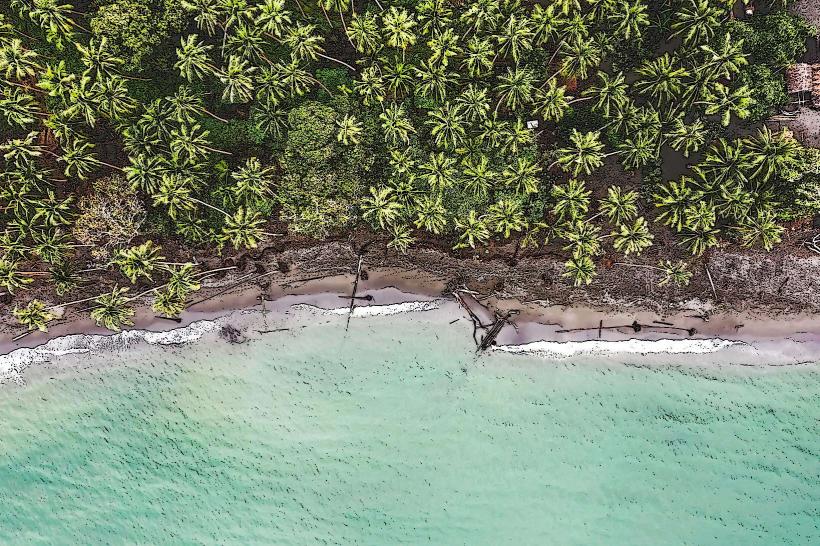Information
Landmark: Mendi RiverCity: Provice Area
Country: Papua New Guinea
Continent: Australia
Mendi River, Provice Area, Papua New Guinea, Australia
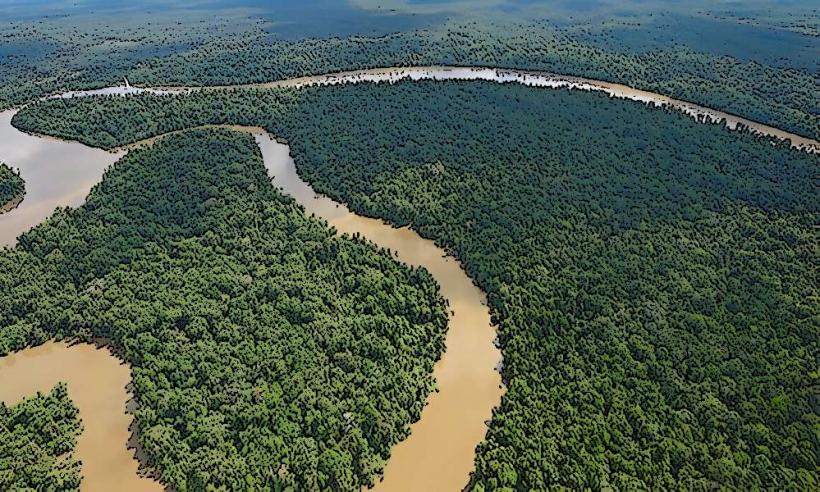
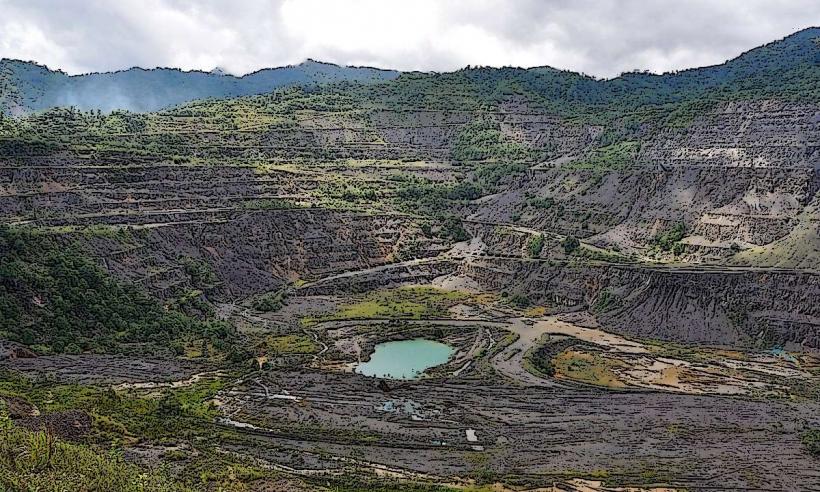
The Mendi River is a significant waterway located in the Southern Highlands Province of Papua New Guinea. It flows through the provincial capital, Mendi.
Visual Characteristics
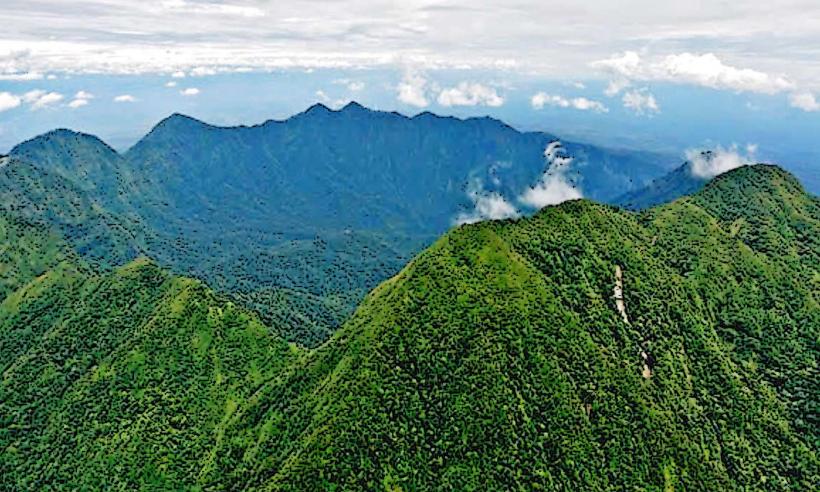
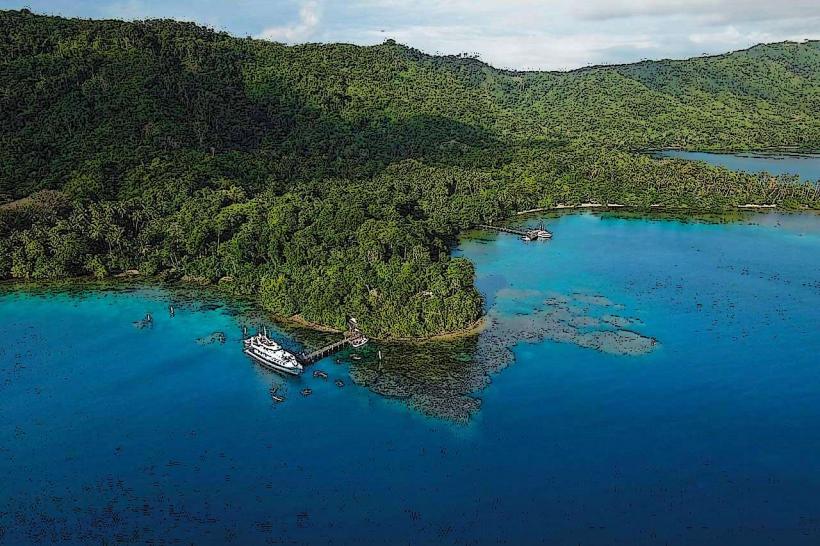
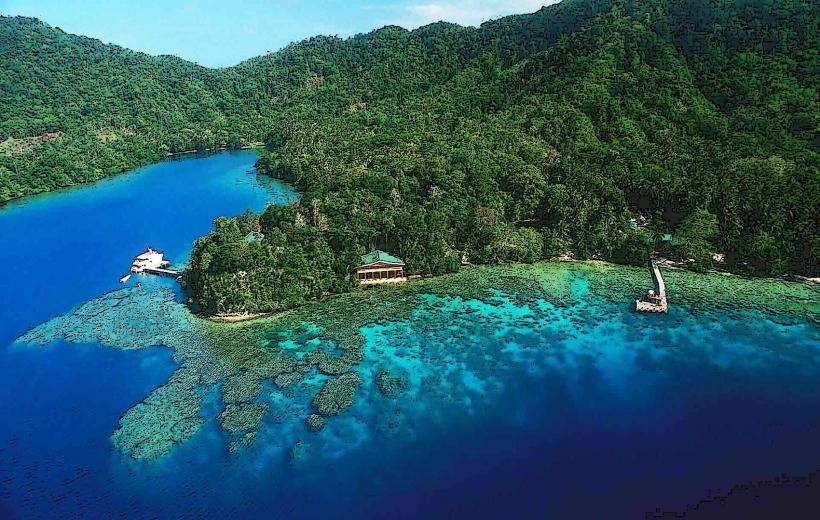
The river exhibits a moderate flow with water clarity varying based on recent rainfall. The riverbanks are characterized by dense tropical vegetation, including various tree species and undergrowth. Sedimentation is observable, particularly after periods of heavy precipitation, leading to a brownish hue in the water.
Location & Access Logistics
The Mendi River traverses the town of Mendi. Access points are available from various roads within Mendi, including the main Highlands Highway which passes near the town. Parking is generally available along accessible riverfront areas, though designated parking facilities are limited. Public transport within Mendi consists of PMVs (Public Motor Vehicles), which operate on routes that can bring passengers close to the river.
Historical & Ecological Origin
The Mendi River is a natural fluvial system, part of the larger watershed of Papua New Guinea. Its formation is a result of ongoing geological processes and erosion over millennia. Ecologically, it supports a freshwater ecosystem typical of the region's tropical climate.
Key Highlights & Activities
Observation of local riverine life is possible. Fishing by local residents occurs along the river. Walking along accessible sections of the riverbank provides views of the surrounding landscape.
Infrastructure & Amenities
Restroom facilities are not consistently available along the riverbanks. Shade is provided by natural tree cover. Cell phone signal (4G/5G) is generally available in Mendi town, extending to some accessible river areas. Food vendors are present in Mendi town, but not directly at all river access points.
Best Time to Visit
The best time of day for clear views of the river and its surroundings is typically during the morning hours before potential afternoon rainfall. The dry season, generally from June to September, offers more predictable weather conditions. High tide is not a relevant factor for this river system.
Facts & Legends
Local folklore associates the Mendi River with ancestral spirits and is considered a vital resource for the communities living along its course. A specific historical oddity is the river's role as a natural boundary during past tribal interactions.
Nearby Landmarks
- Mendi Town Market (0.8km West)
- Southern Highlands Provincial Government Office (1.2km Northwest)
- Mendi General Hospital (1.5km North)
- Mendi Airport (3.0km East)