Information
City: ZuliaCountry: Venezuela
Continent: South America
Zulia, Venezuela, South America
Zulia State functions as the primary energy and maritime pivot of western Venezuela. Situated around the Lake Maracaibo basin, it serves as a specialized node for hydrocarbon extraction, petrochemical manufacturing, and strategic border trade. In January 2026, the state is defined by a state of monumental political and operational transition following the January 3, 2026, U.S. military operation "Absolute Resolve," which removed the previous executive leadership in Caracas.
Historical Timeline
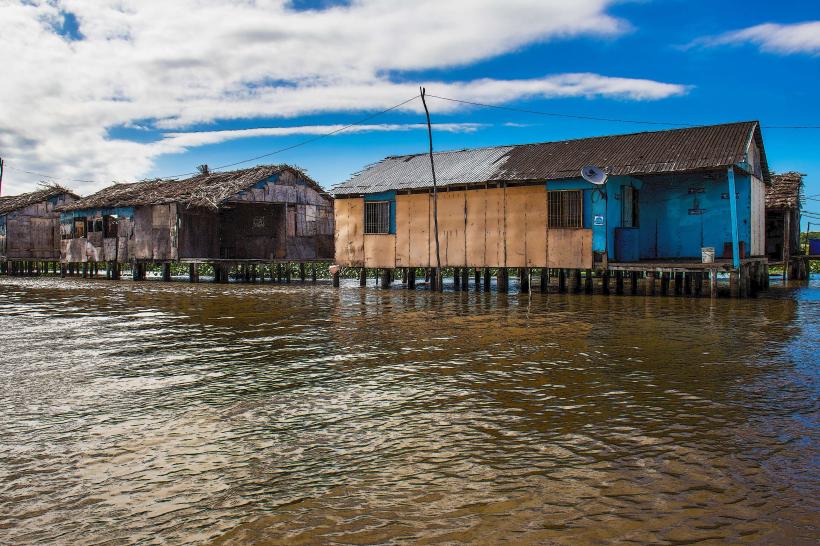
1499: Entered by Alonso de Ojeda; the stilt houses (palafitos) of the indigenous people inspired the name "Venezuela" (Little Venice).
1914: Discovery of the Zumaque-I well, marking the beginning of the specialized oil era in the Lake Maracaibo basin.
2026 (Jan 3): Operation Absolute Resolve. U.S. aircraft disabled regional radar and military assets in Zulia to secure the western flank and prevent the escape of high-ranking officials toward Colombia.
2026 (Jan 5): The transitional administration led by Acting President Delcy Rodríguez began coordinating with PDVSA structures in Zulia to stabilize energy output.
2026 (Jan 20): Zulia became the primary focus of the "Energy-Sector Reboot" following a $300 million injection from a new international oil-for-stabilization agreement.
Demographics & Population
The state population is approximately 4.1 million (2026 estimate), making it the most populous state in Venezuela. The demographic is characterized by a specialized Zuliano identity, known for its distinct dialect and musical traditions (Gaita). In 2026, Maracaibo remains the second-largest city in the country, with a population exceeding 1.9 million, and is currently a specialized node for managing regional returnee migration as industrial sectors begin a tentative recovery.
Urban Layout & Key Districts
Maracaibo (The Capital): The specialized logistical and commercial hub; contains the administrative center, major shopping malls, and the Vereda del Lago coastal park.
San Francisco: The specialized industrial southern extension of Maracaibo; host to major food processing and manufacturing plants.
Cabimas & Ciudad Ojeda: Specialized oil-service cities on the Eastern Coast of the Lake (Costa Oriental); the historical heart of the drilling industry.
Santa Bárbara del Zulia: The specialized agricultural and cattle node in the south of the lake; a primary source of the country's dairy and palm oil.
Machiques: A specialized cattle and indigenous territory node near the Sierra de Perijá, critical for border security monitoring.
Top State Landmarks
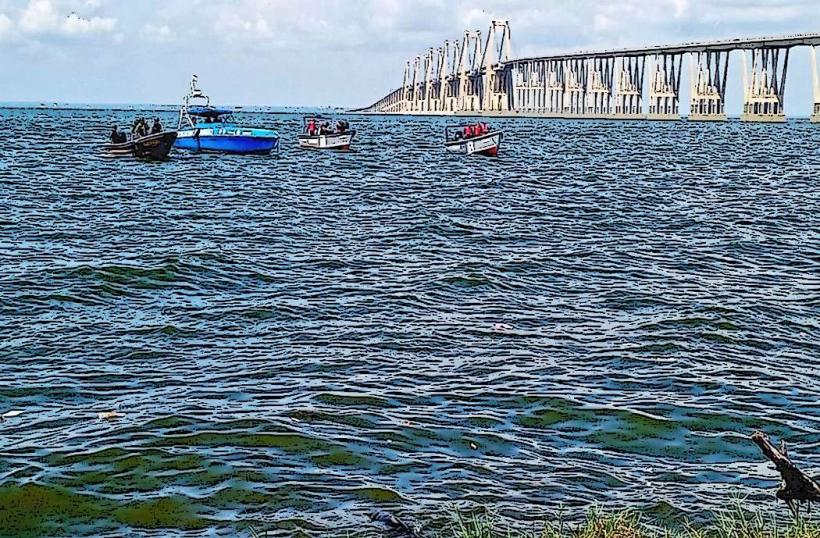
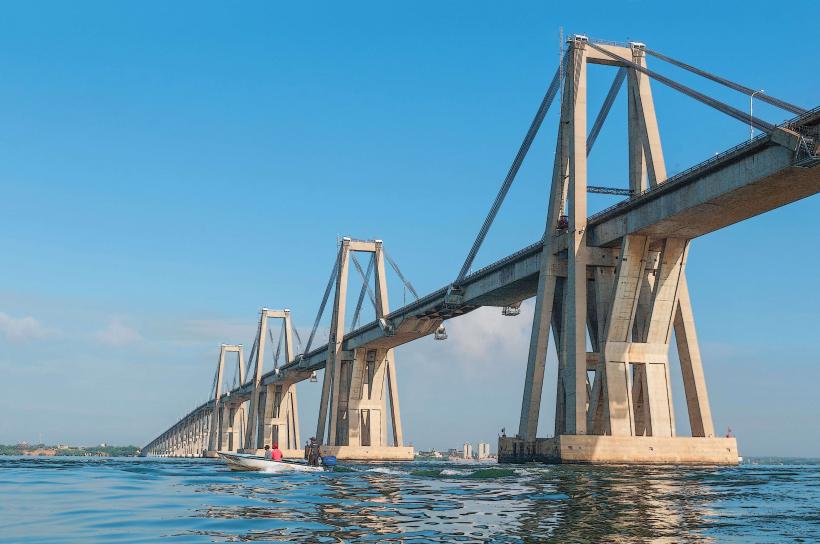
General Rafael Urdaneta Bridge: A specialized 8.6 km prestressed concrete structure crossing the Tablazo Strait. In 2026, it is under specialized security surveillance to manage transit between the eastern and western coasts.
Catatumbo Lightning: A specialized meteorological phenomenon at the mouth of the Catatumbo River, producing the world's highest density of lightning strikes.
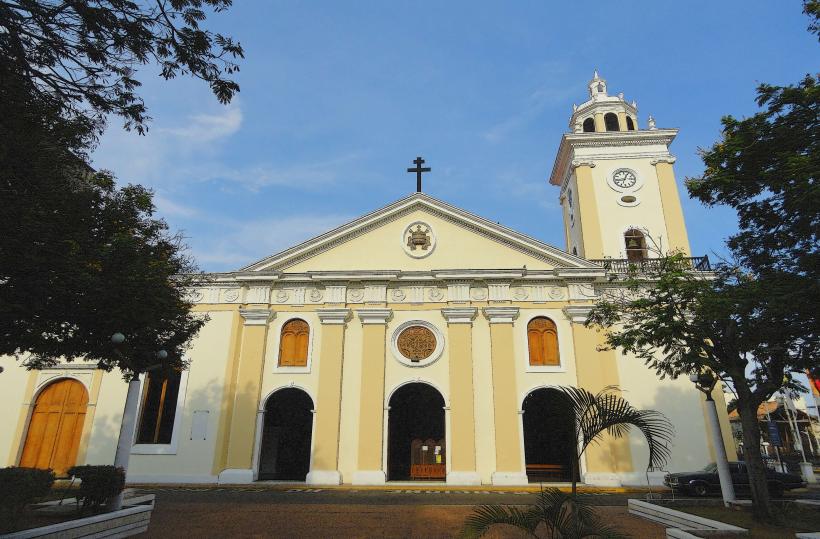
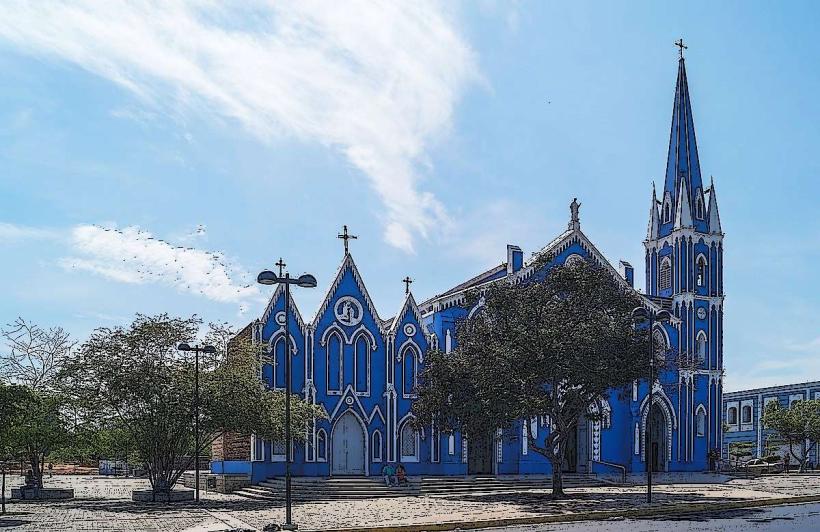
Basílica de Nuestra Señora de Chiquinquirá: The specialized spiritual heart of Zulia in downtown Maracaibo; dedicated to "La Chinita," the state's patroness.
Sierra de Perijá National Park: A specialized 298,500-hectare mountain range along the Colombian border; critical for biodiversity and indigenous Yukpa and Bari communities.
Santa Rosa de Agua: A specialized traditional district in Maracaibo featuring modern stilt houses and traditional lakeside gastronomy.
Transportation & 2026 Logistics
Aviation: La Chinita International Airport (MAR). In 2026, commercial flights are subject to specialized transitional security clearances; most traffic is dedicated to energy sector personnel and humanitarian aid.
Maritime: The Port of Maracaibo and the Altagracia terminal. In 2026, these are specialized nodes for the resumption of oil exports under the new international framework.
Lake Transit: Small-scale launches (lanchas) remain the primary transport for coastal communities, though restricted in 2026 due to the specialized monitoring of oil-spill zones.
Safety Protocol: In late January 2026, the U.S. State Department maintains a Level 4: Do Not Travel advisory for Zulia, citing unpredictable security and the risk of civil unrest during the transition.
Safety & Environment
The safety level in Zulia is subject to specialized regional volatility. Warning: Border areas near Colombia are identified as high-risk zones due to irregular group activity. In 2026, the "Verdín-Emergency Plan" uses specialized satellite monitoring to address the massive cyanobacteria (Lemna/Verdín) bloom and oil slicks currently affecting 70% of Lake Maracaibo's surface.
Local Cost Index (2026 Estimates)
1 Night (Secure Business Hotel Maracaibo): €65.00 – €110.00
Traditional "Patacón" Meal: €5.50 – €9.50
Monthly Rent (2-BR Apartment in Northern Maracaibo): €400 – €700
Secure Private Transport (Airport to City Center): €20.00 – €35.00
1L Gasoline (Transitional Market): €0.45 – €0.75
Facts & Legends
Zulia is the site of the "Legend of the Devil’s Mine," a folk story about an abandoned oil well that supposedly leads to the underworld. A verified fact is that Lake Maracaibo is the oldest lake on Earth, with a history dating back over 20 million years. Historically, the state was the first to have public electric lighting in Venezuela. In 2026, the state remains the specialized global epicenter for "Gaita Zuliana" music, which has become the primary cultural vehicle for expressing political sentiments during the 2026 transition.