Information
Country: NorwayContinent: Europe
Norway, Europe
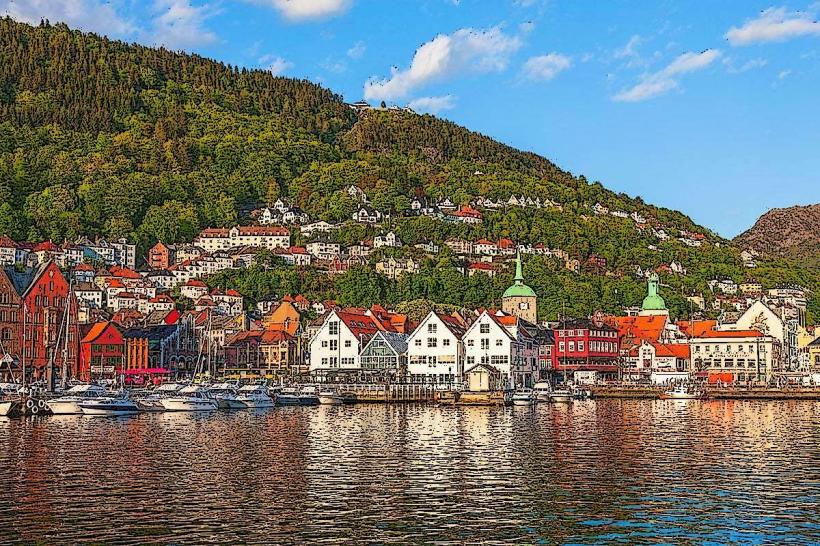
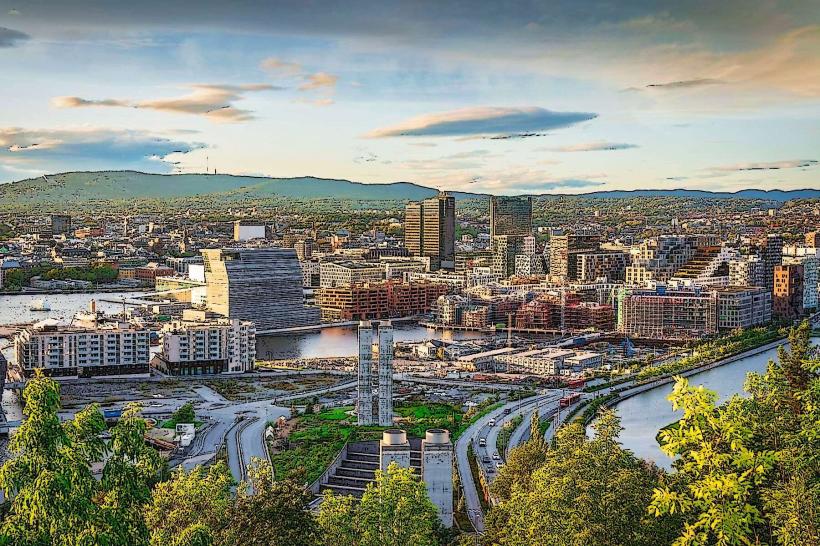
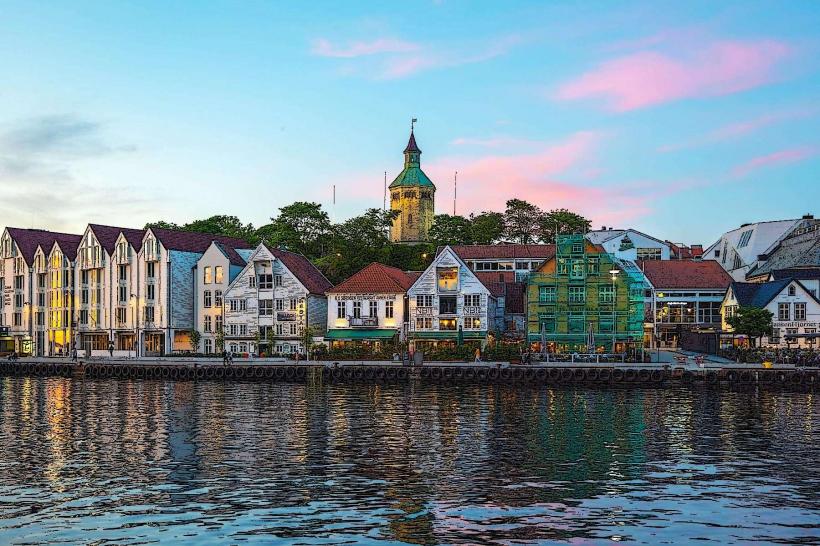
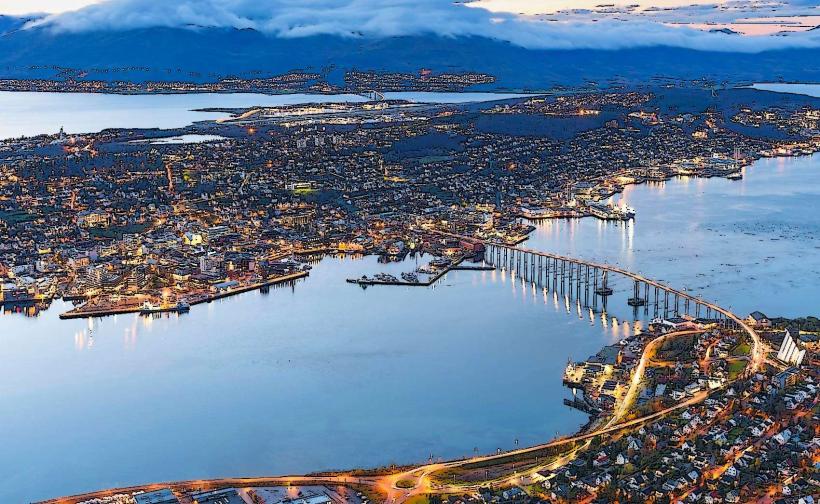
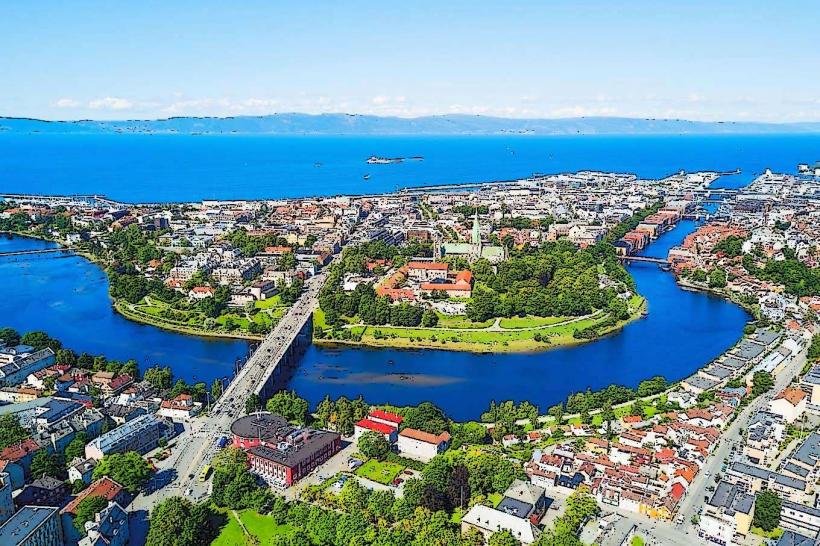
Norway is located in Northern Europe, occupying the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. It shares a 2,542 km land border with Sweden to the east, Finland to the northeast, and Russia to the far northeast. Its geography is defined by a deeply indented coastline of over 1,000 fjords, high mountain plateaus (fjells), and approximately 239,000 islands; the capital city is Oslo.
Visa & Entry Policy
Norway is a member of the Schengen Area. Citizens of the US, UK, and EU do not require a visa for stays up to 90 days within a 180-day period. Starting in late 2026, non-EU visa-exempt travelers must obtain an ETIAS (European Travel Information and Authorisation System) authorization prior to arrival. Passports must be valid for at least three months beyond the intended departure date.
Language & Communication
The official language is Norwegian, which has two written standards: Bokmål and Nynorsk. English proficiency is among the highest globally, with near-universal fluency in urban areas and high proficiency even in remote villages. North Sámi, Lule Sámi, and South Sámi are official minority languages in specific northern regions.
Currency & Payment Systems
The currency is the Norwegian Krone (NOK). Norway is one of the most digitalized economies in the world; card payments and mobile apps (Vipps) are the standard. Many businesses-including hotels, cafes, and public transport-operate on a "cash-free" basis. While cash remains legal tender, its use is minimal and often discouraged for small transactions. ATMs (Minibank) are available but decreasing in number.
National Transport Grid
Intercity travel is facilitated by the Vy Group and SJ Nord rail networks, which connect Oslo to Bergen, Trondheim, and Stavanger. The coastal ferry system, including the Hurtigruten and Havila voyages, serves as a vital transit link for northern communities. Due to mountainous terrain, domestic flights (operated by SAS, Norwegian, and Widerøe) are an essential and frequent mode of transport for long distances.
Digital Infrastructure
Primary mobile network providers are Telenor, Telia, and Ice. 5G coverage reached 99% of the population by early 2025. 4G reliability is exceptionally high, even in remote fjords and tunnels, though signal voids may occur in the high-altitude interior of national parks like Jotunheimen.
Climate & Seasonality
The climate is temperate along the coast due to the Gulf Stream, while the interior and north are subarctic. Summers (June–August) feature the "Midnight Sun" north of the Arctic Circle. Winters (December–February) are cold and dark, marked by the "Polar Night" in the north. Precipitation is highest in the autumn months, particularly on the west coast.
Health & Safety
No mandatory vaccinations are required. Tap water is of superior natural quality and safe for consumption nationwide. The universal emergency number is 112. Specific lines include 110 (Fire), 113 (Ambulance), and 02800 (Non-emergency Police).
Top 3 Major Regions & Cities
Eastern Norway (Østlandet): Primary hub is Oslo.
Western Norway (Vestlandet): Primary hub is Bergen (Gateway to the Fjords).
Northern Norway (Nord-Norge): Primary hub is Tromsø (The Arctic Capital).
Local Cost Index
1L Water: 25 NOK ($2.35 USD)
1 Domestic Beer (0.5L): 95 NOK ($9.00 USD)
1 Sim Card (Prepaid Data): 300 NOK ($28.30 USD)
Facts & Legends
In Norse mythology, the mountains of Jotunheimen were the "Home of the Giants" (Jotnar). National folklore is dominated by trolls-mythical beings who turn to stone if caught in sunlight-and the Huldra, a seductive forest spirit with a cow’s tail. Historically, Norway is the birthplace of modern skiing; the word "ski" itself is a Norwegian term meaning "split piece of wood."