Information
Landmark: Laguna de SinamaicaCity: Zulia
Country: Venezuela
Continent: South America
Laguna de Sinamaica, Zulia, Venezuela, South America
Laguna de Sinamaica is a large coastal lagoon located in the Zulia state of Venezuela.
It is characterized by its extensive network of stilt houses (palafitos) built over the water.
Visual Characteristics
The lagoon's water is brackish, varying in color from muddy brown to greenish depending on sediment and tidal conditions. The dominant feature is the presence of numerous wooden stilt houses, constructed from local timber, with corrugated metal or thatched roofs. Vegetation around the lagoon includes mangrove forests and sparse coastal scrub.
Location & Access Logistics
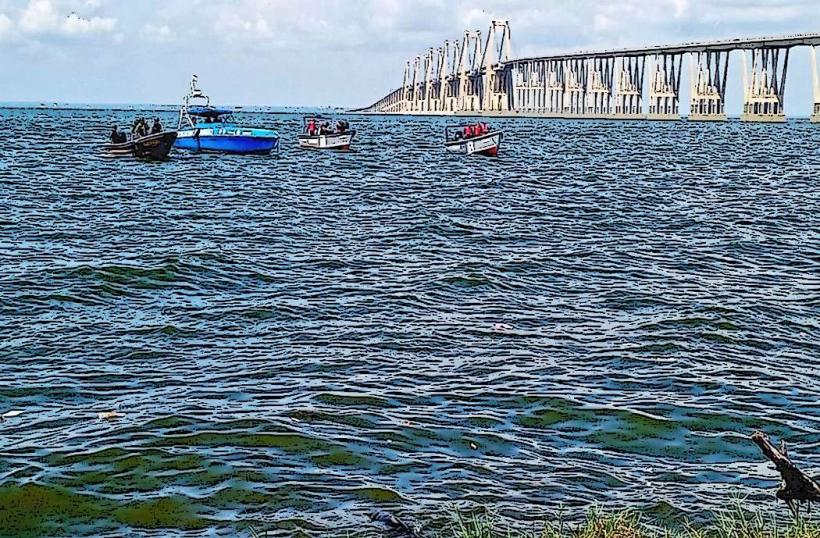
Laguna de Sinamaica is situated approximately 120 kilometers northwest of Maracaibo. Access is primarily via the national highway, Carretera Nacional Troncal 6, which runs adjacent to the lagoon. From the town of Sinamaica, local boat operators offer transport into the lagoon. Parking is available in Sinamaica, though it is informal and often unpaved.
Historical & Ecological Origin
The stilt houses are a traditional architectural adaptation by the indigenous Añú people to cope with the seasonal flooding and tidal fluctuations of the lagoon. Ecologically, Laguna de Sinamaica is a vital estuarine system, supporting mangrove ecosystems and serving as a nursery ground for various fish species.
Key Highlights & Activities
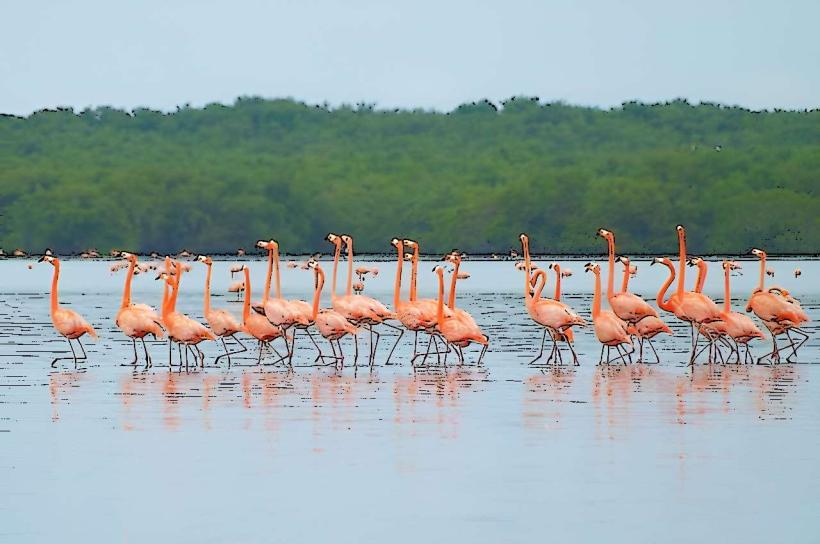
Boat tours through the palafito villages are the primary activity. Visitors can observe the daily life of the Añú communities. Fishing is a common practice. Birdwatching is possible, with species like flamingos and various waterbirds present.
Infrastructure & Amenities
Basic amenities are limited. Some palafitos may offer simple food and drink for visitors. Restrooms are generally not available to the public. Cell phone signal is intermittent. Shade is provided by the stilt houses and mangrove canopies.
Best Time to Visit
The dry season, from December to April, generally offers more stable weather conditions. The best time of day for photography is early morning or late afternoon when the light is softer. Tidal charts should be consulted as water levels can significantly impact boat access to certain areas.
Facts & Legends
The stilt houses are often referred to as the "Venice of Venezuela." A local legend speaks of a mythical water spirit that protects the lagoon and its inhabitants.
Nearby Landmarks
- Parque Nacional Ciénagas del Catatumbo (approx. 60km Southeast)
- Maracaibo Lake (directly connected)
- City of Maracaibo (approx. 120km Southeast)