Information
Landmark: Lake MurrayCity: Provice Area
Country: Papua New Guinea
Continent: Australia
Lake Murray, Provice Area, Papua New Guinea, Australia
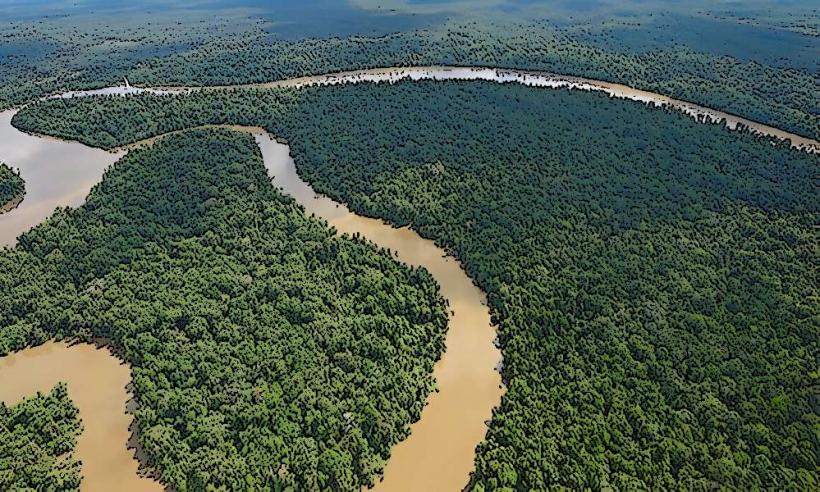
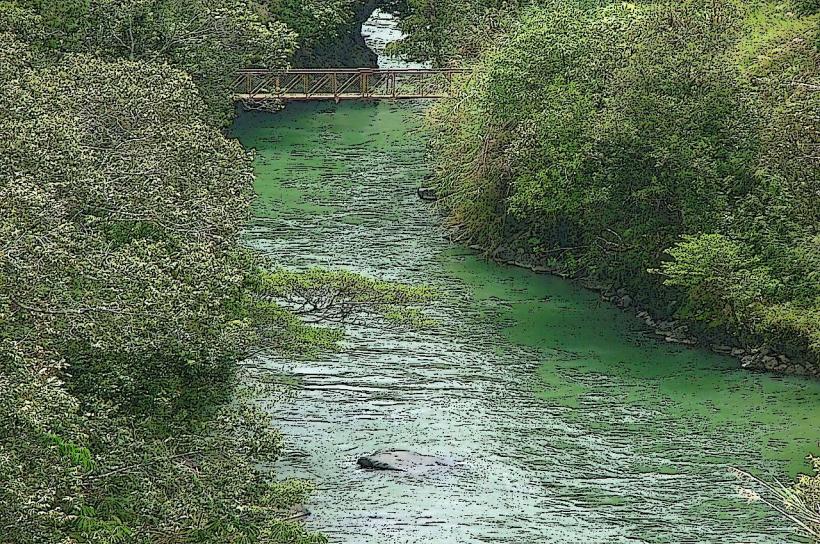
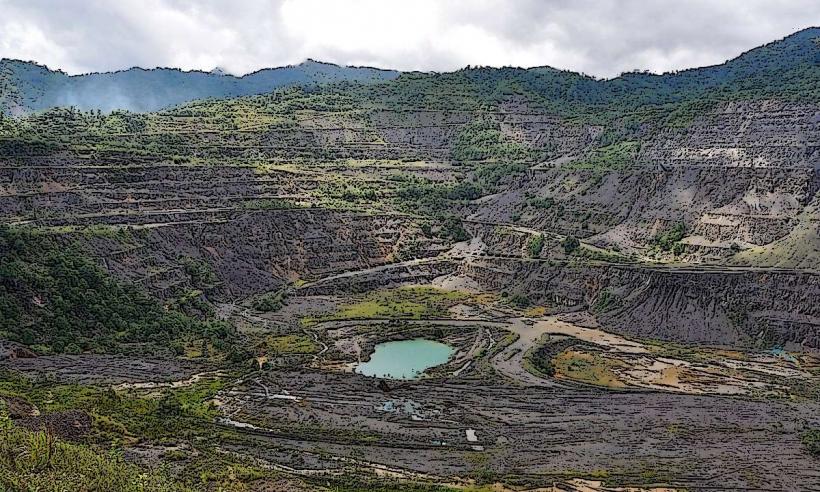
Lake Murray is a large freshwater lake located in the Western Province of Papua New Guinea. It is the largest lake in Papua New Guinea by surface area.
Visual Characteristics
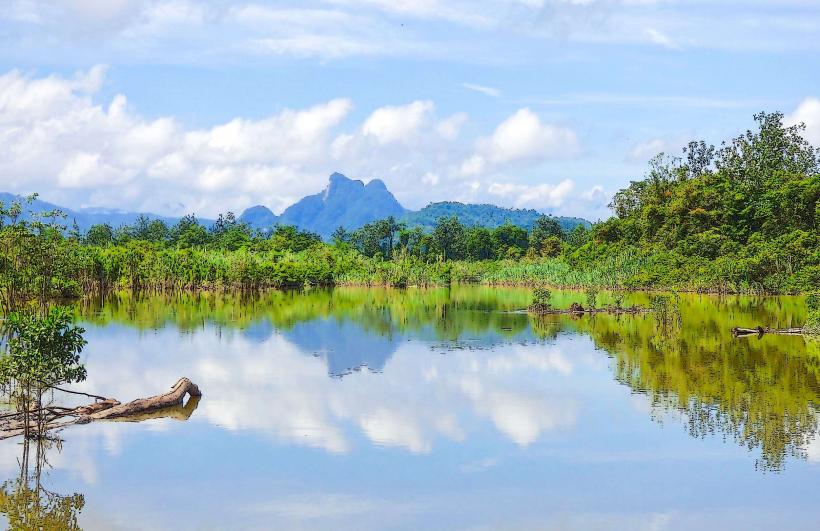
The lake's surface is predominantly dark brown to black due to tannins from decaying vegetation. Its perimeter is irregular, characterized by extensive swampy areas and dense tropical rainforest. Water depth varies significantly, with shallower areas near the shore and deeper channels in the central regions. Floating islands of vegetation are a common feature.
Location & Access Logistics
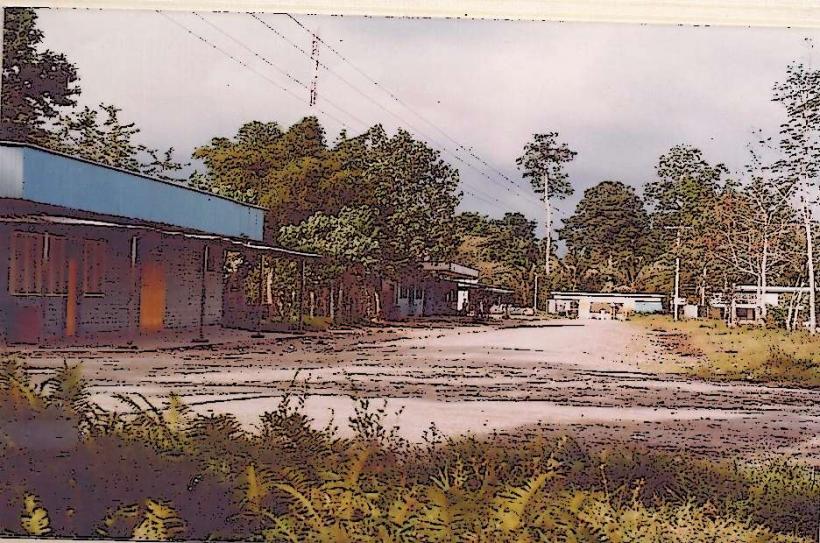
Lake Murray is situated approximately 300 kilometers northwest of Daru, the provincial capital. Access is primarily via small aircraft landing at the Lake Murray airstrip (IATA: LMY). Boat access is possible via the Strickland River, but this route is lengthy and dependent on water levels. There are no established road networks directly connecting to the lake from major towns. Limited local boat hire is available at the airstrip settlement.
Historical & Ecological Origin
Lake Murray is a natural freshwater lake formed by the geological processes of riverine sedimentation and oxbow lake formation. It is part of the vast Fly River basin. The lake and its surrounding wetlands are classified as a Ramsar site, recognized for their ecological importance as a habitat for diverse aquatic and avian species.
Key Highlights & Activities
Activities include birdwatching, particularly for endemic species. Fishing for local species like barramundi is possible. Boat excursions on the lake offer opportunities to observe the surrounding ecosystem. Guided walks through the adjacent rainforest can be arranged with local guides.
Infrastructure & Amenities
Basic accommodation is available in the form of guesthouses near the airstrip. Limited food supplies can be purchased from local vendors. Restroom facilities are rudimentary. Cell phone signal is generally absent. Shade is provided by the dense forest canopy in surrounding areas.
Best Time to Visit
The dry season, from May to October, offers more stable weather conditions and lower water levels, potentially improving access. The wet season (November to April) sees higher water levels, which can impact travel. Early morning and late afternoon provide optimal lighting for photography due to the angle of the sun.
Facts & Legends
Local folklore speaks of large, unseen creatures inhabiting the deeper parts of the lake. A verified historical fact is the lake's significant role as a traditional transportation route for indigenous communities living in the region.
Nearby Landmarks
- Strickland River (0.5km East)
- Lake Murray Airstrip (0.2km North)
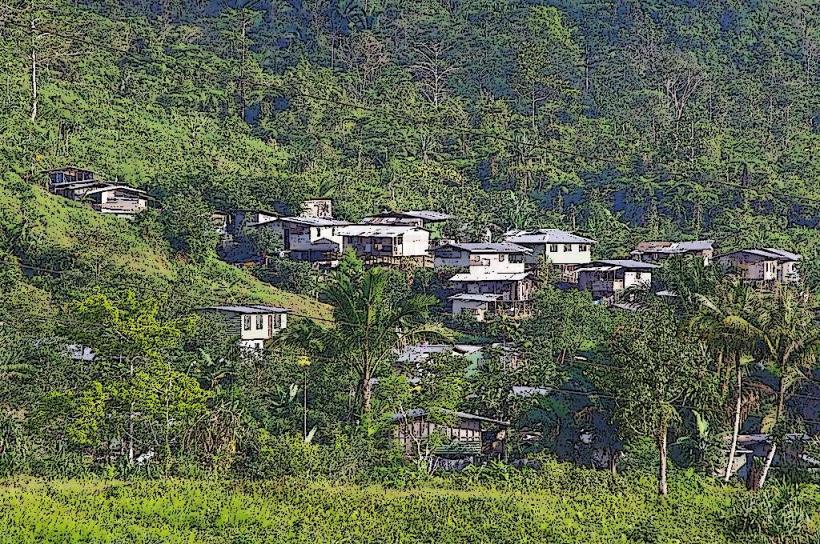
- Various small indigenous villages (variable distances, surrounding area)