Information
Country: GrenadaContinent: North America
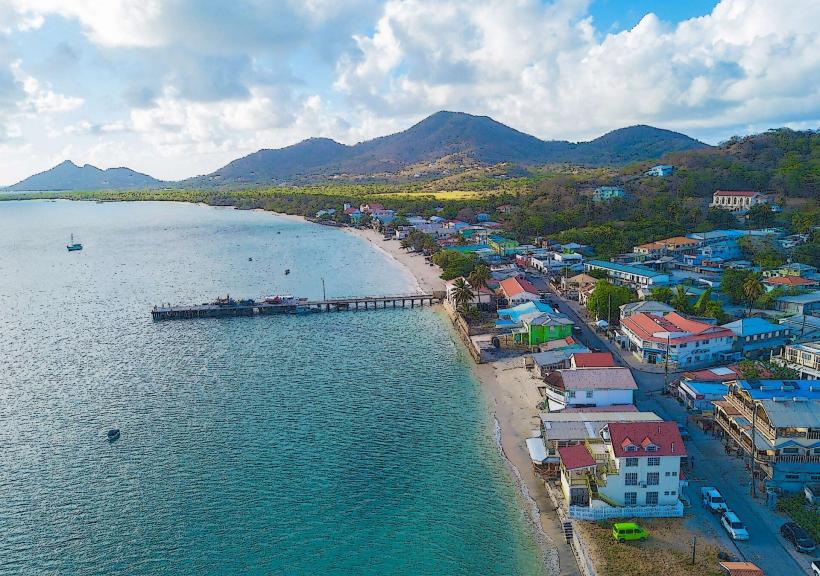
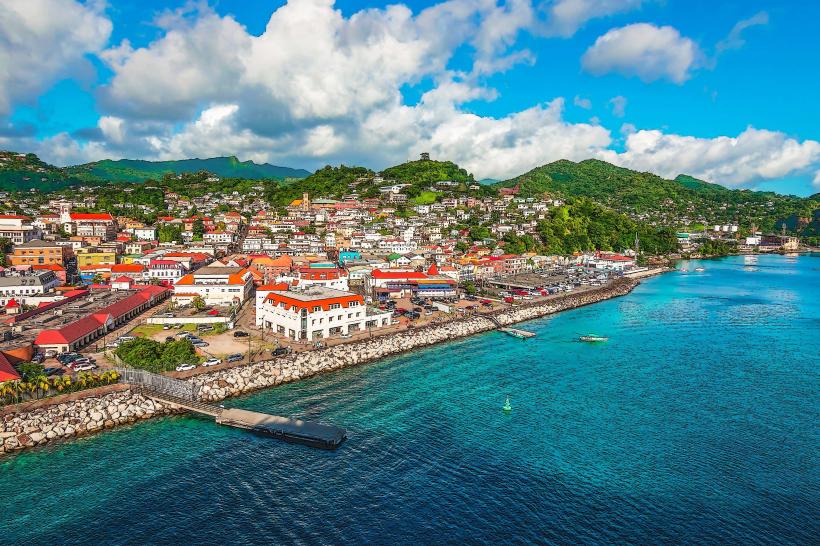
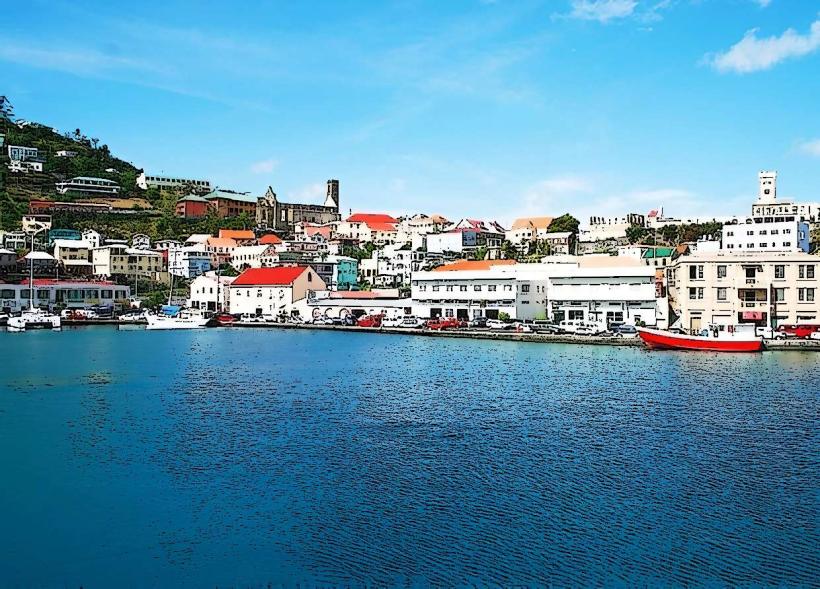
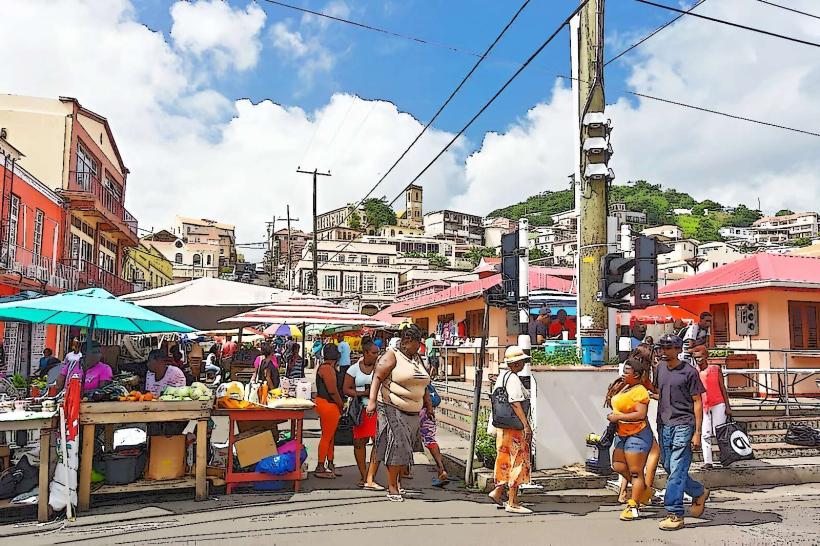
Grenada, North America
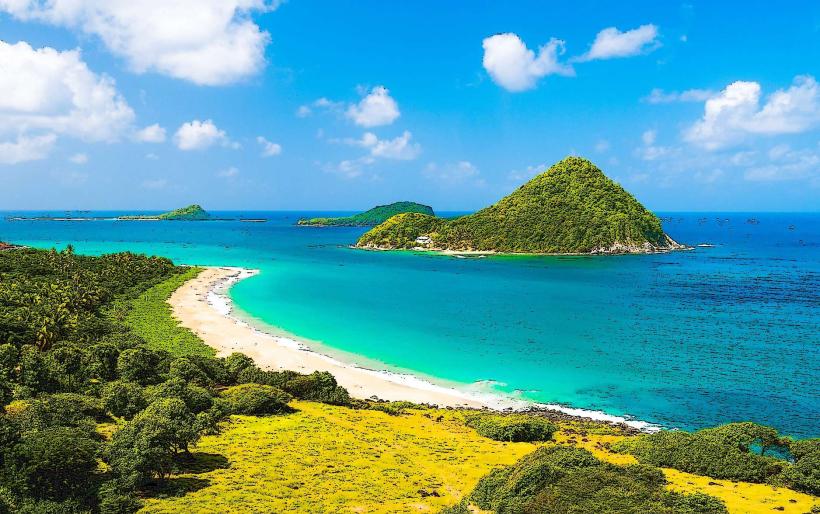
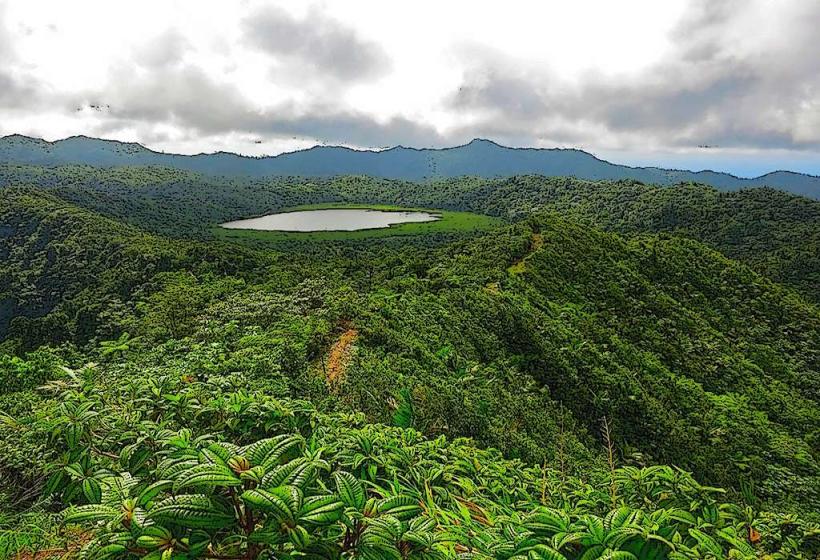
Grenada is an archipelagic state in the West Indies, comprising the main island of Grenada and the smaller islands of Carriacou and Petite Martinique. Known as the "Spice Island," it is a leading global producer of nutmeg and mace; the capital city is St. George’s.
Visa & Entry Policy
EU, US, and UK passport holders are granted visa-free entry for tourist stays of up to 90 days. Entry requires a passport valid for at least six months from the date of arrival and proof of a return or onward ticket. As of 2026, the Digital Nomad Visa (Remote Employment Act) remains active, allowing qualified remote workers to reside in the country for one year with an annual income requirement of $37,000 USD.
Language & Communication
English is the official language and is universal in government, commerce, and education. English proficiency is high and widespread. Grenadian English Creole and Grenadian French Creole (Patois) are the local vernaculars, reflecting African and European heritage, though French Creole is spoken less frequently.
Currency & Payment Systems
The official currency is the Eastern Caribbean Dollar (XCD), pegged to the US Dollar at 2.70 XCD to 1 USD. Credit cards (Visa/Mastercard) are standard in hotels, supermarkets, and major tourist areas. As of 2026, DCash, the ECCB’s central bank digital currency, is fully integrated for contactless mobile payments. Cash is still essential for local buses, taxis, and small vendors in rural parishes.
National Transport Grid
Inter-island transit between St. George’s and Carriacou is serviced by the Osprey Express high-speed ferry. On-island travel relies on a standardized system of privately owned minibuses operating in nine zones; destinations are marked by stickers on the windshield. Taxis are regulated with fixed rates rather than meters. Domestic aviation is handled via Maurice Bishop International (GND) on the main island and Lauriston Airport (CRU) on Carriacou.
Digital Infrastructure
Primary mobile network providers are Flow and Digicel. 4G/LTE coverage is robust across the tri-island state. As of 2026, 5G deployment is active in St. George’s, Grand Anse, and the Maurice Bishop airport corridor. The government’s Digital Government for Resilience (DG4R) project has digitized over 60% of public services.
Climate & Seasonality
The climate is tropical, moderated by northeast trade winds. The dry season runs from January to May. The wet season spans from June to December, coinciding with the Atlantic hurricane season. Average temperatures range between $24°C$ and $30°C$.
Health & Safety
As of January 5, 2026, the US State Department elevated its travel advisory for Grenada to Level 2: Exercise Increased Caution, citing an increase in opportunistic crime such as armed robbery and burglary. Travelers are advised to maintain situational awareness, particularly at night. Yellow Fever vaccination is required if arriving from an endemic zone. The emergency number for all services is 911.
Top 3 Major Regions & Cities
St. George Parish: Hub: St. George’s (Capital/Cruise Port).
Carriacou: Hub: Hillsborough (Tranquility/Traditional boat building).
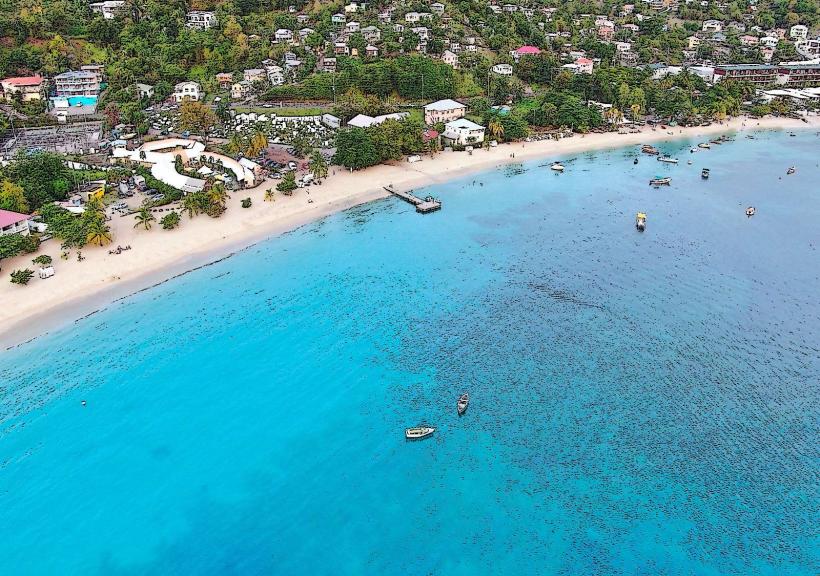
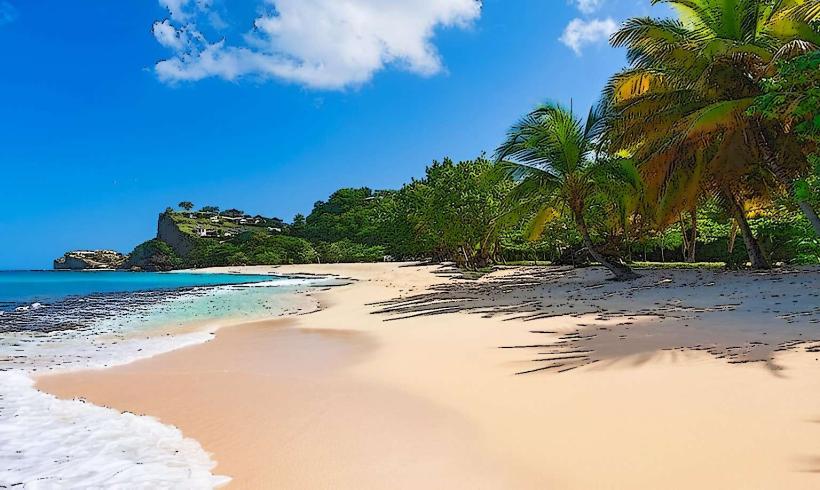
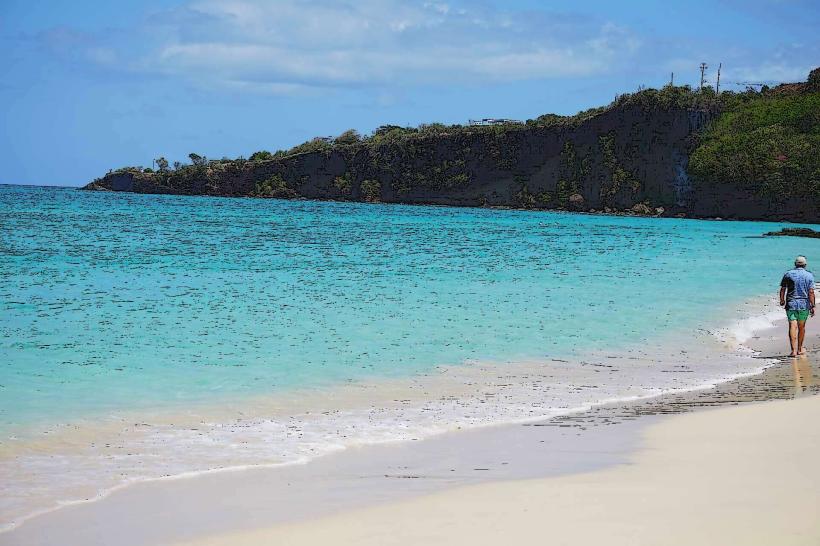
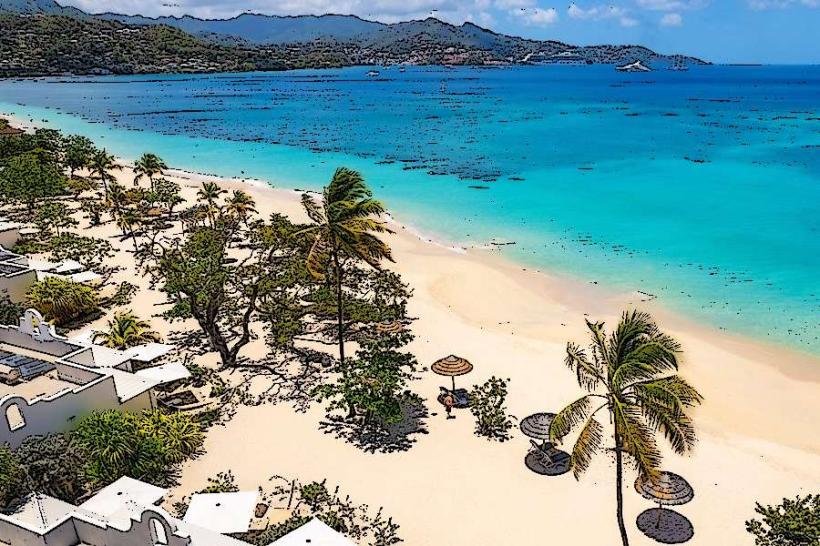
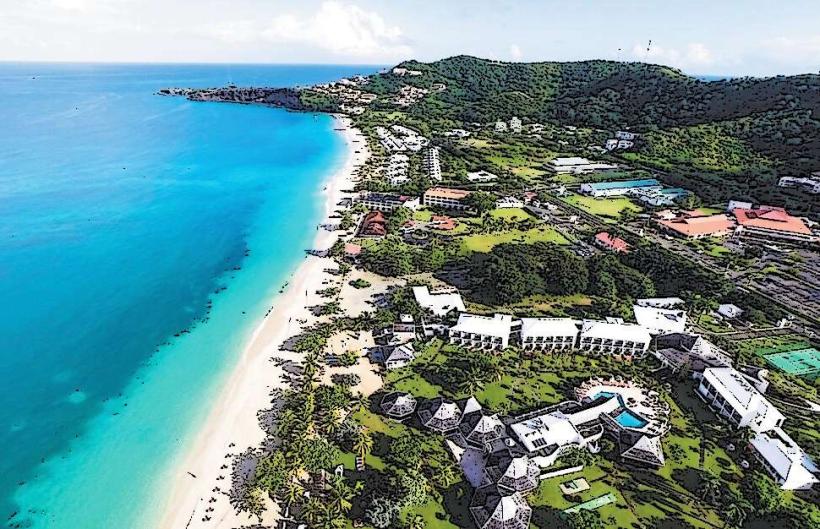
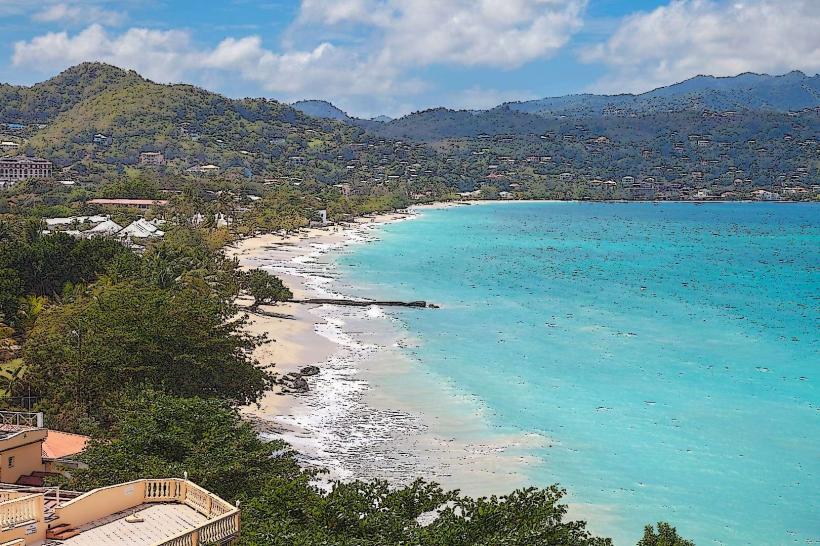
Grand Anse: Hub: St. George’s South (Primary tourism and beach district).
Local Cost Index
1L Water: 4.50 XCD ($1.65 USD)
1 Domestic Beer (0.5L): 6.50 XCD ($2.40 USD)
1 SIM Card (10GB Data): 115.00 XCD ($42.50 USD)
Facts & Legends
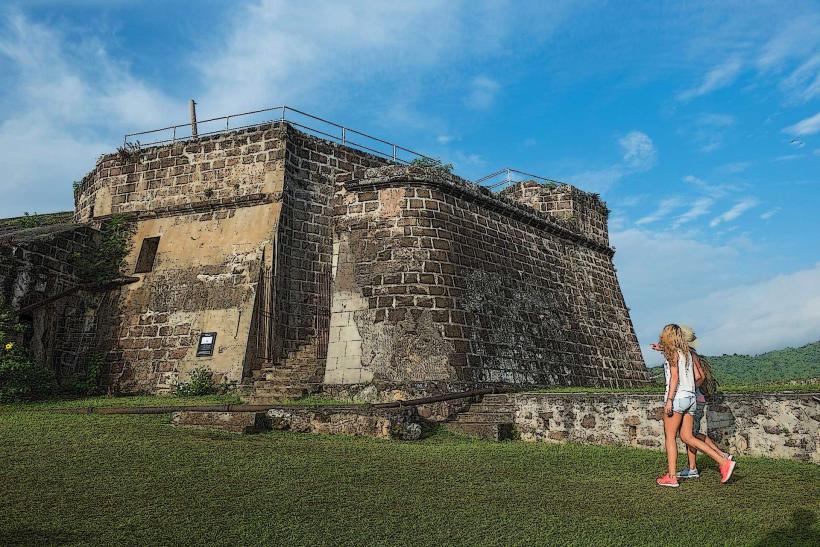
Grenada is home to the world’s first Underwater Sculpture Park at Molinere Bay, which also serves as an artificial reef. Local folklore includes the "Jumbie," a generic term for various spirits, and the "Soucouyant," a shapeshifting vampire that takes the form of a ball of fire at night. Historically, the island was the site of the 1983 US-led invasion following a military coup. A prominent legend tells of Leaper's Hill (Morne des Sauteurs), where the last indigenous Caribs jumped to their deaths in 1651 rather than surrender to French colonizers.