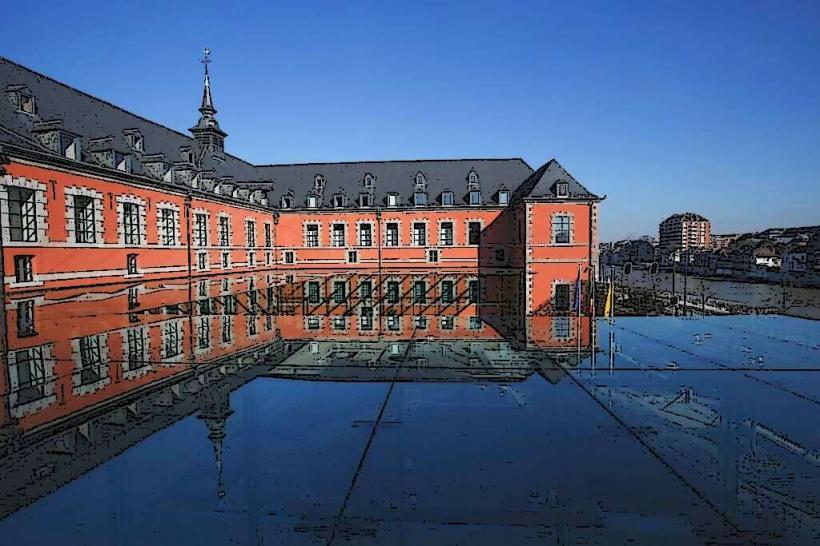
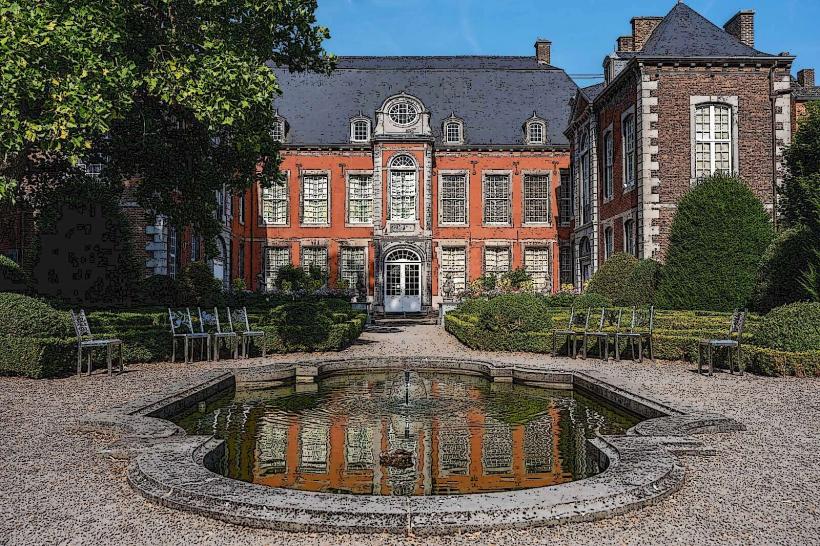
The Archaeological Museum of Namur (Musée archéologique de Namur) is currently housed within the Les Bateliers cultural pole, a site dedicated to the history and heritage of the region.
Visual Characteristics
The museum is situated in the Hôtel des Bateliers, a refined 18th-century noble residence. It features a facade of brick and blue limestone typical of the Mosan style. The interior galleries display a vast chronological range of artifacts, from Prehistoric tools to Gallo-Roman treasures and Merovingian jewelry, all presented within the historic proportions of the mansion.
Location & Access Logistics
The site is located at Rue Joseph Saintraint 7, 5000 Namur.
Public Transport: 10-minute walk from Namur Railway Station.
Parking: Nearest facility is Parking Saint-Aubain.
Access: Entry requires a paid ticket. The site is partially accessible; the ground floor and modern wing (Les Bateliers) are wheelchair accessible, though some historic sections may have limitations.
Historical Origin
The Archaeological Society of Namur founded the museum in 1845. For over a century, it was housed in the historic Meat Hall (Halle aux Viandes) on the Sambre River. It recently moved to the Les Bateliers site to consolidate Namur's archaeological and decorative art collections. The move allowed for the integration of the "Treasure of Oignies" and significant regional finds into a modern museum setting.
Key Highlights & Activities
Gallo-Roman Collection: Features one of the most important collections of Roman-era artifacts in Belgium, including glassware, pottery, and funeral ornaments.
Merovingian Jewelry: Exceptional gold and garnet pieces from early medieval burial sites.
Les Bateliers Gardens: A restored 18th-century formal garden connecting the Archaeological Museum with the Museum of Decorative Arts.
Regional Prehistory: Exhibits detailing the earliest human settlements in the Meuse valley.
Infrastructure & Amenities
The museum shares facilities with the Museum of Decorative Arts. It includes a reception area, a boutique, and educational spaces. Restrooms are available on-site. 5G signal is robust.
Best Time to Visit
Open Tuesday through Sunday from 10:00 to 18:00. Closed on Mondays. Visiting on a weekday morning ensures the quietest environment for examining the intricate archaeological finds.
Facts & Legends
A verified historical detail is that the museum's collection was largely built through the active field research of the Archaeological Society of Namur, which remains one of the oldest and most active in Belgium. A local "legend" often associated with archaeological sites in Namur is the presence of hidden tunnels connecting the historic basements of the Rue Joseph Saintraint directly to the Citadel's underground network.
Nearby Landmarks
Namur Cathedral (Saint-Aubin) – 0.1km West
Félicien Rops Museum – 0.1km East
Citadel of Namur – 0.7km South
Place d'Armes – 0.5km East