Information
Landmark: Narva RiverCity: Narva
Country: Estonia
Continent: Europe
Narva River, Narva, Estonia, Europe
The Narva River is a border river separating Estonia and Russia, flowing north from Lake Peipus into the Gulf of Finland. It serves as a natural boundary for the city of Narva.
Visual Characteristics
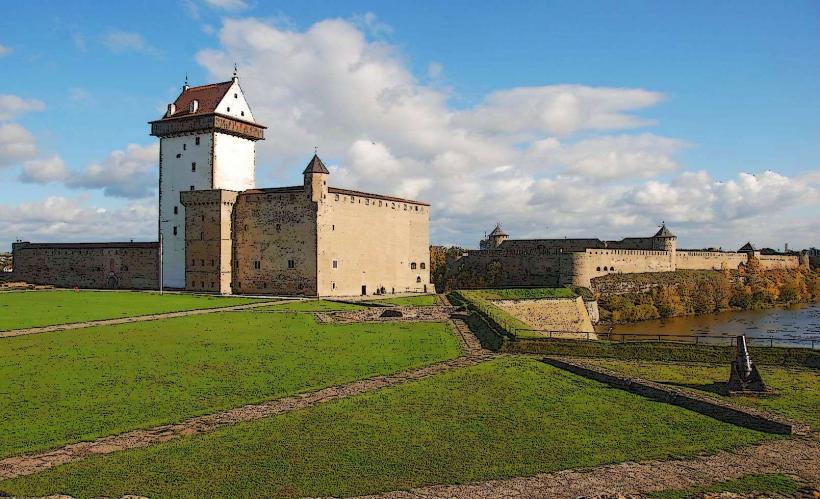
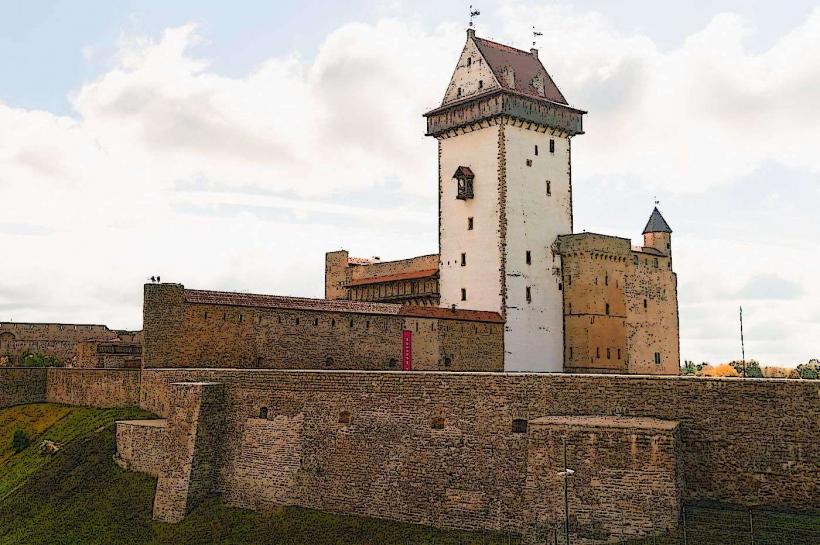
The river's water typically exhibits a brownish hue due to peat content from its source. Its banks feature varying elevations; the western (Estonian) bank is dominated by the limestone walls of Narva Castle, while the eastern (Russian) bank hosts the red brick structures of Ivangorod Fortress. The river's width ranges from approximately 200 to 400 meters, with an average depth of 5 meters.
Location & Access Logistics
The Narva River forms the eastern edge of Narva city. Access points are numerous along the city's riverside promenade, which runs parallel to Koidula Street. The primary crossing point is the Friendship Bridge, connecting Narva, Estonia, with Ivangorod, Russia. Parking is available in designated lots near Narva Castle, approximately 1.5 km from the city center. Local bus lines, including routes 3 and 4, have stops such as "Narva Muuseum" and "Koidula" directly adjacent to the riverfront.
Historical & Ecological Origin
The Narva River is a natural waterway that has historically served as a significant geopolitical border for centuries. Its formation is a post-glacial phenomenon, acting as the sole outflow from Lake Peipus. Ecologically, it is classified as a lowland river, characterized by a relatively slow current and a diverse aquatic ecosystem, including various fish species like salmon and pike.
Key Highlights & Activities
Walking and cycling are possible along the riverside promenade, offering views of both Narva Castle and Ivangorod Fortress. Fishing is permitted with a valid local license. During summer months, occasional boat tours operate from the Narva Marina, providing river perspectives of the border fortifications. Viewing the architectural contrast between the two fortresses across the river is a primary activity.
Infrastructure & Amenities
Public restrooms are available near the Narva Castle complex and at various points along the riverside promenade. Limited natural shade is provided by trees lining sections of the riverbanks. Cell phone signal (4G/5G) is generally strong on the Estonian side of the river. Several cafes and restaurants are located within 500 meters of the riverfront in Narva's Old Town area.
Best Time to Visit
The period from late spring to early autumn (May to September) offers the most favorable weather conditions for visiting. Photography of Narva Castle is optimal in the morning hours, utilizing eastern light, while the Ivangorod Fortress is best photographed in the late afternoon. The river is not subject to significant tidal variations, so no specific high/low tide requirements apply.
Facts & Legends
A local legend recounts that during the Great Northern War, a significant treasure was lost in the river's depths near the fortresses, occasionally glimpsed by fishermen. A verified historical oddity is that the Narva River has continuously served as a border between distinct political entities for over 700 years, making it one of Europe's longest-standing demarcated frontiers.
Nearby Landmarks
- Narva Castle (Hermann Fortress): 0.1km West
- Ivangorod Fortress: 0.2km East (across the river)
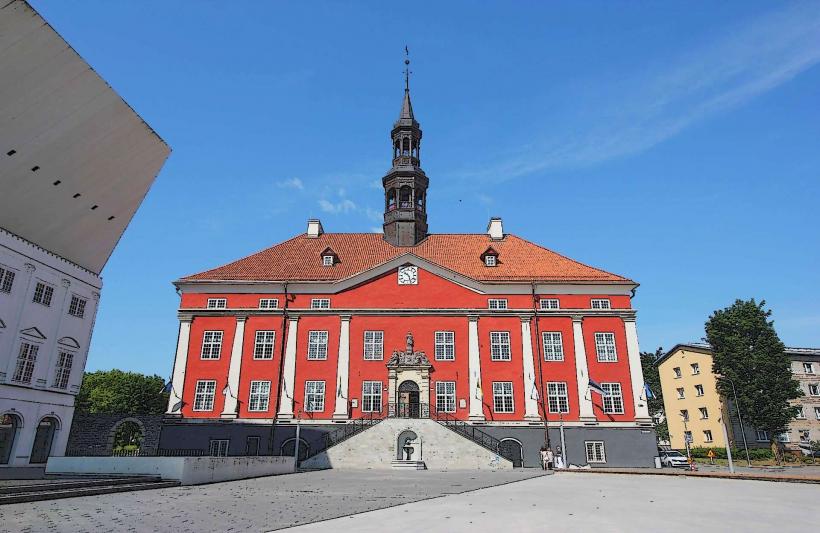
- Narva Town Hall: 0.5km West
- Narva Art Gallery: 0.7km Northwest
- Narva Museum: 0.1km West (located within Narva Castle complex)