Information
Landmark: Puente sobre el Lago de MaracaiboCity: Zulia
Country: Venezuela
Continent: South America
Puente sobre el Lago de Maracaibo, Zulia, Venezuela, South America
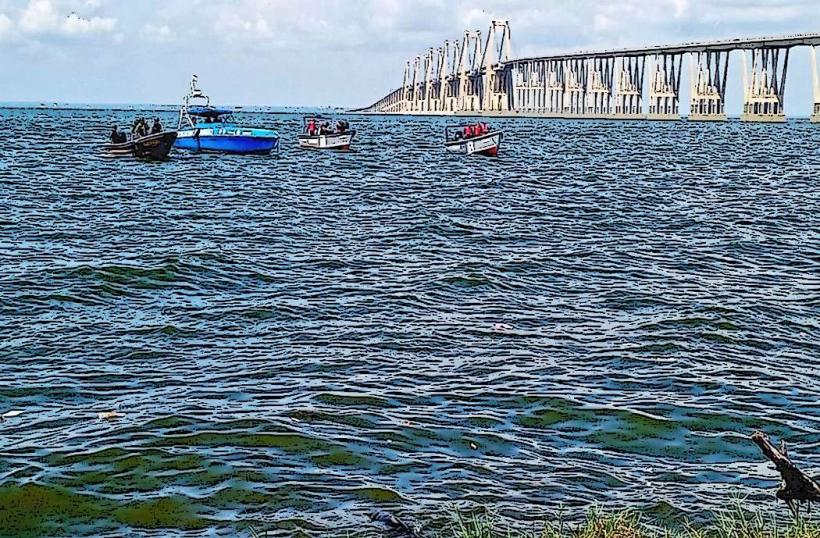
The Puente sobre el Lago de Maracaibo is a concrete and steel bridge spanning the Maracaibo Lake in Zulia, Venezuela.
It connects the city of Maracaibo with the eastern part of Venezuela.
Visual Characteristics
The bridge consists of 135 concrete arches, with the longest span measuring 235 meters. The deck is constructed from steel and concrete, supporting a four-lane roadway. The total length of the bridge is 8.67 kilometers. Its primary color is grey concrete, with steel elements painted in a muted industrial tone.
Location & Access Logistics
The bridge is located approximately 10 kilometers southwest of Maracaibo's city center. Access is via Venezuela's National Route 1 (Troncal 1). There are multiple toll plazas on both the Maracaibo side and the eastern side. Parking is not available on the bridge itself; vehicles must use designated service areas or continue to their destinations. Public transport options include intercity buses that cross the bridge.
Historical & Ecological Origin
Construction began in 1957 and was completed in 1962. The bridge was designed by Italian engineer Riccardo Morandi and built by the companies Grana and SAE. Its original purpose was to facilitate transportation and economic development by connecting the oil-rich Maracaibo region with the rest of the country.
Key Highlights & Activities
Vehicular transit across the bridge is the primary activity. Observation points are limited to service areas. No specific recreational activities are permitted on the bridge structure itself.
Infrastructure & Amenities
Restrooms are available at toll plazas and designated service areas. Shade is minimal, primarily found in service areas. Cell phone signal (4G/5G) is generally available across the bridge. Food vendors are located at service areas on either end of the bridge, not directly on the structure.
Best Time to Visit
For photography, early morning (6:00 AM - 8:00 AM) offers favorable lighting conditions with fewer vehicles. Late afternoon (4:00 PM - 6:00 PM) also provides good light. The best months for weather are generally December through March, which represent the dry season. There are no tidal considerations for crossing the bridge.
Facts & Legends
The bridge is known for its resilience, having withstood several seismic events and the impact of lightning strikes. A local legend suggests that the bridge's construction was aided by a pact with a mythical sea creature to ensure its stability over the lake.
Nearby Landmarks
- Plaza de la República (2.5km West)
- Estadio Olímpico Metropolitano de Maracaibo (4.0km West)
- Parque Metropolitano de Maracaibo (3.8km West)
- Centro de Arte de Maracaibo Lía Bermúdez (4.5km West)