Information
Landmark: Lago de MaracaiboCity: Zulia
Country: Venezuela
Continent: South America
Lago de Maracaibo, Zulia, Venezuela, South America
Lago de Maracaibo is a large brackish estuary located in northwestern Venezuela. It is connected to the Gulf of Venezuela and the Caribbean Sea.
Visual Characteristics
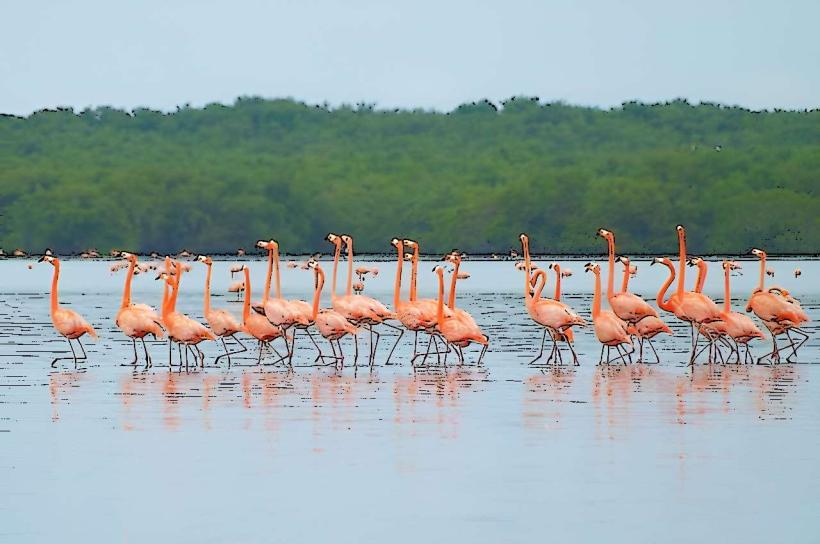
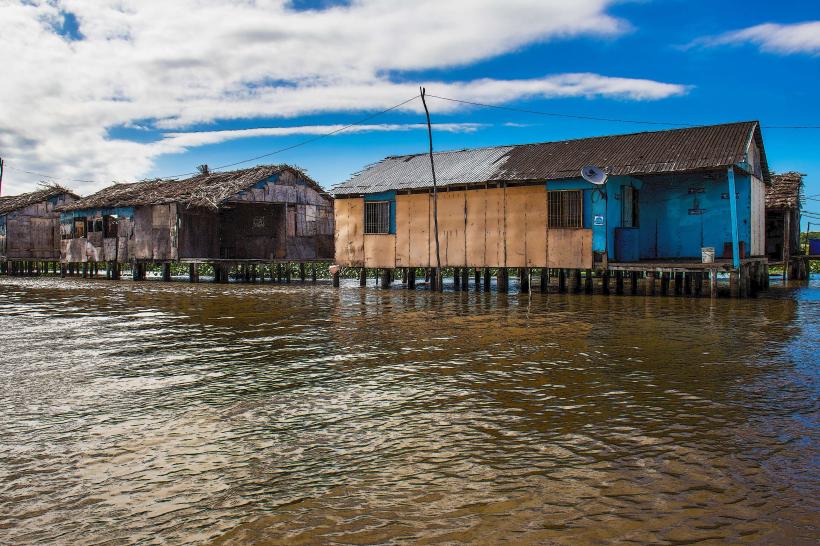
The lake's surface is characterized by a greenish-brown hue due to sediment and organic matter. Its perimeter is irregular, featuring numerous bays and peninsulas. The surrounding landscape is predominantly flat, with marshy areas and mangrove vegetation along sections of the coastline.
Location & Access Logistics
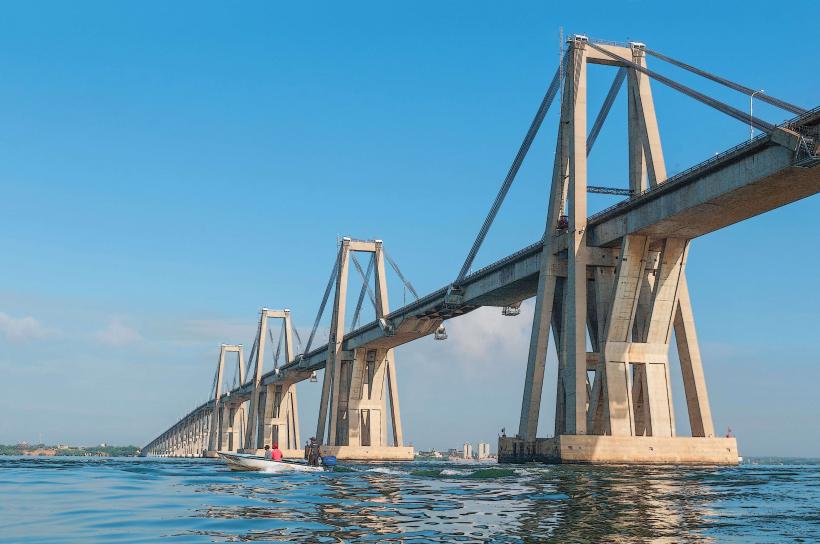
Lago de Maracaibo is situated within the Zulia state. Access points are numerous, with major urban centers like Maracaibo bordering its western shore. The General Rafael Urdaneta Bridge spans the Tablazo Strait, connecting Maracaibo to the eastern side of the lake. Public transportation within Maracaibo provides access to the lakefront. Road access is facilitated by the regional highway network, with Route 1 providing significant connectivity.
Historical & Ecological Origin
Geologically, Lago de Maracaibo is considered a remnant of a larger ancient lake basin. Its current form is a result of tectonic subsidence and the subsequent ingress of seawater, creating a brackish environment. Historically, it has been a vital waterway for trade and transportation since pre-Columbian times.
Key Highlights & Activities
Fishing is a primary activity, with commercial and recreational operations targeting various fish species. Birdwatching is possible in the surrounding wetlands, particularly for migratory species. Boat tours offer views of the lake's expanse and coastal areas. The Catatumbo lightning phenomenon, occurring frequently over the southern part of the lake, is a notable natural event.
Infrastructure & Amenities
Infrastructure varies significantly along the lake's extensive shoreline. Urban areas like Maracaibo offer full amenities, including restaurants and accommodation. Remote sections have minimal facilities. Cell phone signal is generally available in populated areas but can be intermittent in more isolated regions. Restrooms and shade are common in developed waterfront areas.
Best Time to Visit
The dry season, from December to April, generally offers clearer skies and more stable weather conditions. The period from July to October can experience higher rainfall. For observing the Catatumbo lightning, the months of July to October are often cited as having the highest frequency, with activity typically occurring after sunset.
Facts & Legends
The Catatumbo lightning is a persistent atmospheric phenomenon, generating thousands of lightning strikes per night for extended periods. It is recognized as the world's most intense concentration of lightning. Local folklore attributes the phenomenon to various spiritual or natural causes.
Nearby Landmarks
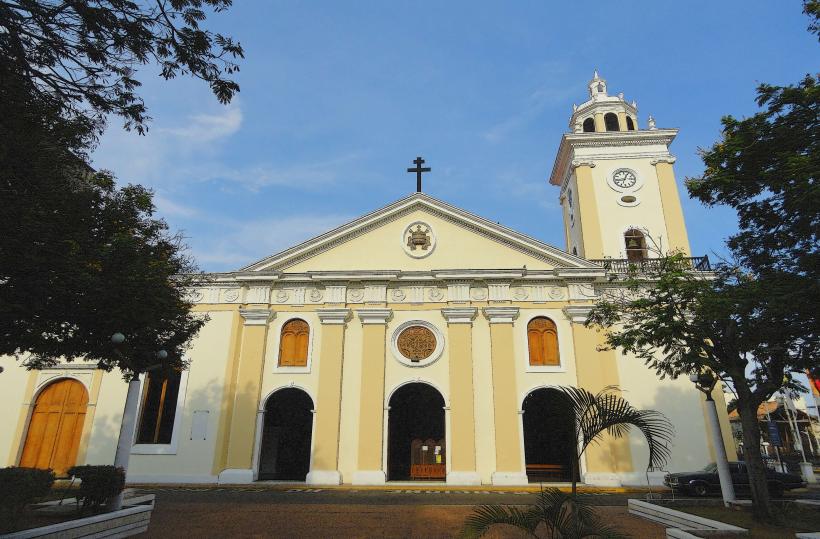
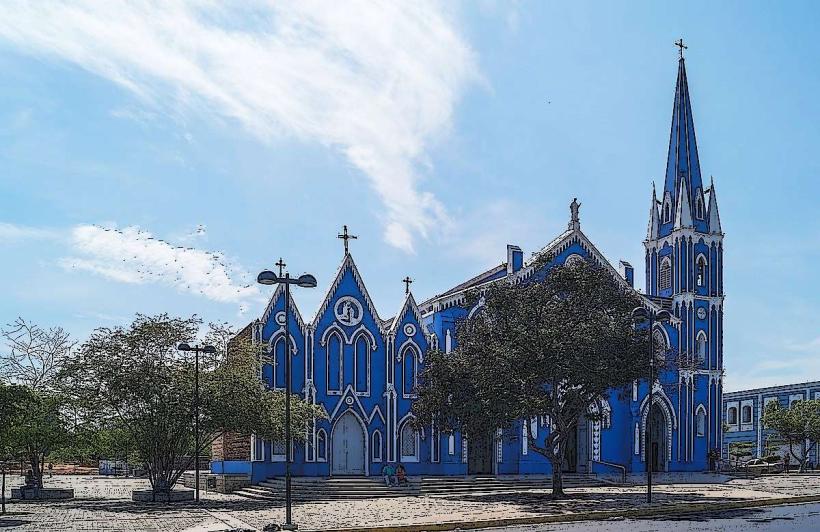
- Maracaibo Cathedral (1.5km West)
- General Rafael Urdaneta Bridge (3km West)
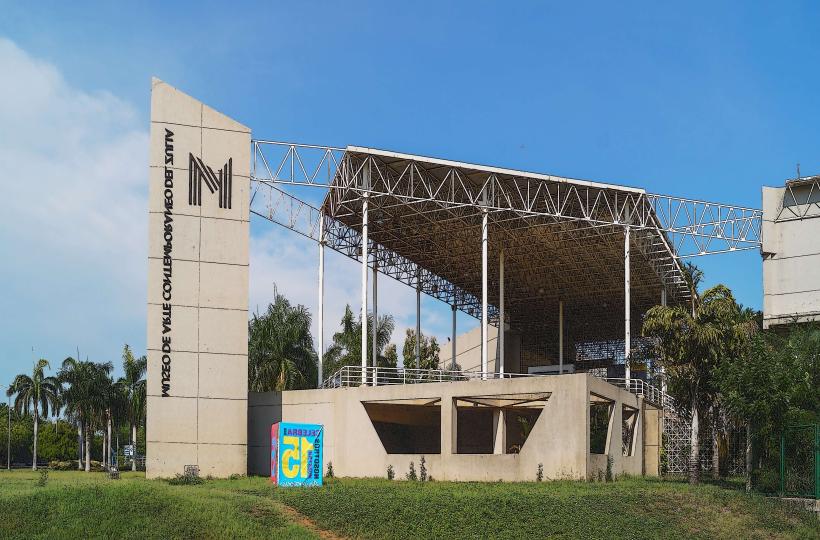
- Museo de Arte Contemporáneo de Zulia (MACZUL) (2km West)
- Parque Metropolitano de Maracaibo (4km Southwest)