Information
Landmark: Bangudae PetroglyphsCity: Ulsan
Country: South Korea
Continent: Asia
Bangudae Petroglyphs, Ulsan, South Korea, Asia
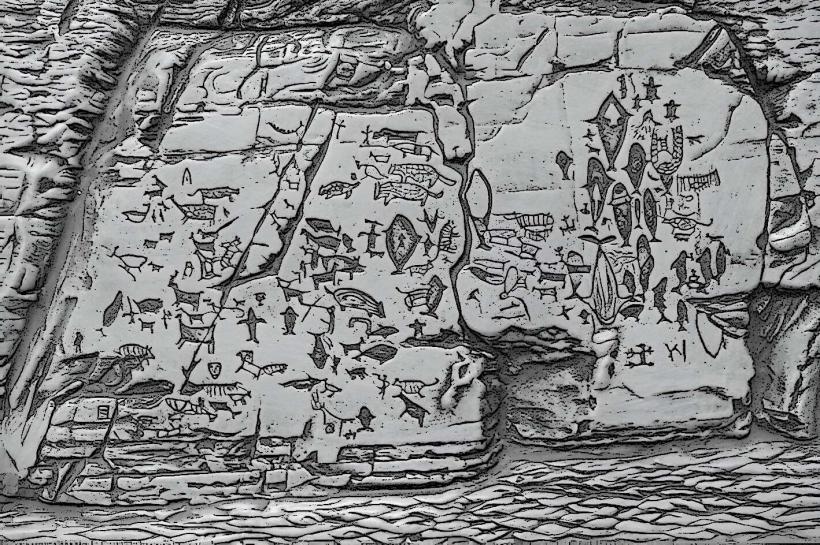
The Bangudae Petroglyphs are a collection of prehistoric rock carvings located in Ulsan, South Korea. These carvings depict scenes of hunting, animals, and human activities from the Neolithic and Bronze Ages.
Visual Characteristics
The petroglyphs are etched into a large, dark grey granite rock face. The carvings vary in depth and clarity, with some figures appearing as simple outlines and others more detailed. The rock face itself is approximately 10 meters high and 30 meters wide. The surrounding landscape is characterized by steep, forested hillsides.
Location & Access Logistics
The Bangudae Petroglyphs are situated approximately 35 kilometers northwest of Ulsan city center. Access is via National Route 35, then turning onto Local Road 1001. Parking is available at a designated lot near the site entrance. Public transport options are limited; Bus Line 147 from Ulsan Intercity Bus Terminal stops at a point approximately 2 kilometers from the petroglyphs, requiring a walk or taxi for the remainder of the journey.
Historical & Ecological Origin
The petroglyphs are believed to have been created between 4000 BCE and 1000 BCE, spanning the late Neolithic and Bronze Ages. Their exact purpose remains a subject of academic debate, with theories suggesting ritualistic significance, shamanistic practices, or a record of hunting success. The site is located within a valley formed by the Ganjeoncheon Stream, part of the Yeongnam Alps region, known for its diverse flora and fauna.
Key Highlights & Activities
Observation of the petroglyphs is the primary activity. Designated viewing platforms provide vantage points for examining the carvings. Interpretive panels offer information on the figures depicted. Hiking trails in the surrounding hills are accessible, though not directly connected to the petroglyph viewing area.
Infrastructure & Amenities
Restrooms are available at the parking area. Limited shade is provided by the viewing platforms. Cell phone signal (4G/5G) is generally available. No food vendors are present at the immediate site; visitors should bring their own provisions or plan to eat in nearby towns.
Best Time to Visit
For optimal viewing of the carvings, late afternoon light (approximately 2-3 hours before sunset) provides the best contrast and shadow definition. The months of April to October generally offer the most favorable weather conditions, with lower rainfall. The site is accessible year-round, but winter months can present icy conditions on pathways.
Facts & Legends
One of the most frequently depicted figures is the tiger, often shown in dynamic poses, suggesting its importance in the beliefs of the ancient inhabitants. Local folklore speaks of the carvings being created by ancient shamans to communicate with spirits of the land and animals.
Nearby Landmarks
- Cheonjeon-ri Petroglyphs (1.5km Southeast)
- Ulsan Grand Park (30km Southeast)
- Daewangam Park (38km Southeast)
- Jangsaengpo Whale Culture Village (36km Southeast)