Information
Landmark: Kursiu LagoonCity: Klaipeda
Country: Lithuania
Continent: Europe
Kursiu Lagoon, Klaipeda, Lithuania, Europe
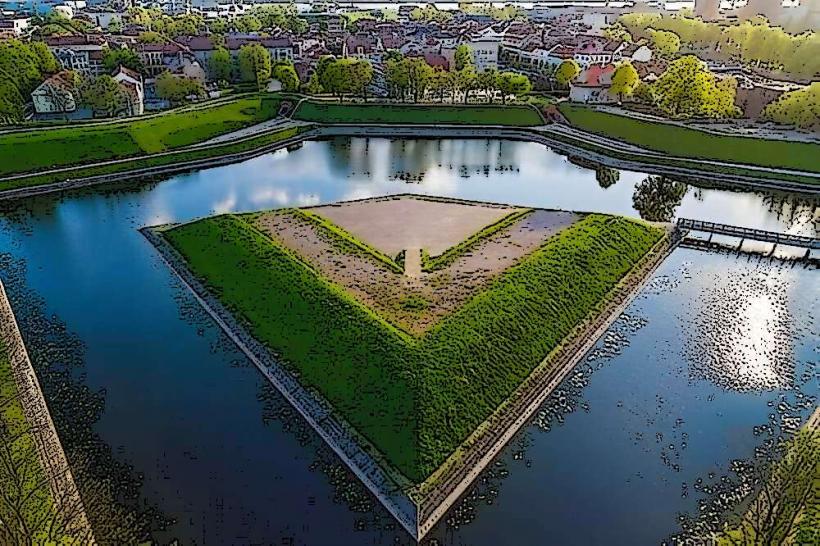
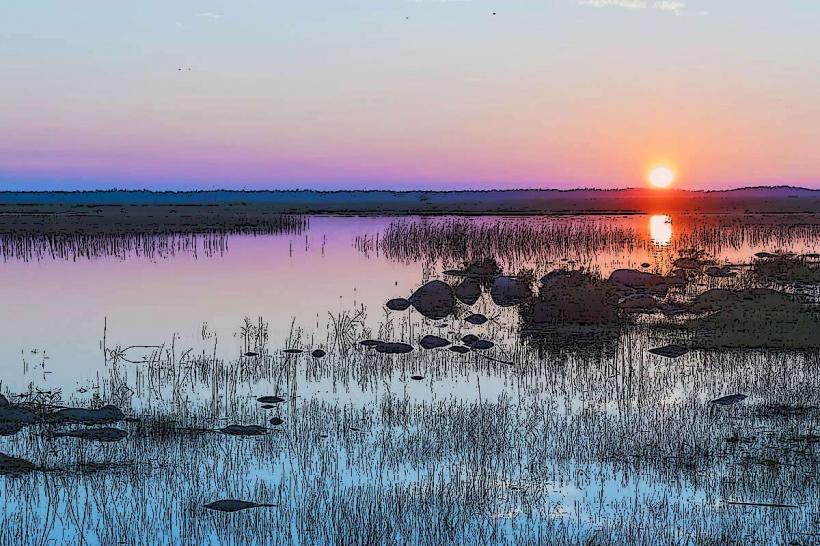
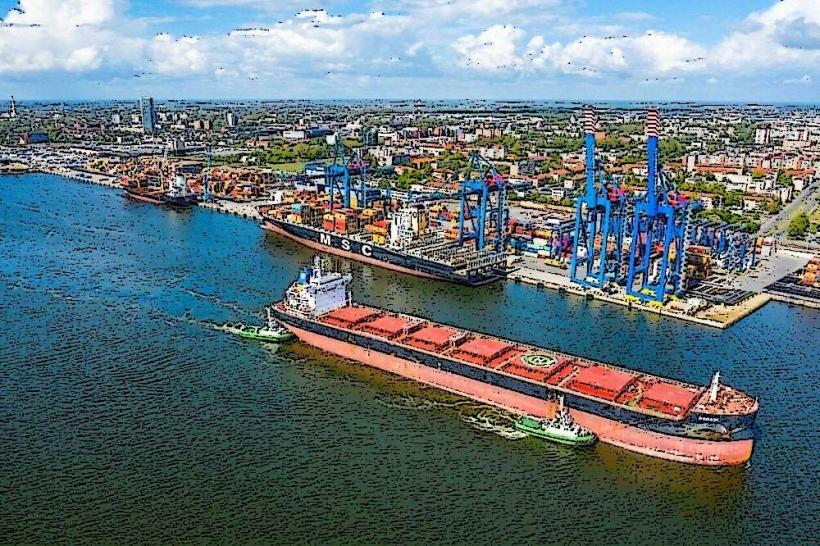
The Kursiu Lagoon, also known as the Curonian Lagoon, is a freshwater lagoon separated from the Baltic Sea by the Curonian Spit. Its eastern shore borders the city of Klaipeda, Lithuania, and extends south into the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia.
Visual Characteristics
The lagoon is a large, shallow body of water, approximately 99 km long and up to 28 km wide. Its average depth is 3.8 meters, with a maximum depth of 5.8 meters. The water is typically brackish, often appearing greenish-brown due to sediment and algal presence. The eastern shores are generally low-lying and sandy, characterized by reeds and marsh vegetation. The western boundary is formed by the Curonian Spit, a narrow, sandy peninsula featuring extensive dune systems and pine forests.
Location & Access Logistics
The Kursiu Lagoon directly borders the city of Klaipeda on its eastern side. Access points are numerous along the city's waterfront. From Klaipeda city center, various local roads, such as Smiltelės gatvė, lead to the lagoon shore. Parking is available at designated areas along the waterfront and near the Old Ferry Terminal. Klaipeda city buses provide public transport options to areas adjacent to the lagoon. The Old Ferry Terminal offers regular pedestrian and vehicle ferry services to Smiltynė on the Curonian Spit, providing direct access to the lagoon's western shore.
Historical & Ecological Origin
The Kursiu Lagoon is a geological formation classified as a freshwater lagoon. It formed approximately 5,000 years ago through the accumulation of sand, which created the Curonian Spit and gradually enclosed a former bay of the Baltic Sea. The lagoon is primarily fed by the Nemunas River, which contributes over 90% of its freshwater inflow, along with several smaller rivers.
Key Highlights & Activities
Sailing, kayaking, windsurfing, and kitesurfing are popular activities, particularly in areas with consistent wind conditions. Fishing for species such as perch, pike, and bream is common. Designated paths on the Curonian Spit facilitate cycling. The lagoon is a significant stopover point for migratory birds, making birdwatching a notable activity. Ferry trips from Klaipeda to Smiltynė offer scenic views of the lagoon.
Infrastructure & Amenities
Restrooms are available at the ferry terminals in Klaipeda and Smiltynė, as well as in nearby towns on the Curonian Spit. Shade is limited directly on the open lagoon shore but can be found in forested areas of the Curonian Spit. Cell phone signal, including 4G and 5G, is generally reliable along the eastern shore and on the Curonian Spit. Food vendors, including restaurants and cafes, are present in Klaipeda, Smiltynė, Juodkrantė, and Nida, with some seasonal kiosks near popular access points.
Best Time to Visit
The period from June to August offers the warmest temperatures suitable for water activities. For photography, morning or late afternoon light provides softer illumination, particularly beneficial for capturing the landscapes of the Curonian Spit. Wind conditions should be monitored for activities like windsurfing and kitesurfing.
Facts & Legends
Despite its connection to the Baltic Sea, the Kursiu Lagoon is predominantly freshwater due to the substantial inflow from the Nemunas River. The Curonian Spit, which separates the lagoon from the sea, is a UNESCO World Heritage site recognized for its unique moving sand dunes. Local folklore attributes the creation of the Curonian Spit to the giantess Neringa, who is said to have built the peninsula to protect local fishermen from the rough Baltic Sea.
Nearby Landmarks
- Curonian Spit (Smiltynė section): 0.5km West (via ferry)
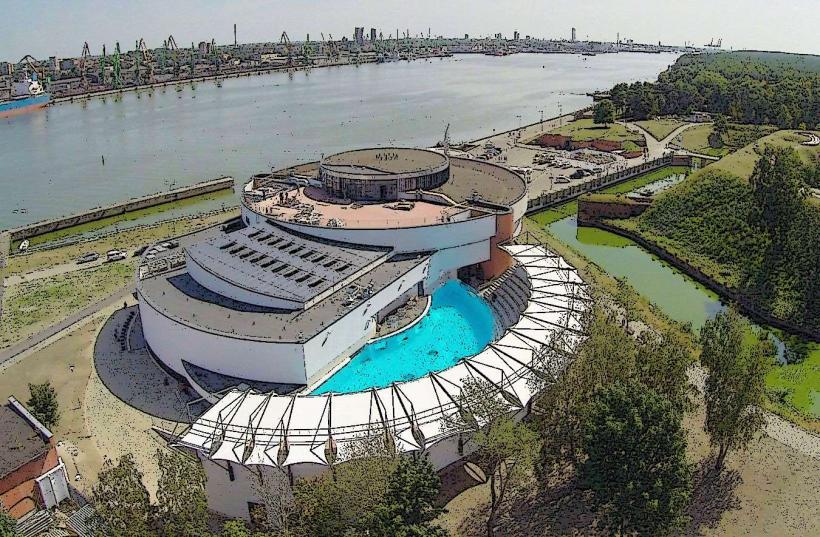
- Lithuanian Sea Museum and Dolphinarium: 1km West (on Smiltynė, accessible by ferry)
- Old Ferry Terminal (Klaipeda side): 0.1km East
- Klaipeda Old Town: 1.5km East
- Meridianas sailing ship: 1.5km East